Price gouging occurs when sellers increase prices excessively during high demand or emergencies, exploiting consumers, while price fixing involves competitors colluding to set prices at an artificial level, undermining market competition. Both practices distort supply and demand dynamics, leading to inefficiencies and consumer harm. Explore more to understand their economic impact and regulatory responses.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between price gouging and price fixing is crucial for maintaining fair market practices and protecting consumer rights. Price gouging involves excessive pricing during emergencies, while price fixing is a coordinated effort among competitors to set prices, undermining competition. Recognizing these distinctions helps regulators enforce appropriate antitrust laws and ensures economic stability. Knowing the specific legal frameworks around each practice aids businesses and consumers in navigating market dynamics effectively.
Comparison Table
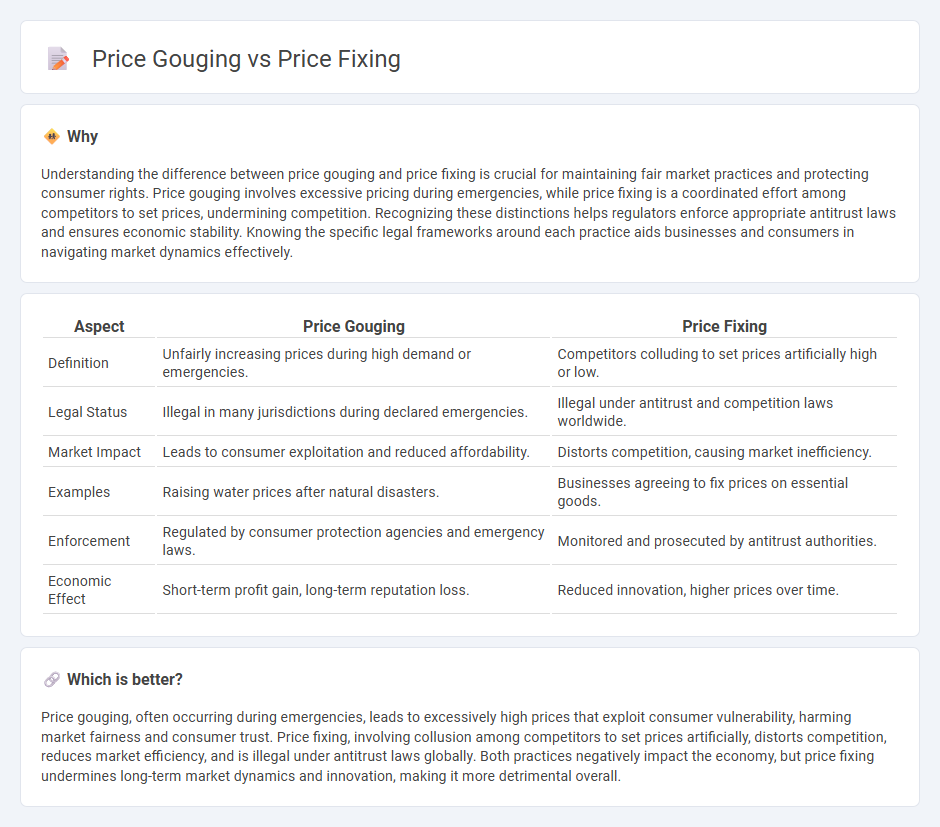
| Aspect | Price Gouging | Price Fixing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unfairly increasing prices during high demand or emergencies. | Competitors colluding to set prices artificially high or low. |
| Legal Status | Illegal in many jurisdictions during declared emergencies. | Illegal under antitrust and competition laws worldwide. |
| Market Impact | Leads to consumer exploitation and reduced affordability. | Distorts competition, causing market inefficiency. |
| Examples | Raising water prices after natural disasters. | Businesses agreeing to fix prices on essential goods. |
| Enforcement | Regulated by consumer protection agencies and emergency laws. | Monitored and prosecuted by antitrust authorities. |
| Economic Effect | Short-term profit gain, long-term reputation loss. | Reduced innovation, higher prices over time. |
Which is better?
Price gouging, often occurring during emergencies, leads to excessively high prices that exploit consumer vulnerability, harming market fairness and consumer trust. Price fixing, involving collusion among competitors to set prices artificially, distorts competition, reduces market efficiency, and is illegal under antitrust laws globally. Both practices negatively impact the economy, but price fixing undermines long-term market dynamics and innovation, making it more detrimental overall.
Connection
Price gouging and price fixing both involve artificial manipulation of prices, leading to unfair market conditions and harm to consumers. Price gouging occurs during emergencies when sellers increase prices excessively, while price fixing is a coordinated effort among competitors to set prices at an unfair level. Both practices disrupt competitive markets, reduce consumer trust, and often result in legal penalties under antitrust laws.
Key Terms
Collusion
Price fixing involves collusion between competitors to set prices at a predetermined level, restricting market competition and manipulating consumer costs unlawfully. Price gouging occurs when sellers exploit high demand during emergencies by excessively raising prices without collusion. Explore how legal frameworks differentiate these practices and their impact on market dynamics.
Market Manipulation
Price fixing involves collusion among competitors to set prices at a certain level, deliberately restricting competition and manipulating market conditions to control supply and demand. Price gouging occurs when sellers exploit emergencies or shortages by charging excessively high prices beyond what market conditions would justify, often leading to public outcry and regulatory scrutiny. Explore more to understand the legal distinctions and economic impacts of these market manipulation tactics.
Anti-competitive Practices
Price fixing involves competitors colluding to set prices at a certain level, undermining market competition and harming consumers through artificially high prices. Price gouging refers to sellers exploiting emergencies by raising prices excessively, often regulated under consumer protection laws rather than competition law. Explore the nuances of anti-competitive practices to understand their legal distinctions and economic impact.
Source and External Links
Price Fixing - FTC - Price fixing is an agreement among competitors to raise, lower, maintain, or stabilize prices or price levels, which is generally illegal under antitrust laws and can lead to criminal prosecution with penalties including imprisonment and fines.
Price Fixing - Corporate Finance Institute - Price fixing involves competitors agreeing to set prices collectively to control supply and demand, benefiting the colluding firms but harming consumers, and is illegal under U.S. and Canadian competition laws.
price fixing | Wex | US Law | LII - Price fixing is an agreement among competitors to manipulate prices in violation of antitrust laws like the Sherman Act, which can result in felony charges and civil liabilities for harming market competition and consumers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com