Onshoring involves relocating business operations back to the company's home country to enhance control, reduce shipping costs, and support local economies, while outsourcing delegates tasks to third-party providers often in foreign countries to capitalize on lower labor costs and specialized expertise. Economic factors such as labor wages, trade policies, and supply chain resilience heavily influence the decision between onshoring and outsourcing. Explore the economic implications and strategic trade-offs of onshoring versus outsourcing to optimize business outcomes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between onshoring and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing cost efficiency and operational control in business strategies. Onshoring involves relocating business processes to the company's home country, enhancing quality oversight and reducing geopolitical risks. Outsourcing transfers tasks or services to third-party providers, often internationally, to leverage lower labor costs and specialized expertise. Making informed decisions between onshoring and outsourcing directly impacts supply chain resilience, labor market dynamics, and overall economic growth.
Comparison Table
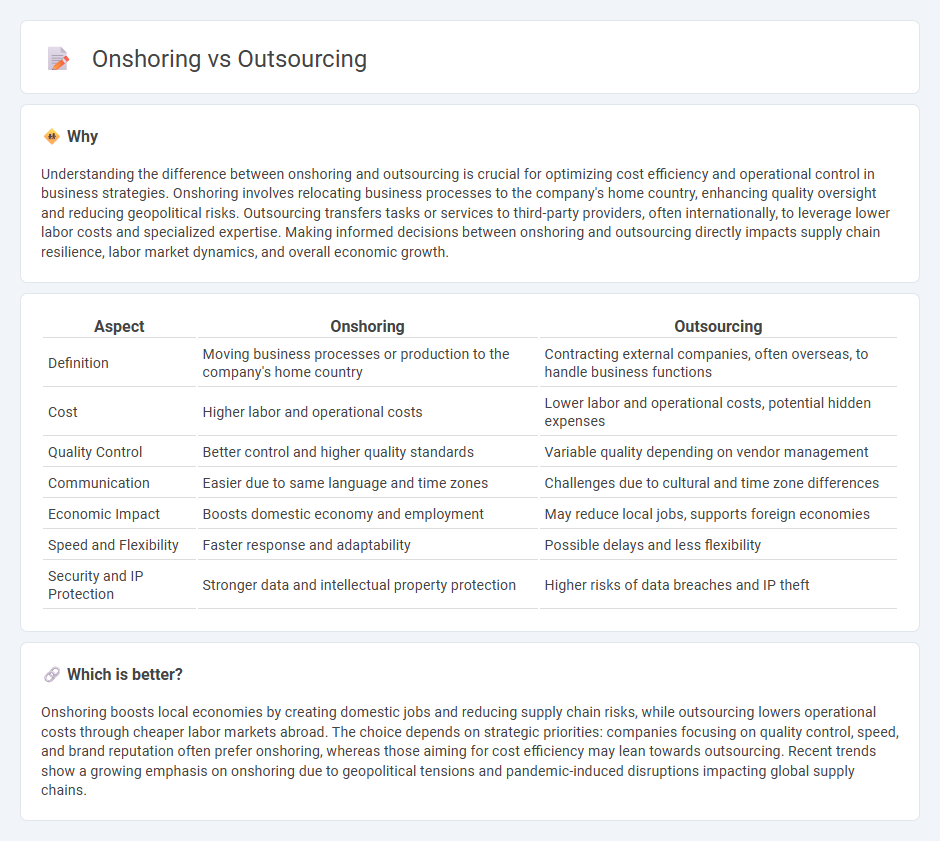
| Aspect | Onshoring | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving business processes or production to the company's home country | Contracting external companies, often overseas, to handle business functions |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs | Lower labor and operational costs, potential hidden expenses |
| Quality Control | Better control and higher quality standards | Variable quality depending on vendor management |
| Communication | Easier due to same language and time zones | Challenges due to cultural and time zone differences |
| Economic Impact | Boosts domestic economy and employment | May reduce local jobs, supports foreign economies |
| Speed and Flexibility | Faster response and adaptability | Possible delays and less flexibility |
| Security and IP Protection | Stronger data and intellectual property protection | Higher risks of data breaches and IP theft |
Which is better?
Onshoring boosts local economies by creating domestic jobs and reducing supply chain risks, while outsourcing lowers operational costs through cheaper labor markets abroad. The choice depends on strategic priorities: companies focusing on quality control, speed, and brand reputation often prefer onshoring, whereas those aiming for cost efficiency may lean towards outsourcing. Recent trends show a growing emphasis on onshoring due to geopolitical tensions and pandemic-induced disruptions impacting global supply chains.
Connection
Onshoring and outsourcing are interconnected strategies that businesses use to optimize costs and improve operational flexibility. Onshoring involves relocating production or services back to the company's home country, enhancing control and reducing supply chain risks. Outsourcing, by contrast, delegates specific tasks or functions to external providers, often abroad, to leverage cost advantages and specialized expertise.
Key Terms
Labor Cost
Labor cost plays a critical role in the outsourcing versus onshoring decision, with outsourcing typically offering lower wage expenses due to access to global talent markets in countries like India, the Philippines, or Eastern Europe. Onshoring, while often incurring higher labor costs, provides benefits such as improved communication, quicker turnaround times, and better alignment with domestic regulations. Discover how these factors impact your operational efficiency and budget by exploring detailed case studies and industry analyses.
Supply Chain
Outsourcing in supply chain management leverages global suppliers to reduce production costs and increase flexibility, whereas onshoring emphasizes proximity, improving lead times and supply chain transparency. Companies focusing on onshoring benefit from reduced transportation risks and enhanced control over quality standards. Explore more about optimizing your supply chain strategy through outsourcing or onshoring to drive efficiency and resilience.
Domestic Production
Domestic production emphasizes onshoring to boost local economies, reduce supply chain risks, and ensure quality control by keeping operations within national borders. Outsourcing often involves relocating production to foreign countries to lower labor costs, but it can lead to longer lead times and potential communication barriers. Explore the benefits and challenges of both strategies to optimize your production approach.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) | Indeed.com - Outsourcing is the practice of hiring external contractors or companies to perform tasks, aiming to reduce costs and improve productivity through types like onshore, offshore, and nearshore outsourcing, covering functions such as HR, customer support, accounting, and engineering.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing is contracting third-party providers to perform tasks or services, often requiring focus on managing partnerships and contract details, frequently applied to IT services, customer support, manufacturing, and financial functions.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing enables businesses to reduce costs, access specialized expertise, focus on core activities, and improve performance by contracting external firms for tasks like IT support and customer service, though it may pose communication challenges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com