Slowbalisation describes the recent deceleration in global economic integration marked by reduced international trade growth, supply chain diversification, and rising protectionist policies, contrasting with globalisation's rapid expansion of cross-border commerce and investment since the late 20th century. Key indicators include declining global trade volumes as a percentage of GDP and shifts towards regionalisation over global value chains, driven by geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic's impact on supply stability. Explore the evolving dynamics shaping international economic relations and their implications for businesses and policymakers.
Why it is important
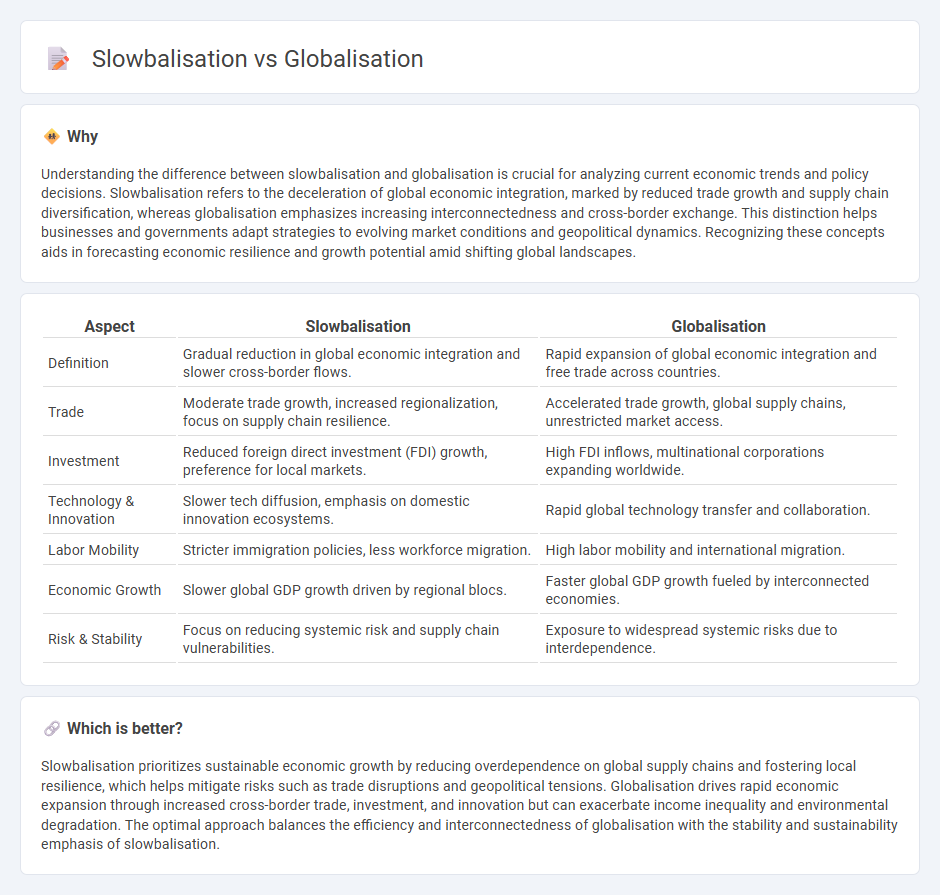
Understanding the difference between slowbalisation and globalisation is crucial for analyzing current economic trends and policy decisions. Slowbalisation refers to the deceleration of global economic integration, marked by reduced trade growth and supply chain diversification, whereas globalisation emphasizes increasing interconnectedness and cross-border exchange. This distinction helps businesses and governments adapt strategies to evolving market conditions and geopolitical dynamics. Recognizing these concepts aids in forecasting economic resilience and growth potential amid shifting global landscapes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalisation | Globalisation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual reduction in global economic integration and slower cross-border flows. | Rapid expansion of global economic integration and free trade across countries. |
| Trade | Moderate trade growth, increased regionalization, focus on supply chain resilience. | Accelerated trade growth, global supply chains, unrestricted market access. |
| Investment | Reduced foreign direct investment (FDI) growth, preference for local markets. | High FDI inflows, multinational corporations expanding worldwide. |
| Technology & Innovation | Slower tech diffusion, emphasis on domestic innovation ecosystems. | Rapid global technology transfer and collaboration. |
| Labor Mobility | Stricter immigration policies, less workforce migration. | High labor mobility and international migration. |
| Economic Growth | Slower global GDP growth driven by regional blocs. | Faster global GDP growth fueled by interconnected economies. |
| Risk & Stability | Focus on reducing systemic risk and supply chain vulnerabilities. | Exposure to widespread systemic risks due to interdependence. |
Which is better?
Slowbalisation prioritizes sustainable economic growth by reducing overdependence on global supply chains and fostering local resilience, which helps mitigate risks such as trade disruptions and geopolitical tensions. Globalisation drives rapid economic expansion through increased cross-border trade, investment, and innovation but can exacerbate income inequality and environmental degradation. The optimal approach balances the efficiency and interconnectedness of globalisation with the stability and sustainability emphasis of slowbalisation.
Connection
Slowbalisation refers to the gradual deceleration of global economic integration, reflecting reduced growth rates in international trade, investment, and supply chain expansion. Globalisation represents the increasing interconnectedness of economies through cross-border commerce, capital flows, and technological exchange, which has plateaued due to geopolitical tensions, protectionism, and pandemic-related disruptions. The interplay between slowbalisation and globalisation highlights a transition phase where global economic networks are becoming less dynamic, altering trade patterns and challenging previously established globalization paradigms.
Key Terms
Trade liberalization
Trade liberalization has been a driving force behind globalization, fostering the reduction of tariffs and barriers to facilitate the free flow of goods and services across international borders. Slowbalisation, however, highlights the deceleration of this process due to rising protectionism, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions. Explore further to understand how these contrasting trends impact global economic dynamics and policy decisions.
Supply chains
Globalisation expanded supply chains by integrating worldwide production and distribution networks, boosting efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Slowbalisation reflects a strategic shift towards regionalising supply chains to enhance resilience, reduce dependencies, and address geopolitical risks. Explore how evolving supply chain strategies impact global trade dynamics and business competitiveness.
Protectionism
Protectionism has surged amid slowbalisation, contrasting the free trade ethos of globalisation by emphasizing tariffs, import quotas, and domestic industry support. This shift reflects growing economic nationalism and supply chain resilience concerns, slowing international market integration. Explore how protectionist policies reshape global trade dynamics and economic strategies.
Source and External Links
Globalisation - Manual for Human Rights Education with ... - Globalisation describes the economic, cultural, social, and political changes over the past 50 years, involving increased integration of trade, technology, and ideas, influencing many aspects of life globally with both positive and negative effects.
Globalization - Globalization is the increasing interdependence and integration of economies, cultures, and societies worldwide, driven by trade, investment, migration, and communication technologies, classified into economic, cultural, and political dimensions.
What is Globalization: Pros, Cons, and History - Globalization is the process by which goods, services, ideas, and information spread globally, changing international economic activity, trade, and cultural exchange, while creating both opportunities and challenges for societies and businesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com