Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the company's original country to reduce supply chain vulnerabilities and increase domestic employment. Onshoring refers to relocating operations closer to the home country but not necessarily within it, often to nearby regions to balance cost efficiency and logistical convenience. Explore the key differences and economic impacts of reshoring versus onshoring to understand their strategic significance.
Why it is important
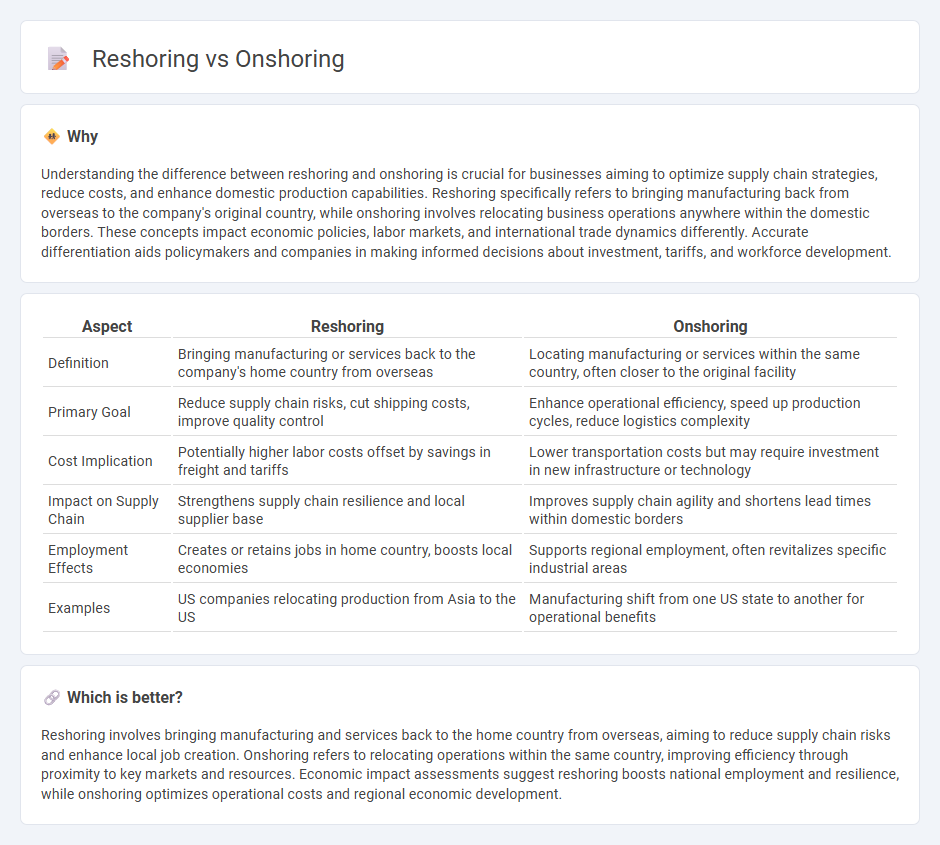
Understanding the difference between reshoring and onshoring is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize supply chain strategies, reduce costs, and enhance domestic production capabilities. Reshoring specifically refers to bringing manufacturing back from overseas to the company's original country, while onshoring involves relocating business operations anywhere within the domestic borders. These concepts impact economic policies, labor markets, and international trade dynamics differently. Accurate differentiation aids policymakers and companies in making informed decisions about investment, tariffs, and workforce development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reshoring | Onshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing or services back to the company's home country from overseas | Locating manufacturing or services within the same country, often closer to the original facility |
| Primary Goal | Reduce supply chain risks, cut shipping costs, improve quality control | Enhance operational efficiency, speed up production cycles, reduce logistics complexity |
| Cost Implication | Potentially higher labor costs offset by savings in freight and tariffs | Lower transportation costs but may require investment in new infrastructure or technology |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Strengthens supply chain resilience and local supplier base | Improves supply chain agility and shortens lead times within domestic borders |
| Employment Effects | Creates or retains jobs in home country, boosts local economies | Supports regional employment, often revitalizes specific industrial areas |
| Examples | US companies relocating production from Asia to the US | Manufacturing shift from one US state to another for operational benefits |
Which is better?
Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country from overseas, aiming to reduce supply chain risks and enhance local job creation. Onshoring refers to relocating operations within the same country, improving efficiency through proximity to key markets and resources. Economic impact assessments suggest reshoring boosts national employment and resilience, while onshoring optimizes operational costs and regional economic development.
Connection
Reshoring and onshoring both focus on relocating manufacturing and supply chain operations back to a company's home country to reduce dependency on foreign markets and improve supply chain resilience. These strategies help enhance local employment, decrease transportation costs, and mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. Companies adopt reshoring and onshoring to foster economic growth by boosting domestic production and strengthening national industries.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Onshoring involves relocating supply chain operations closer to the home country to reduce lead times and enhance control, while reshoring specifically refers to bringing previously offshore manufacturing back domestically to improve quality and responsiveness. Both strategies aim to mitigate risks such as trade disruptions and rising transportation costs by localizing production and logistics. Discover the advantages and challenges of onshoring and reshoring to optimize your supply chain resilience.
Domestic Production
Onshoring involves relocating business processes or manufacturing back to the company's original country to boost domestic production and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers. Reshoring specifically refers to bringing manufacturing operations from overseas back to the home country to enhance supply chain resilience and create local jobs. Explore detailed comparisons and strategic benefits of onshoring versus reshoring to optimize your domestic production strategy.
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly impact decisions between onshoring and reshoring, with onshoring typically involving higher wages due to domestic labor market standards. Reshoring strategically balances labor expenses by relocating production closer to end markets while leveraging existing workforce skills, mitigating outsourcing risks. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how labor cost dynamics influence manufacturing location strategies.
Source and External Links
Reshoring, nearshoring, friendshoring, onshoring, and offshoring - Onshoring is a strategy of moving part or all of a business's operations, like manufacturing, back to the company's home country to improve control, support local labor markets, and respond quickly to market changes.
What Is Onshoring? - Thomasnet - Onshoring is relocating or sourcing business production within a nation's borders, often contrasted with reshoring (bringing back overseas operations) and nearshoring (moving operations to nearby countries).
What Is Onshoring? - NetSuite - Onshoring refers to bringing manufacturing or sourcing operations back to a company's home country from overseas due to risks like tariffs and logistical disruptions, despite challenges like higher domestic labor costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com