A soft landing in the economy occurs when growth slows to a sustainable pace without triggering a recession, maintaining stable inflation and steady employment. Overheating happens when demand exceeds supply, leading to rapid inflation, wage pressures, and potential asset bubbles. Explore the dynamics of economic cycles to understand how policymakers strive to balance growth and stability.
Why it is important
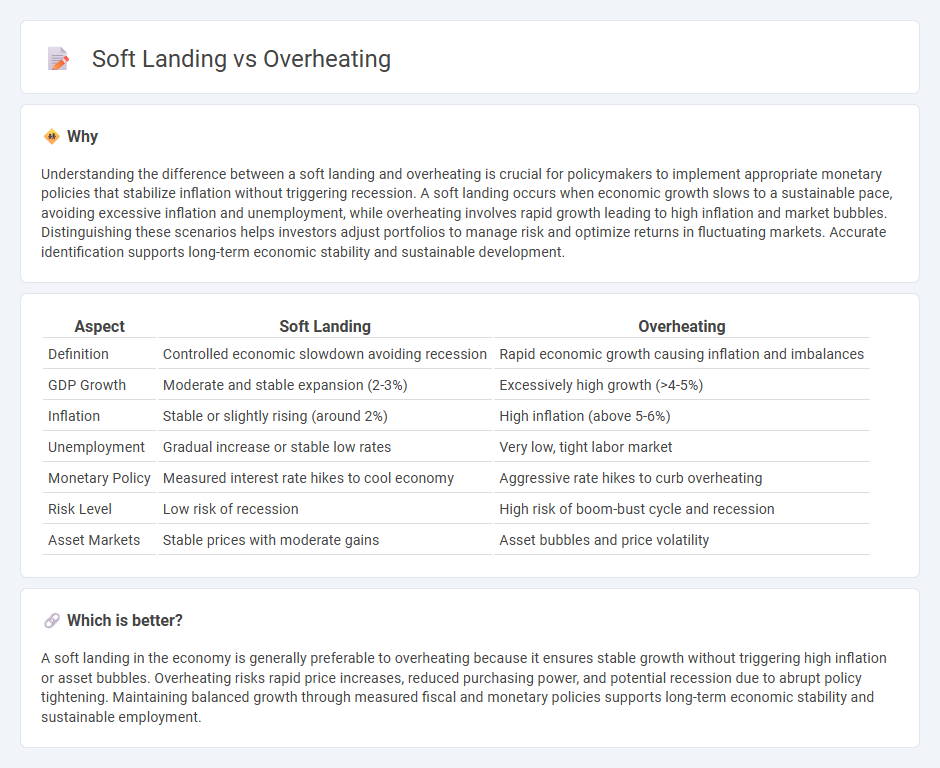
Understanding the difference between a soft landing and overheating is crucial for policymakers to implement appropriate monetary policies that stabilize inflation without triggering recession. A soft landing occurs when economic growth slows to a sustainable pace, avoiding excessive inflation and unemployment, while overheating involves rapid growth leading to high inflation and market bubbles. Distinguishing these scenarios helps investors adjust portfolios to manage risk and optimize returns in fluctuating markets. Accurate identification supports long-term economic stability and sustainable development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Landing | Overheating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled economic slowdown avoiding recession | Rapid economic growth causing inflation and imbalances |
| GDP Growth | Moderate and stable expansion (2-3%) | Excessively high growth (>4-5%) |
| Inflation | Stable or slightly rising (around 2%) | High inflation (above 5-6%) |
| Unemployment | Gradual increase or stable low rates | Very low, tight labor market |
| Monetary Policy | Measured interest rate hikes to cool economy | Aggressive rate hikes to curb overheating |
| Risk Level | Low risk of recession | High risk of boom-bust cycle and recession |
| Asset Markets | Stable prices with moderate gains | Asset bubbles and price volatility |
Which is better?
A soft landing in the economy is generally preferable to overheating because it ensures stable growth without triggering high inflation or asset bubbles. Overheating risks rapid price increases, reduced purchasing power, and potential recession due to abrupt policy tightening. Maintaining balanced growth through measured fiscal and monetary policies supports long-term economic stability and sustainable employment.
Connection
Soft landing refers to an economic scenario where growth slows down just enough to prevent inflation from rising uncontrollably, avoiding overheating, which occurs when demand outstrips supply causing rapid inflation and asset bubbles. Central banks often aim for a soft landing by adjusting interest rates to balance economic expansion without triggering overheating. Achieving this delicate equilibrium helps sustain long-term economic stability and prevents recessions triggered by abrupt corrections.
Key Terms
Inflation
Overheating occurs when inflation rises rapidly due to excessive demand surpassing supply, causing price levels to spike and eroding purchasing power. A soft landing aims to slow inflation gradually through monetary policy adjustments without triggering recession or sharp employment drops. Explore detailed strategies and economic impacts of inflation control methods for deeper insights.
Monetary policy
Overheating in the economy occurs when demand outpaces supply, leading to inflationary pressures, prompting central banks to tighten monetary policy by raising interest rates to cool down growth. In contrast, a soft landing aims for a gradual slowdown of the economy without triggering a recession, achieved through calibrated monetary policy adjustments that balance growth and inflation control. Explore deeper insights into how central banks navigate these challenges in monetary policy strategies.
GDP growth
Overheating occurs when GDP growth surpasses the economy's sustainable capacity, leading to inflationary pressures and asset bubbles, while a soft landing refers to a controlled slowdown that prevents recession without triggering high unemployment. Sustainable GDP growth rates usually range between 2% to 3%, balancing expansion and inflation control to maintain economic stability. Explore more about how policymakers manage these dynamics to achieve optimal growth outcomes.
Source and External Links
Hyperthermia - Hyperthermia is a condition where the body's temperature exceeds normal levels due to failed thermoregulation, often caused by heat stroke or drug reactions.
3 Signs You May Be Dangerously Overheated - This article discusses signs of heat-related illnesses like heat exhaustion and heat stroke, emphasizing the importance of immediate medical attention.
When Your Car Overheats - This webpage explains common causes of engine overheating, such as low coolant levels or cooling system leaks, and provides guidance on what to do if it happens.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com