Nearshoring involves relocating business processes to nearby countries, reducing transportation costs and improving supply chain responsiveness compared to onshoring, which keeps operations within the home country to maintain control and support local economies. Industries like manufacturing and technology are increasingly adopting nearshoring to benefit from geographic proximity and shared time zones. Explore the economic impacts and strategic advantages of nearshoring versus onshoring to optimize your business operations.
Why it is important
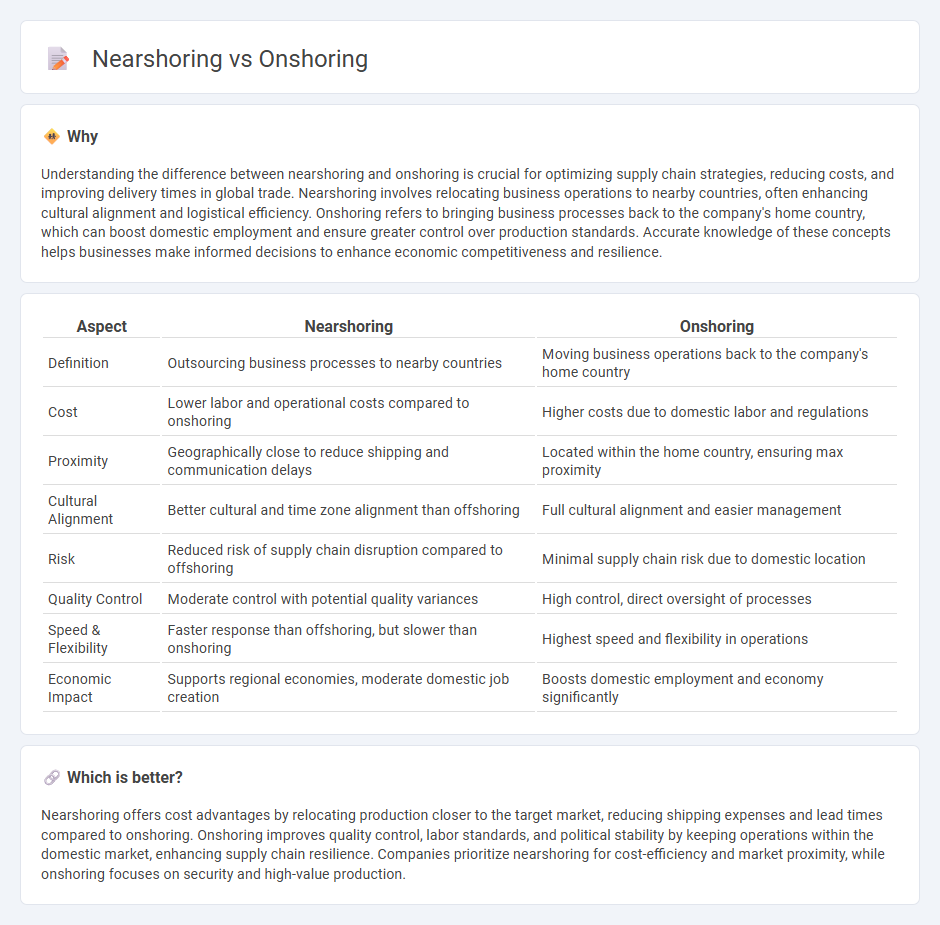
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and onshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain strategies, reducing costs, and improving delivery times in global trade. Nearshoring involves relocating business operations to nearby countries, often enhancing cultural alignment and logistical efficiency. Onshoring refers to bringing business processes back to the company's home country, which can boost domestic employment and ensure greater control over production standards. Accurate knowledge of these concepts helps businesses make informed decisions to enhance economic competitiveness and resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Onshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Outsourcing business processes to nearby countries | Moving business operations back to the company's home country |
| Cost | Lower labor and operational costs compared to onshoring | Higher costs due to domestic labor and regulations |
| Proximity | Geographically close to reduce shipping and communication delays | Located within the home country, ensuring max proximity |
| Cultural Alignment | Better cultural and time zone alignment than offshoring | Full cultural alignment and easier management |
| Risk | Reduced risk of supply chain disruption compared to offshoring | Minimal supply chain risk due to domestic location |
| Quality Control | Moderate control with potential quality variances | High control, direct oversight of processes |
| Speed & Flexibility | Faster response than offshoring, but slower than onshoring | Highest speed and flexibility in operations |
| Economic Impact | Supports regional economies, moderate domestic job creation | Boosts domestic employment and economy significantly |
Which is better?
Nearshoring offers cost advantages by relocating production closer to the target market, reducing shipping expenses and lead times compared to onshoring. Onshoring improves quality control, labor standards, and political stability by keeping operations within the domestic market, enhancing supply chain resilience. Companies prioritize nearshoring for cost-efficiency and market proximity, while onshoring focuses on security and high-value production.
Connection
Nearshoring and onshoring are connected through their shared goal of optimizing supply chains by relocating production closer to the end consumer. Both strategies reduce lead times, lower transportation costs, and mitigate risks associated with long-distance logistics and international trade disruptions. Firms increasingly adopt nearshoring and onshoring to enhance operational resilience and respond swiftly to market fluctuations.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Onshoring involves relocating supply chain operations back to the company's home country to reduce risks associated with long-distance logistics and enhance control over production quality. Nearshoring shifts these operations to nearby countries, offering cost savings and shorter transportation times while maintaining proximity for easier collaboration and quicker response to market changes. Explore the benefits and challenges of onshoring versus nearshoring to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly impact the decision between onshoring and nearshoring, with onshoring typically involving higher wages due to domestic market standards, while nearshoring offers more competitive labor rates by utilizing skilled workers in geographically closer countries. Companies must analyze wage differentials, training expenses, and labor law compliance to optimize overall operational efficiency. Explore detailed comparisons of labor cost savings and productivity benefits to make an informed sourcing strategy choice.
Geographic Proximity
Onshoring involves relocating business operations to the company's home country, ensuring maximum geographic proximity that reduces shipping costs and simplifies communication across similar time zones. Nearshoring, by contrast, shifts activities to nearby countries, balancing cost savings with geographic closeness to enhance supply chain agility and faster market responsiveness. Discover the strategic benefits and decisive factors that influence choosing between onshoring and nearshoring.
Source and External Links
Reshoring, nearshoring, friendshoring, onshoring, and ... - Onshoring is the strategy of moving business operations back to the company's home country, allowing easier management and quicker response to market changes while supporting local labor markets, exemplified by General Motors bringing car production back to the US.
What Is Onshoring? - Onshoring refers to relocating business production within national borders, often used to increase supply chain control and help domestic economies, and differs subtly from reshoring and nearshoring.
What Is Onshoring? - Onshoring involves bringing sourcing and manufacturing back home after offshoring overseas, motivated by rising costs, trade tensions, and desire for local control, though it may include challenges like higher labor costs and need for new infrastructure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com