Veblen goods are luxury items that experience increased demand as prices rise, driven by their status symbol appeal rather than intrinsic utility. Club goods, in contrast, are non-rivalrous and excludable, such as private parks or subscription services, where consumption by one member does not reduce availability to others within the club. Explore the unique economic principles and market behaviors distinguishing these two categories.
Why it is important
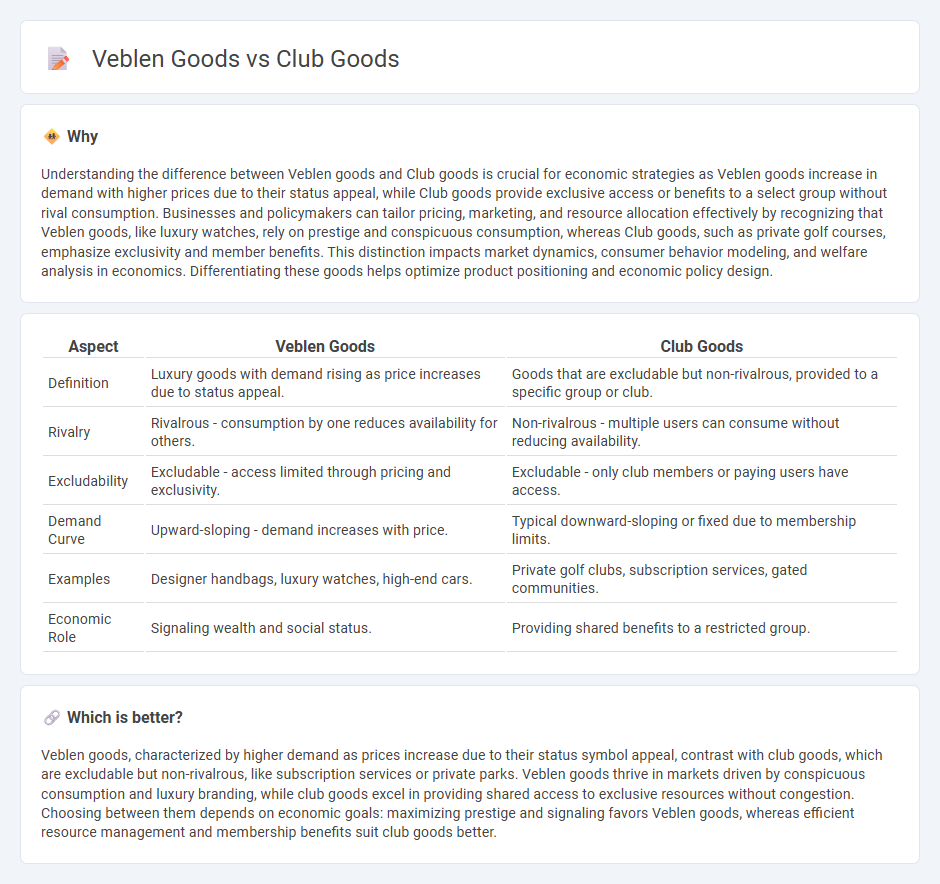
Understanding the difference between Veblen goods and Club goods is crucial for economic strategies as Veblen goods increase in demand with higher prices due to their status appeal, while Club goods provide exclusive access or benefits to a select group without rival consumption. Businesses and policymakers can tailor pricing, marketing, and resource allocation effectively by recognizing that Veblen goods, like luxury watches, rely on prestige and conspicuous consumption, whereas Club goods, such as private golf courses, emphasize exclusivity and member benefits. This distinction impacts market dynamics, consumer behavior modeling, and welfare analysis in economics. Differentiating these goods helps optimize product positioning and economic policy design.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Veblen Goods | Club Goods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Luxury goods with demand rising as price increases due to status appeal. | Goods that are excludable but non-rivalrous, provided to a specific group or club. |
| Rivalry | Rivalrous - consumption by one reduces availability for others. | Non-rivalrous - multiple users can consume without reducing availability. |
| Excludability | Excludable - access limited through pricing and exclusivity. | Excludable - only club members or paying users have access. |
| Demand Curve | Upward-sloping - demand increases with price. | Typical downward-sloping or fixed due to membership limits. |
| Examples | Designer handbags, luxury watches, high-end cars. | Private golf clubs, subscription services, gated communities. |
| Economic Role | Signaling wealth and social status. | Providing shared benefits to a restricted group. |
Which is better?
Veblen goods, characterized by higher demand as prices increase due to their status symbol appeal, contrast with club goods, which are excludable but non-rivalrous, like subscription services or private parks. Veblen goods thrive in markets driven by conspicuous consumption and luxury branding, while club goods excel in providing shared access to exclusive resources without congestion. Choosing between them depends on economic goals: maximizing prestige and signaling favors Veblen goods, whereas efficient resource management and membership benefits suit club goods better.
Connection
Veblen goods and Club goods are connected through their association with exclusivity and social status, driving demand beyond basic utility. Veblen goods, such as luxury watches or designer handbags, increase in desirability as their price rises due to perceived prestige. Club goods, like private golf courses or elite gym memberships, offer restricted access that enhances their value by limiting consumption to a select group, reinforcing exclusivity in economic behavior.
Key Terms
Excludability
Club goods possess high excludability, allowing providers to restrict access to members or paying customers, such as in private clubs or subscription services. Veblen goods, while often excludable due to luxury pricing, rely more on their perceived prestige and conspicuous consumption than strict exclusion mechanisms. Explore further to understand how excludability shapes consumer behavior differently in club goods versus Veblen goods.
Non-rivalry
Club goods exhibit non-rivalry, meaning multiple individuals can consume them simultaneously without diminishing availability for others, as seen in private parks or subscription services. Veblen goods, characterized by their status-driven demand, do not inherently display non-rivalry since consumption by one reduces availability but often thrive on exclusivity and conspicuousness. Explore more to understand how non-rivalry shapes the economic dynamics of these unique goods.
Conspicuous consumption
Club goods are excludable and rivalry-limited, typically consumed by defined groups who pay for access, making exclusivity a key factor in their appeal. Veblen goods attract conspicuous consumption through status signaling, where higher prices increase desirability due to perceived prestige. Explore how the dynamics of exclusivity and social status drive consumer behavior in different market segments.
Source and External Links
Club Good - Wikipedia - Club goods are excludable but non-rivalrous goods in economics, meaning access can be restricted (e.g., by a fee), but one person's use does not reduce availability for others until congestion occurs.
Club Goods - Fiveable - Club goods are non-rival in consumption (use by one doesn't diminish another's) but excludable (access can be limited), such as private parks or subscription services.
Encyclopedia of Law & Economics - Public Goods And Club Goods - Club goods are essentially public goods made excludable, often through membership fees, and exhibit economies of scale until crowding introduces rivalry.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com