Deinfluencing reshapes consumer behavior by encouraging individuals to reject overhyped products and prioritize authentic needs over marketing trends, challenging traditional brand loyalty. This shift impacts economic patterns by influencing spending habits and forcing brands to adapt strategies to maintain consumer trust. Explore how deinfluencing transforms market dynamics and brand-consumer relationships.
Why it is important
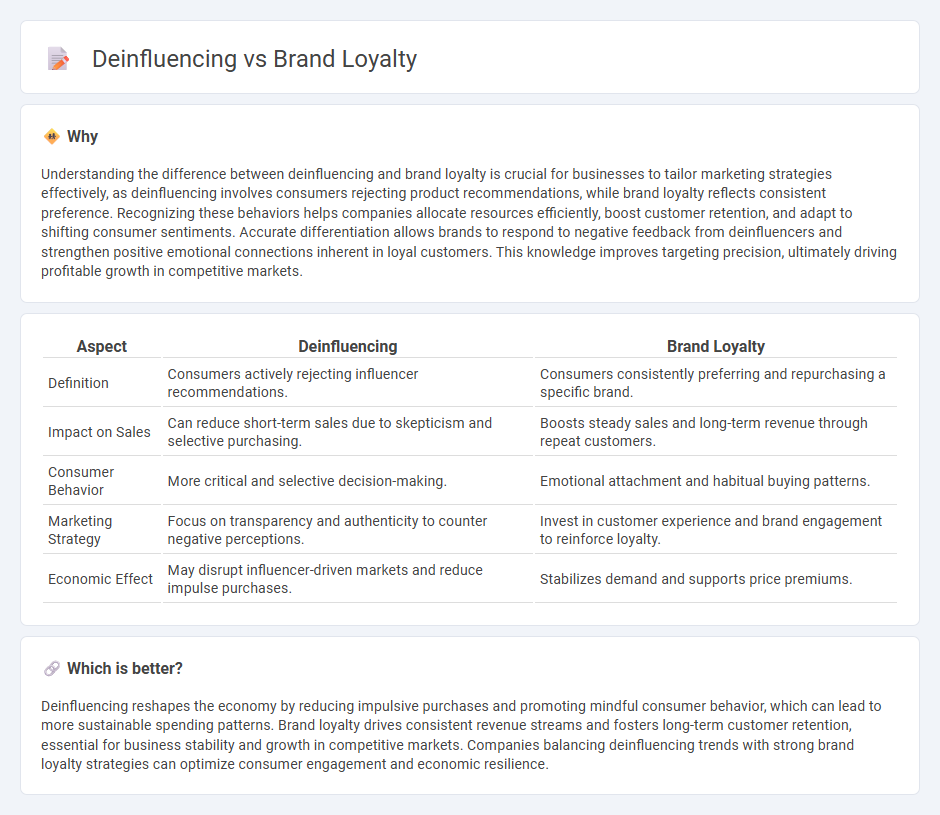
Understanding the difference between deinfluencing and brand loyalty is crucial for businesses to tailor marketing strategies effectively, as deinfluencing involves consumers rejecting product recommendations, while brand loyalty reflects consistent preference. Recognizing these behaviors helps companies allocate resources efficiently, boost customer retention, and adapt to shifting consumer sentiments. Accurate differentiation allows brands to respond to negative feedback from deinfluencers and strengthen positive emotional connections inherent in loyal customers. This knowledge improves targeting precision, ultimately driving profitable growth in competitive markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deinfluencing | Brand Loyalty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consumers actively rejecting influencer recommendations. | Consumers consistently preferring and repurchasing a specific brand. |
| Impact on Sales | Can reduce short-term sales due to skepticism and selective purchasing. | Boosts steady sales and long-term revenue through repeat customers. |
| Consumer Behavior | More critical and selective decision-making. | Emotional attachment and habitual buying patterns. |
| Marketing Strategy | Focus on transparency and authenticity to counter negative perceptions. | Invest in customer experience and brand engagement to reinforce loyalty. |
| Economic Effect | May disrupt influencer-driven markets and reduce impulse purchases. | Stabilizes demand and supports price premiums. |
Which is better?
Deinfluencing reshapes the economy by reducing impulsive purchases and promoting mindful consumer behavior, which can lead to more sustainable spending patterns. Brand loyalty drives consistent revenue streams and fosters long-term customer retention, essential for business stability and growth in competitive markets. Companies balancing deinfluencing trends with strong brand loyalty strategies can optimize consumer engagement and economic resilience.
Connection
Deinfluencing impacts economy by altering consumer behavior, reducing blind brand loyalty and encouraging more critical purchasing decisions. Brands facing deinfluencing trends must strengthen authentic engagement and product quality to maintain customer trust and loyalty. This shift prompts companies to adapt marketing strategies, which can influence overall market dynamics and economic growth.
Key Terms
Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior in brand loyalty emphasizes repeated purchasing and emotional attachment to a preferred brand, driven by trust and satisfaction over time. Deinfluencing reflects a growing trend where consumers actively reject promotional content, seeking authenticity and resisting overconsumption fueled by social media influencers. Explore how these contrasting dynamics reshape marketing strategies and consumer engagement in today's marketplace.
Market Influence
Market influence reflects the degree to which brand loyalty drives consumer purchasing decisions by fostering trust and emotional attachment, resulting in repeat sales and long-term revenue growth. Deinfluencing counters this by encouraging consumers to critically assess marketing messages and reduce impulsive buying, thereby shifting market power toward authentic, value-driven brand choices. Dive deeper into how these opposing forces reshape modern market dynamics and consumer behavior.
Purchasing Power
Brand loyalty significantly influences purchasing power by encouraging repeat purchases and higher customer lifetime value, which strengthens a brand's market position. Deinfluencing disrupts this dynamic by promoting mindful consumption and skepticism toward marketing, often leading consumers to shift spending away from established brands. Explore the impact of these trends on consumer behavior and market strategies for a deeper understanding.
Source and External Links
What Is Brand Loyalty? (+ Strategies To Create It) - Brand loyalty means customers repeatedly choose the same brand over competitors, often due to trust, consistency, and an emotional connection, leading to repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth.
Brand Loyalty Examples: 26 Companies Leading the Way - Brand loyalty occurs when customers consistently select a brand despite alternatives, driven by perceived quality, values, and emotional bonds, not just price or convenience.
Brand Loyalty: A Guide for Business Owners - Brand loyalty is a customer's strong attachment to a company, often making them willing to pay more and avoid substitutes because the brand feels like part of their identity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com