Greedflation describes price increases driven by companies exploiting market power to boost profits rather than higher costs. Stagflation combines stagnant economic growth with high inflation and unemployment, posing complex challenges for policymakers. Explore the differences and impacts of these economic phenomena to better understand current market dynamics.
Why it is important
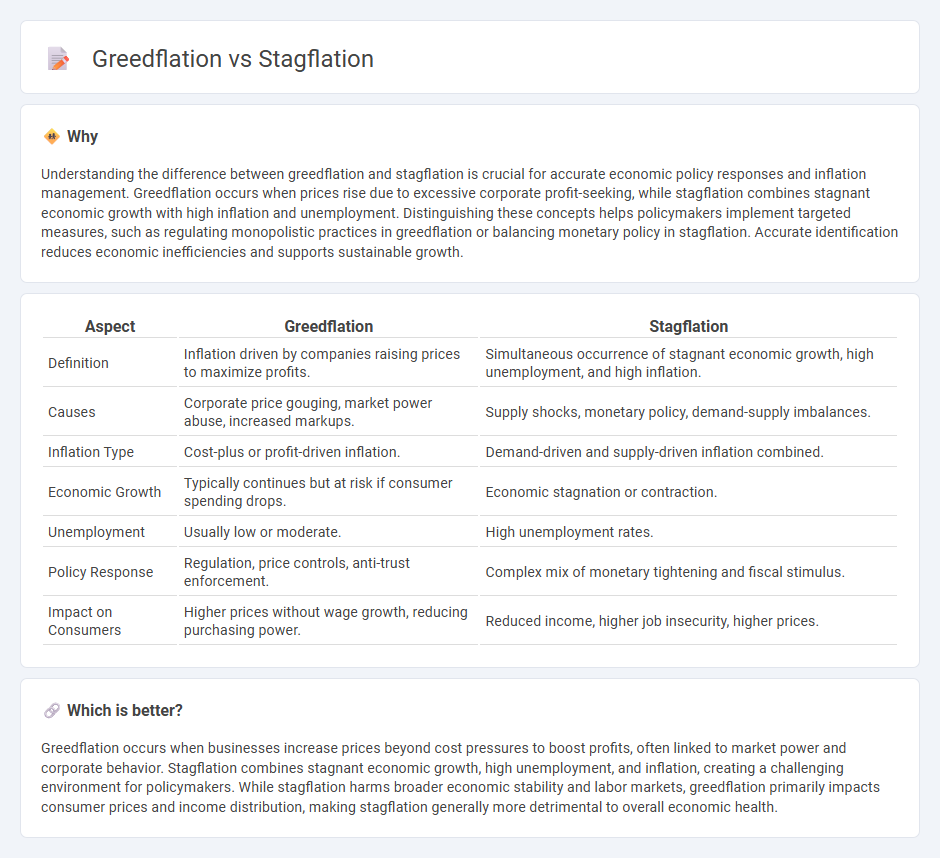
Understanding the difference between greedflation and stagflation is crucial for accurate economic policy responses and inflation management. Greedflation occurs when prices rise due to excessive corporate profit-seeking, while stagflation combines stagnant economic growth with high inflation and unemployment. Distinguishing these concepts helps policymakers implement targeted measures, such as regulating monopolistic practices in greedflation or balancing monetary policy in stagflation. Accurate identification reduces economic inefficiencies and supports sustainable growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greedflation | Stagflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation driven by companies raising prices to maximize profits. | Simultaneous occurrence of stagnant economic growth, high unemployment, and high inflation. |
| Causes | Corporate price gouging, market power abuse, increased markups. | Supply shocks, monetary policy, demand-supply imbalances. |
| Inflation Type | Cost-plus or profit-driven inflation. | Demand-driven and supply-driven inflation combined. |
| Economic Growth | Typically continues but at risk if consumer spending drops. | Economic stagnation or contraction. |
| Unemployment | Usually low or moderate. | High unemployment rates. |
| Policy Response | Regulation, price controls, anti-trust enforcement. | Complex mix of monetary tightening and fiscal stimulus. |
| Impact on Consumers | Higher prices without wage growth, reducing purchasing power. | Reduced income, higher job insecurity, higher prices. |
Which is better?
Greedflation occurs when businesses increase prices beyond cost pressures to boost profits, often linked to market power and corporate behavior. Stagflation combines stagnant economic growth, high unemployment, and inflation, creating a challenging environment for policymakers. While stagflation harms broader economic stability and labor markets, greedflation primarily impacts consumer prices and income distribution, making stagflation generally more detrimental to overall economic health.
Connection
Greedflation, driven by excessive corporate price hikes beyond cost increases, exacerbates stagflation by fueling inflation while economic growth stalls and unemployment rises. Both phenomena create a vicious cycle where soaring prices reduce consumer purchasing power, leading to decreased demand and slowed GDP expansion. Central banks face challenges in balancing interest rate hikes to combat inflation without deepening economic stagnation.
Key Terms
Inflation
Stagflation occurs when inflation rises alongside stagnant economic growth and high unemployment, resulting in diminished purchasing power and economic uncertainty. Greedflation, by contrast, is driven primarily by corporate price gouging and profit-seeking behavior, causing inflation to surge despite stable demand and supply conditions. Explore the detailed economic factors behind inflation dynamics to deepen your understanding of stagflation and greedflation.
Unemployment
Stagflation is characterized by high unemployment combined with stagnant economic growth and rising inflation, creating a challenging labor market and eroding consumer purchasing power. Greedflation, on the other hand, involves rising prices driven primarily by corporate profit-seeking behaviors, often with a less direct impact on unemployment rates compared to stagflation. Explore the nuances of how unemployment dynamics differ in stagflation versus greedflation scenarios for a deeper understanding.
Corporate Profit Margins
Stagflation is characterized by high inflation, slow economic growth, and rising unemployment, typically squeezing corporate profit margins due to increased costs and reduced consumer spending. In contrast, greedflation occurs when companies deliberately raise prices beyond cost increases to boost profit margins, exploiting inflationary conditions for greater corporate gains. Explore how these phenomena impact market dynamics and investor strategies in depth.
Source and External Links
Overview, Examples, Why Stagflation is Feared - Stagflation is an economic condition characterized by high inflation, slow economic growth, and high unemployment, creating a policy dilemma since actions to reduce inflation may increase unemployment and vice versa.
Is the worst of both worlds returning? Understanding stagflation risk - Stagflation describes a period of rising prices alongside stagnant or declining GDP growth, often accompanied by increasing unemployment and a high "misery index" that combines inflation and joblessness rates.
Stagflation - Wikipedia - Stagflation is the simultaneous occurrence of high inflation, stagnant economic growth, and elevated unemployment, defying traditional economic theories that suggest inflation and unemployment move in opposite directions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com