Friendshoring focuses on relocating supply chains to allied countries to enhance economic security and reduce geopolitical risks, promoting collaboration among trusted partners. Protectionism emphasizes safeguarding domestic industries through tariffs and trade barriers to limit foreign competition and preserve jobs. Explore how these strategies impact global trade dynamics and economic growth.
Why it is important
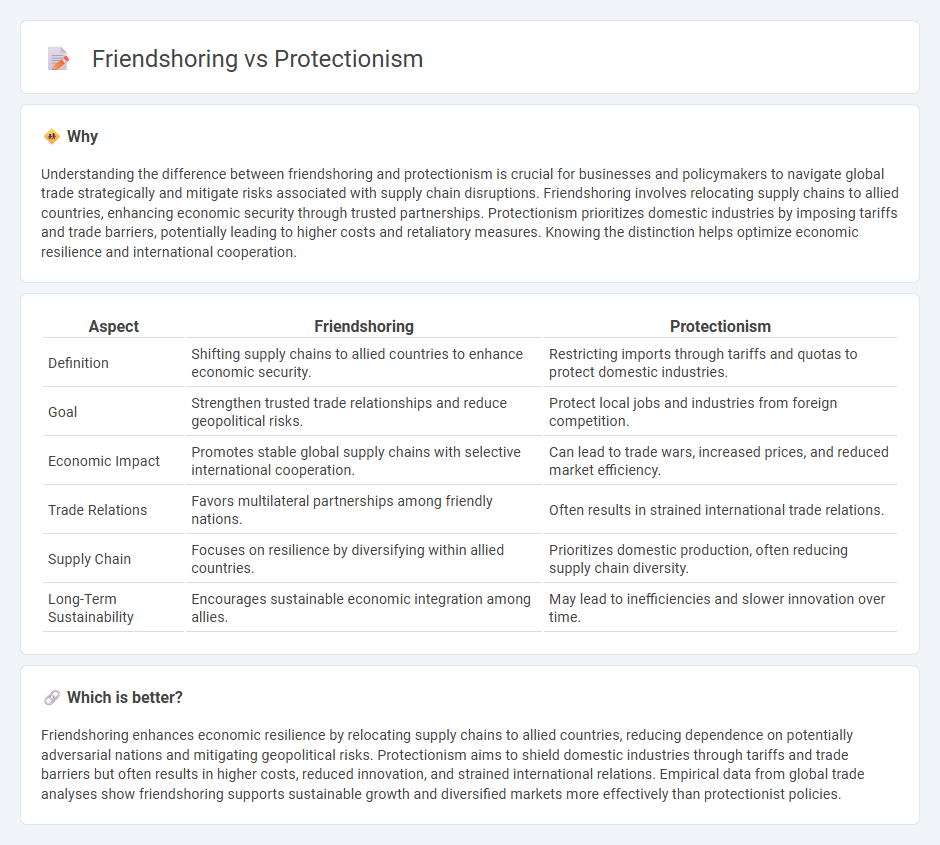
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and protectionism is crucial for businesses and policymakers to navigate global trade strategically and mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Friendshoring involves relocating supply chains to allied countries, enhancing economic security through trusted partnerships. Protectionism prioritizes domestic industries by imposing tariffs and trade barriers, potentially leading to higher costs and retaliatory measures. Knowing the distinction helps optimize economic resilience and international cooperation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Protectionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shifting supply chains to allied countries to enhance economic security. | Restricting imports through tariffs and quotas to protect domestic industries. |
| Goal | Strengthen trusted trade relationships and reduce geopolitical risks. | Protect local jobs and industries from foreign competition. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes stable global supply chains with selective international cooperation. | Can lead to trade wars, increased prices, and reduced market efficiency. |
| Trade Relations | Favors multilateral partnerships among friendly nations. | Often results in strained international trade relations. |
| Supply Chain | Focuses on resilience by diversifying within allied countries. | Prioritizes domestic production, often reducing supply chain diversity. |
| Long-Term Sustainability | Encourages sustainable economic integration among allies. | May lead to inefficiencies and slower innovation over time. |
Which is better?
Friendshoring enhances economic resilience by relocating supply chains to allied countries, reducing dependence on potentially adversarial nations and mitigating geopolitical risks. Protectionism aims to shield domestic industries through tariffs and trade barriers but often results in higher costs, reduced innovation, and strained international relations. Empirical data from global trade analyses show friendshoring supports sustainable growth and diversified markets more effectively than protectionist policies.
Connection
Friendshoring and protectionism both aim to secure supply chains and protect domestic industries by prioritizing trade with allied countries. Friendshoring reduces dependency on politically unstable or adversarial nations, while protectionism imposes tariffs and trade barriers to shield local economies. Together, they reflect a strategic shift toward economic nationalism and supply chain resilience amid global uncertainties.
Key Terms
Tariffs
Protectionism primarily involves imposing tariffs to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, thereby increasing the cost of imported goods and encouraging local production. Friendshoring, while potentially maintaining some tariffs, emphasizes sourcing from allied nations to ensure supply chain security and political alignment rather than maximizing tariff barriers. Explore how tariffs influence global trade strategies in protectionism and friendshoring to understand evolving economic policies.
Supply Chains
Protectionism emphasizes tariffs and trade barriers to secure domestic supply chains and reduce foreign dependency. Friendshoring shifts supply chains to politically aligned countries, enhancing security through trusted partnerships while maintaining global trade flexibility. Explore how these strategies impact global logistics and economic resilience.
Trade Agreements
Trade agreements play a crucial role in shaping protectionism by establishing barriers such as tariffs and quotas to safeguard domestic industries, while friendshoring emphasizes forging partnerships with politically aligned countries to enhance supply chain security. Protectionist policies often lead to restrictive trade agreements that prioritize national economic interests, whereas friendshoring encourages collaboration through bilateral or multilateral agreements that promote trust and stable trade flows. Explore the evolving dynamics between protectionism and friendshoring in global trade frameworks to understand their impact on economic diplomacy.
Source and External Links
Protectionism - Definition, Types, Advantages and Disadvantages - Protectionism is a trade policy where a government promotes domestic producers by imposing tariffs, quotas, or subsidies to limit foreign competition and boost local production.
Protectionism - Wikipedia - Protectionism involves restricting imports through tariffs, quotas, administrative barriers, and subsidies to shield domestic industries from lower-priced foreign goods and maintain local employment.
Protectionism | Macroeconomics - Lumen Learning - Protectionism manifests mainly as tariffs, import quotas, and non-tariff barriers, which increase import costs and limit foreign goods to protect domestic markets and jobs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com