Economic soft landing occurs when growth slows down just enough to prevent inflation without triggering a recession, maintaining stable employment levels and consumer confidence. In contrast, economic expansion involves sustained increases in GDP, investment, and job creation, driving higher demand and business profitability. Explore more to understand how these dynamics shape fiscal policies and market strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a soft landing and expansion is crucial for investors and policymakers to make informed decisions that minimize economic risks and maximize growth opportunities. A soft landing refers to a scenario where the economy slows down just enough to curb inflation without triggering a recession, maintaining steady employment levels. Expansion denotes a period of sustained economic growth characterized by increased GDP, consumer spending, and job creation. Recognizing these distinctions helps anticipate market trends and adjust fiscal or monetary policies effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Landing | Expansion |
|---|---|---|
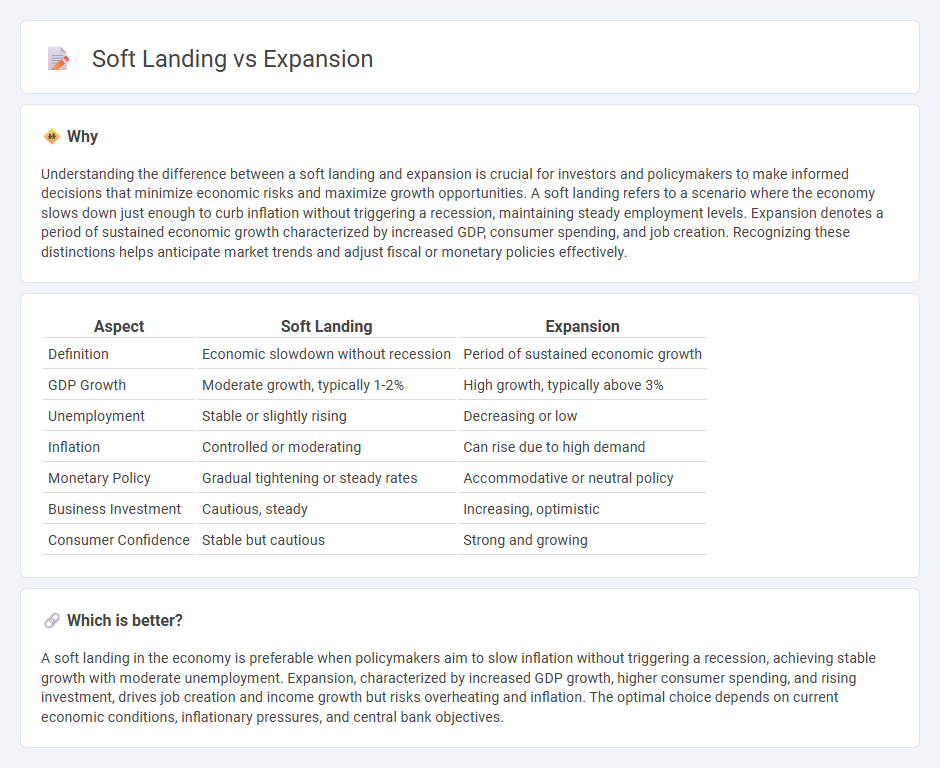
| Definition | Economic slowdown without recession | Period of sustained economic growth |
| GDP Growth | Moderate growth, typically 1-2% | High growth, typically above 3% |
| Unemployment | Stable or slightly rising | Decreasing or low |
| Inflation | Controlled or moderating | Can rise due to high demand |
| Monetary Policy | Gradual tightening or steady rates | Accommodative or neutral policy |
| Business Investment | Cautious, steady | Increasing, optimistic |
| Consumer Confidence | Stable but cautious | Strong and growing |
Which is better?
A soft landing in the economy is preferable when policymakers aim to slow inflation without triggering a recession, achieving stable growth with moderate unemployment. Expansion, characterized by increased GDP growth, higher consumer spending, and rising investment, drives job creation and income growth but risks overheating and inflation. The optimal choice depends on current economic conditions, inflationary pressures, and central bank objectives.
Connection
A soft landing occurs when an economy slows down just enough to curb inflation without triggering a recession, creating a favorable environment for sustainable expansion. Controlled interest rates and steady consumer demand during a soft landing support business investments and job growth, key drivers of economic expansion. Policymakers aim for a soft landing to maintain balanced growth, ensuring that expansion is steady rather than overheated or volatile.
Key Terms
GDP Growth
GDP growth during an economic expansion typically accelerates as consumer spending, business investment, and industrial production increase consistently. In contrast, a soft landing aims to slow GDP growth to a sustainable rate, preventing overheating and reducing inflation risks without triggering a recession. Explore detailed strategies and economic indicators influencing these outcomes to understand their impact on macroeconomic stability.
Inflation Rate
Expansion phases typically see rising inflation rates due to increased consumer demand and higher production costs, whereas soft landings aim to slow economic growth just enough to stabilize inflation without triggering a recession. Managing the inflation rate effectively during a soft landing involves careful monetary policy adjustments to avoid overheating or deflationary pressures. Explore how inflation rate trends influence policymakers' decisions in economic cycles to learn more.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy plays a crucial role in determining whether an economy experiences expansion or a soft landing, with expansion characterized by accommodative policies that lower interest rates to stimulate growth and increase spending. In contrast, a soft landing is achieved by carefully tightening monetary policy, such as raising interest rates gradually to control inflation without triggering a recession. Explore further insights into how central banks balance these strategies to stabilize the economy.
Source and External Links
EXPANSION | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Expansion refers to an increase in the size, number, or importance of something, like the rapid growth of an industry or trade.
EXPANSION definition in American English - Collins Dictionary - Expansion is the process or act of becoming greater in size, number, or amount, including economic and industrial growth or mathematical developments.
Expansion (geometry) - Wikipedia - In geometry, expansion is an operation on polytopes where facets separate and move apart, creating new uniform shapes combining features of original and dual polyhedra.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com