Shadow bailouts refer to indirect government interventions that support struggling financial institutions without public disclosure, often through central bank facilities or regulatory forbearance. Currency swap lines are reciprocal agreements between central banks to exchange currencies and provide liquidity during periods of market stress, stabilizing foreign exchange markets and ensuring global financial stability. Explore how these mechanisms influence economic resilience and crisis management strategies.
Why it is important
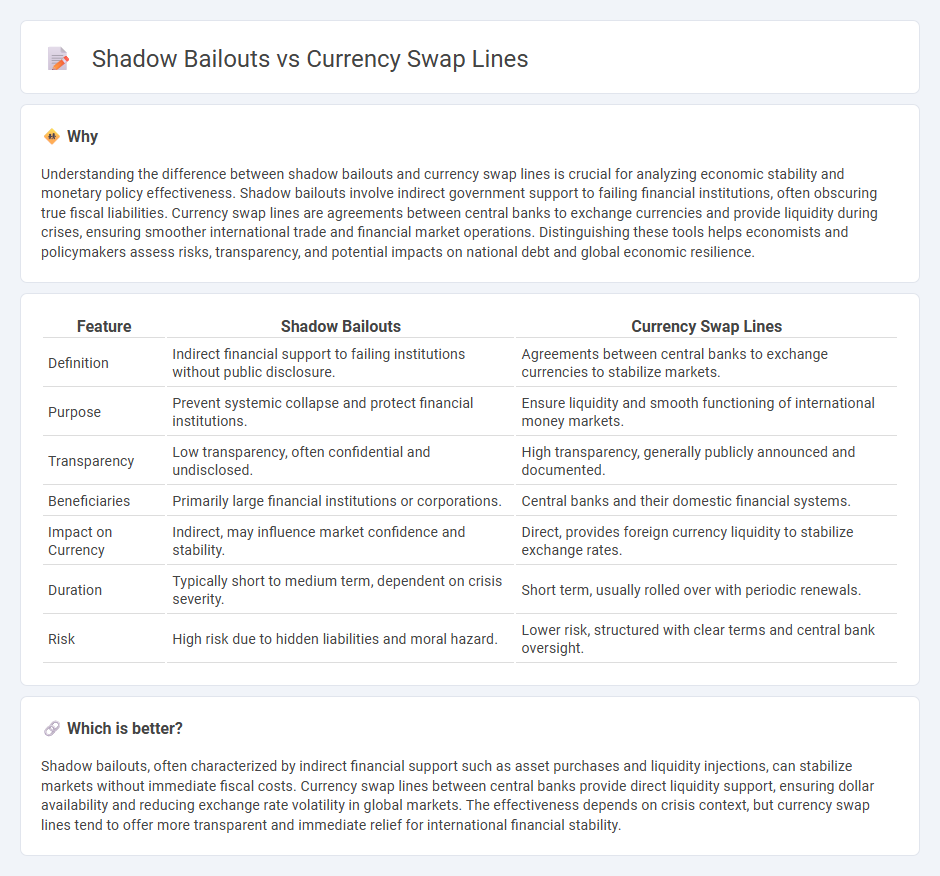
Understanding the difference between shadow bailouts and currency swap lines is crucial for analyzing economic stability and monetary policy effectiveness. Shadow bailouts involve indirect government support to failing financial institutions, often obscuring true fiscal liabilities. Currency swap lines are agreements between central banks to exchange currencies and provide liquidity during crises, ensuring smoother international trade and financial market operations. Distinguishing these tools helps economists and policymakers assess risks, transparency, and potential impacts on national debt and global economic resilience.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Shadow Bailouts | Currency Swap Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indirect financial support to failing institutions without public disclosure. | Agreements between central banks to exchange currencies to stabilize markets. |
| Purpose | Prevent systemic collapse and protect financial institutions. | Ensure liquidity and smooth functioning of international money markets. |
| Transparency | Low transparency, often confidential and undisclosed. | High transparency, generally publicly announced and documented. |
| Beneficiaries | Primarily large financial institutions or corporations. | Central banks and their domestic financial systems. |
| Impact on Currency | Indirect, may influence market confidence and stability. | Direct, provides foreign currency liquidity to stabilize exchange rates. |
| Duration | Typically short to medium term, dependent on crisis severity. | Short term, usually rolled over with periodic renewals. |
| Risk | High risk due to hidden liabilities and moral hazard. | Lower risk, structured with clear terms and central bank oversight. |
Which is better?
Shadow bailouts, often characterized by indirect financial support such as asset purchases and liquidity injections, can stabilize markets without immediate fiscal costs. Currency swap lines between central banks provide direct liquidity support, ensuring dollar availability and reducing exchange rate volatility in global markets. The effectiveness depends on crisis context, but currency swap lines tend to offer more transparent and immediate relief for international financial stability.
Connection
Shadow bailouts and currency swap lines are interconnected mechanisms that stabilize economies during financial distress by providing indirect liquidity support. Shadow bailouts involve central banks using currency swap lines to exchange currencies, enabling access to foreign reserves without direct government intervention, thus avoiding overt fiscal bailout perceptions. These swap lines function as a critical tool to maintain currency stability and prevent liquidity crises in global financial markets.
Key Terms
**Currency Swap Lines:**
Currency swap lines are agreements between central banks to exchange currencies, providing liquidity and stabilizing forex markets during financial crises. These arrangements enable timely access to foreign currency, mitigating risks of market panic and ensuring smooth international trade and financial flows. Explore how currency swap lines function as critical tools to prevent financial turmoil and contrast them with shadow bailouts.
Central Banks
Central bank currency swap lines provide liquidity by allowing central banks to exchange their currencies, stabilizing foreign exchange markets and supporting international trade during financial crises. These swap lines contrast with shadow bailouts, which involve indirect financial assistance through third-party institutions to avoid direct government intervention. Explore the mechanisms and impacts of central bank swap lines compared to shadow bailouts to understand their roles in maintaining global economic stability.
Liquidity Provision
Currency swap lines are agreements between central banks to exchange currency, providing essential liquidity to stabilize international markets during financial stress. Shadow bailouts refer to indirect financial support mechanisms that enhance liquidity without official bailout declarations, often through covert central bank operations. Explore the detailed mechanisms and impacts of these liquidity provision strategies for comprehensive insights.
Source and External Links
What are currency swap lines? - European Central Bank - Currency swap lines are agreements between two central banks to exchange currencies, allowing one central bank to obtain foreign currency liquidity from another to provide it to domestic banks, crucial for maintaining liquidity during financial stress, such as the ECB's swap line with the US Federal Reserve providing dollars to euro area banks in 2008.
Central bank liquidity swaps - Federal Reserve Board - The Federal Reserve's central bank liquidity swap lines improve liquidity in dollar funding markets globally by enabling foreign central banks to deliver U.S. dollar funding domestically during stress periods, involving two-part transactions to exchange currencies at market rates and later reversing the exchange with interest paid.
Central bank liquidity swap - Wikipedia - Central bank liquidity swaps, particularly U.S. dollar swap lines, are extensively used due to the dollar's reserve currency status and provide liquidity from the Federal Reserve to foreign central banks, with programs expanding significantly during crises since their establishment in 2007 to help overseas markets access dollar funding.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com