Nearshoring increases supply chain efficiency by relocating production closer to the end market, reducing transportation costs and lead times. Homesourcing leverages domestic labor markets to enhance control and ensure higher quality standards while supporting local economies. Explore the benefits and challenges of nearshoring and homesourcing to determine the best strategic fit for your business.
Why it is important
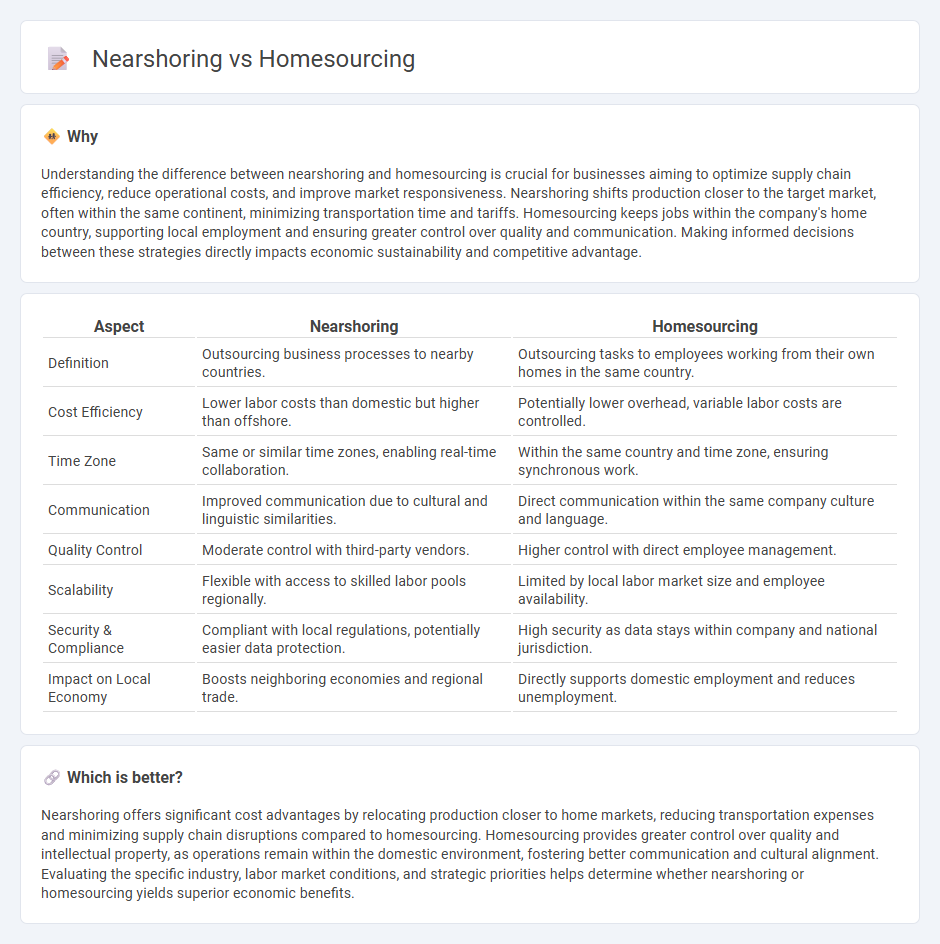
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and homesourcing is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize supply chain efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve market responsiveness. Nearshoring shifts production closer to the target market, often within the same continent, minimizing transportation time and tariffs. Homesourcing keeps jobs within the company's home country, supporting local employment and ensuring greater control over quality and communication. Making informed decisions between these strategies directly impacts economic sustainability and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Homesourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourcing business processes to nearby countries. | Outsourcing tasks to employees working from their own homes in the same country. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower labor costs than domestic but higher than offshore. | Potentially lower overhead, variable labor costs are controlled. |
| Time Zone | Same or similar time zones, enabling real-time collaboration. | Within the same country and time zone, ensuring synchronous work. |
| Communication | Improved communication due to cultural and linguistic similarities. | Direct communication within the same company culture and language. |
| Quality Control | Moderate control with third-party vendors. | Higher control with direct employee management. |
| Scalability | Flexible with access to skilled labor pools regionally. | Limited by local labor market size and employee availability. |
| Security & Compliance | Compliant with local regulations, potentially easier data protection. | High security as data stays within company and national jurisdiction. |
| Impact on Local Economy | Boosts neighboring economies and regional trade. | Directly supports domestic employment and reduces unemployment. |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers significant cost advantages by relocating production closer to home markets, reducing transportation expenses and minimizing supply chain disruptions compared to homesourcing. Homesourcing provides greater control over quality and intellectual property, as operations remain within the domestic environment, fostering better communication and cultural alignment. Evaluating the specific industry, labor market conditions, and strategic priorities helps determine whether nearshoring or homesourcing yields superior economic benefits.
Connection
Nearshoring and homesourcing are connected through their shared goal of reducing operational costs and increasing efficiency by relocating business processes closer to the target market or within domestic borders. Both strategies enhance supply chain resilience and mitigate risks associated with offshore outsourcing, such as geopolitical instability and long shipping times. This alignment supports businesses in responding swiftly to market changes while leveraging local talent pools to improve service quality and customer satisfaction.
Key Terms
Labor Cost
Labor cost plays a crucial role in the choice between homesourcing and nearshoring, directly impacting a company's operational budget. Homesourcing leverages domestic labor, often resulting in higher wages but increased control and quality assurance. Explore detailed comparisons of labor cost implications to optimize your outsourcing strategy effectively.
Geographic Proximity
Homesourcing involves outsourcing work to professionals within the same country, ensuring minimal geographic distance and similar time zones, which enhances communication and cultural alignment. Nearshoring refers to outsourcing to neighboring or nearby countries, reducing travel costs and time zone differences compared to offshoring, while also benefiting from shared regional markets. Explore the benefits and challenges of homesourcing and nearshoring to determine the best strategy for your business.
Remote Work
Homesourcing leverages domestic remote employees, enhancing control and cultural alignment while minimizing time zone challenges compared to nearshoring, which outsources tasks to nearby countries offering cost-effective labor and diverse talent pools. Remote work thrives in homesourcing environments due to seamless communication and shared language, whereas nearshoring balances efficiency and proximity to headquarters while managing cross-border regulations. Explore the nuances between homesourcing and nearshoring to optimize your remote work strategy.
Source and External Links
Homesourcing - The Free Dictionary - Homesourcing, also called homeshoring, is the practice of paying employees to work from home rather than in an office, combining the benefits of working from home with cost advantages similar to offshoring.
Homesourcing - CallFire - Homesourcing enables companies to manage remote agents working from home via virtual call centers, reducing overhead and improving operational flexibility with cloud technology for inbound and outbound calls.
Homeshoring Definition - Collins Dictionary - Homeshoring (or homesourcing) is the business practice of employing staff to work from home instead of a traditional office setting, often to decrease costs and increase convenience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com