Economic strategies such as de-risking and pruning focus on minimizing financial losses and enhancing stability by selectively managing investments and operations. De-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk assets and markets, while pruning targets cutting underperforming or non-essential sectors within an economy to improve overall efficiency. Explore these methods further to understand their impact on sustainable economic growth and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-risking and pruning is crucial for effective economic risk management and decision-making. De-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk activities or markets to protect financial stability, while pruning refers to cutting off unproductive or non-strategic assets to enhance operational efficiency. Recognizing these distinct strategies helps policymakers and investors optimize resource allocation and mitigate potential economic downturns. Accurate application of de-risking and pruning drives sustainable growth and resilience in volatile economic environments.
Comparison Table
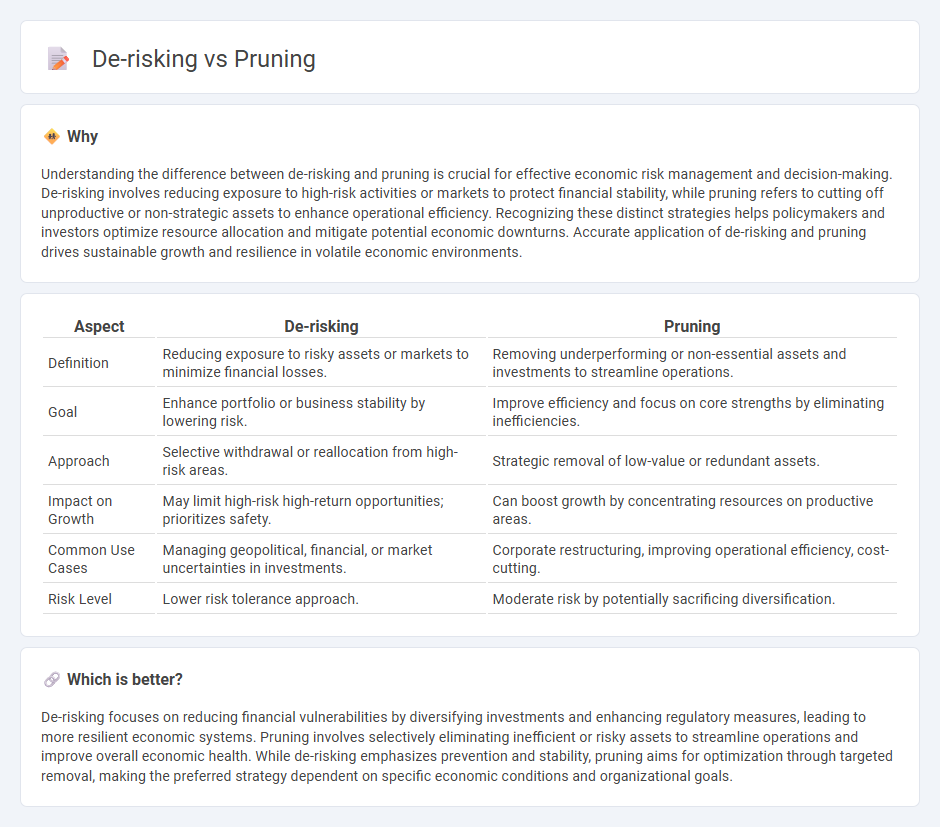
| Aspect | De-risking | Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing exposure to risky assets or markets to minimize financial losses. | Removing underperforming or non-essential assets and investments to streamline operations. |
| Goal | Enhance portfolio or business stability by lowering risk. | Improve efficiency and focus on core strengths by eliminating inefficiencies. |
| Approach | Selective withdrawal or reallocation from high-risk areas. | Strategic removal of low-value or redundant assets. |
| Impact on Growth | May limit high-risk high-return opportunities; prioritizes safety. | Can boost growth by concentrating resources on productive areas. |
| Common Use Cases | Managing geopolitical, financial, or market uncertainties in investments. | Corporate restructuring, improving operational efficiency, cost-cutting. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk tolerance approach. | Moderate risk by potentially sacrificing diversification. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on reducing financial vulnerabilities by diversifying investments and enhancing regulatory measures, leading to more resilient economic systems. Pruning involves selectively eliminating inefficient or risky assets to streamline operations and improve overall economic health. While de-risking emphasizes prevention and stability, pruning aims for optimization through targeted removal, making the preferred strategy dependent on specific economic conditions and organizational goals.
Connection
De-risking and pruning both aim to enhance economic stability by reducing exposure to financial uncertainties and inefficiencies. De-risking involves identifying and mitigating potential risks in investments, supply chains, or markets, while pruning focuses on eliminating non-performing assets or underperforming sectors. Together, these strategies foster a more resilient economy by optimizing resource allocation and minimizing vulnerabilities.
Key Terms
Risk Management
Pruning in risk management involves systematically reducing exposure by eliminating non-core assets or activities that pose potential threats, enhancing overall portfolio stability. De-risking focuses on mitigating risks through strategies such as diversification, hedging, or restructuring to protect against significant financial losses. Explore detailed techniques and benefits of pruning and de-risking to strengthen your risk management framework.
Asset Reallocation
Pruning involves systematically reducing underperforming or non-core assets to optimize the investment portfolio, while de-risking emphasizes shifting toward lower-risk assets to minimize exposure and volatility. Asset reallocation strategies prioritize balancing growth potential with risk tolerance by reallocating capital from high-risk investments to more stable alternatives. Explore how effective asset reallocation through pruning and de-risking can enhance portfolio resilience and long-term returns.
Regulatory Compliance
Pruning in regulatory compliance involves systematically removing non-compliant processes to streamline adherence, reducing complexity and minimizing regulatory risks. De-risking focuses on identifying and mitigating potential compliance failures before they occur, often involving enhanced due diligence and risk assessment protocols. Explore further to understand how these strategies safeguard your organization's regulatory standing.
Source and External Links
Pruning - Wikipedia - Pruning is the selective removal of certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots, aiming to remove diseased or unwanted material, improve health, shape, and increase yield or quality, with techniques varying by plant type.
Pruning An Introduction to Why How and When - CT.gov - Pruning involves selective branch cutting using techniques like thinning cuts that remove entire branches or heading cuts that shorten branches to stimulate growth, all focused on improving plant health and aesthetics.
Follow Proper Pruning Techniques - Earth-Kind(r) Landscaping - The best time to prune most plants is during late winter or early spring before growth starts, with improper timing risking plant damage, and prompt pruning essential for storm or damage cleanup to prevent disease.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com