Economic scarring refers to the long-term damage caused by recessions or financial crises, such as persistent unemployment, reduced labor force participation, and diminished capital investment. Creative destruction, a concept popularized by economist Joseph Schumpeter, describes the process where innovation and technological advancements disrupt established industries, leading to economic renewal and growth. Explore more about how these contrasting forces shape economic resilience and transformation.
Why it is important
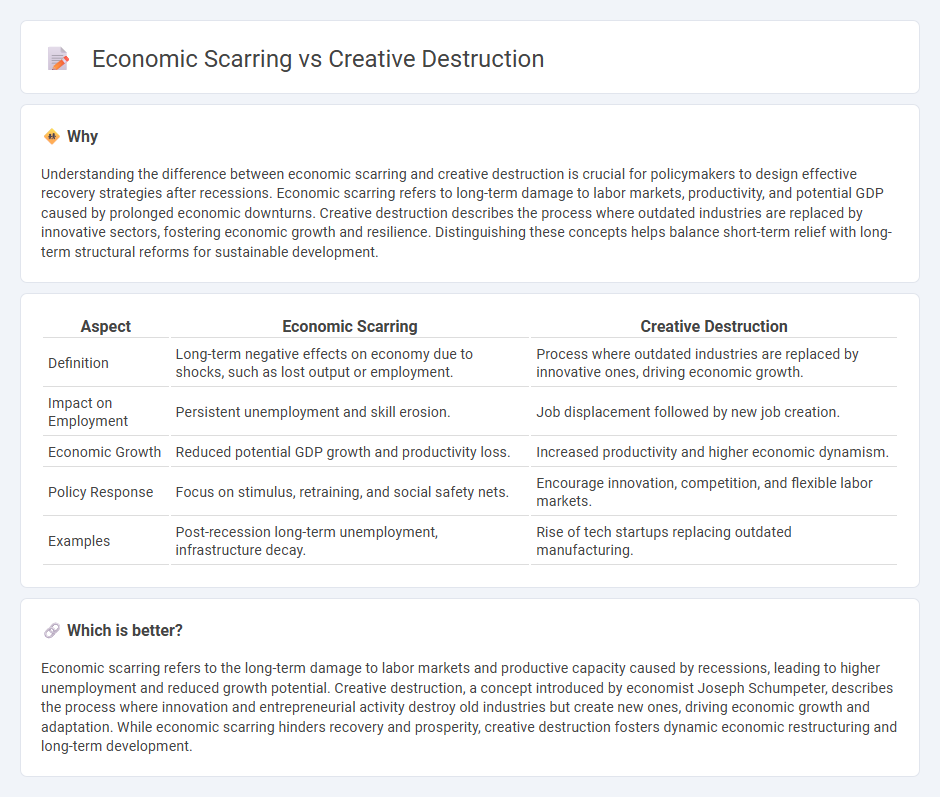
Understanding the difference between economic scarring and creative destruction is crucial for policymakers to design effective recovery strategies after recessions. Economic scarring refers to long-term damage to labor markets, productivity, and potential GDP caused by prolonged economic downturns. Creative destruction describes the process where outdated industries are replaced by innovative sectors, fostering economic growth and resilience. Distinguishing these concepts helps balance short-term relief with long-term structural reforms for sustainable development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Economic Scarring | Creative Destruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Long-term negative effects on economy due to shocks, such as lost output or employment. | Process where outdated industries are replaced by innovative ones, driving economic growth. |
| Impact on Employment | Persistent unemployment and skill erosion. | Job displacement followed by new job creation. |
| Economic Growth | Reduced potential GDP growth and productivity loss. | Increased productivity and higher economic dynamism. |
| Policy Response | Focus on stimulus, retraining, and social safety nets. | Encourage innovation, competition, and flexible labor markets. |
| Examples | Post-recession long-term unemployment, infrastructure decay. | Rise of tech startups replacing outdated manufacturing. |
Which is better?
Economic scarring refers to the long-term damage to labor markets and productive capacity caused by recessions, leading to higher unemployment and reduced growth potential. Creative destruction, a concept introduced by economist Joseph Schumpeter, describes the process where innovation and entrepreneurial activity destroy old industries but create new ones, driving economic growth and adaptation. While economic scarring hinders recovery and prosperity, creative destruction fosters dynamic economic restructuring and long-term development.
Connection
Economic scarring occurs when prolonged downturns cause durable damage to labor markets and productive capacity, while creative destruction drives economic renewal by replacing obsolete industries with innovative ones. The interplay between these forces shapes long-term economic resilience, as creative destruction mitigates scarring by fostering new growth opportunities amid structural shifts. Understanding this dynamic helps policymakers balance short-term recovery efforts with enabling transformative innovation for sustained economic development.
Key Terms
Innovation
Creative destruction drives long-term economic growth by enabling innovation to replace outdated industries with more efficient technologies, fostering dynamic market evolution. Economic scarring hinders this process by causing persistent job losses, reduced human capital, and weakened entrepreneurial activity, which delay technological adoption and productivity gains. Discover how balancing these forces shapes innovation-led recovery and sustainable development.
Productivity
Creative destruction drives productivity by reallocating resources from outdated industries to innovative sectors, fostering long-term economic growth. Economic scarring, however, hampers productivity through persistent unemployment, skills erosion, and reduced capital investment, limiting recovery potential. Explore how balancing these forces can shape sustainable productivity improvements in evolving economies.
Labor market adjustment
Labor market adjustment during periods of creative destruction involves the reallocation of workers from declining industries to emerging sectors, fostering innovation and productivity growth. Economic scarring, however, occurs when prolonged unemployment or underemployment leads to lasting damage on workers' skills and earnings potential, hindering labor market recovery. Explore the intricate balance between these forces to understand how policies can optimize labor market resilience.
Source and External Links
Creative Destruction - Econlib - Creative destruction is the process in capitalism where new products, technologies, and firms continuously replace older ones, driven by entrepreneurship and competition, fueling economic progress and productivity growth.
Creative destruction - Wikipedia - Creative destruction describes how new innovations render old ones obsolete, driving economic growth, though it can also cause disruption and inequality; the concept is central in economics and linked to sustainable development and social change.
Creative destruction - MIT Economics - Creative destruction refers to the constant product and process innovation that replaces outdated production units, significantly contributing to productivity growth and shaping macroeconomic fluctuations and structural change.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com