Eco-anxiety economy reflects growing stress caused by environmental degradation and climate change impacts on financial systems. In contrast, a steady-state economy strives for sustainable resource use and stable population to maintain long-term ecological balance. Explore how these economic models address environmental and social challenges for a resilient future.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between eco-anxiety economy and steady-state economy is crucial for shaping sustainable economic policies that address environmental concerns without sacrificing growth stability. Eco-anxiety economy focuses on the emotional and psychological impacts of climate change on consumers and investors, influencing market behavior and economic decision-making. Steady-state economy emphasizes maintaining economic stability by balancing resource consumption and waste generation within ecological limits. Recognizing these differences helps policymakers implement strategies that foster resilient economies while mitigating environmental degradation.
Comparison Table
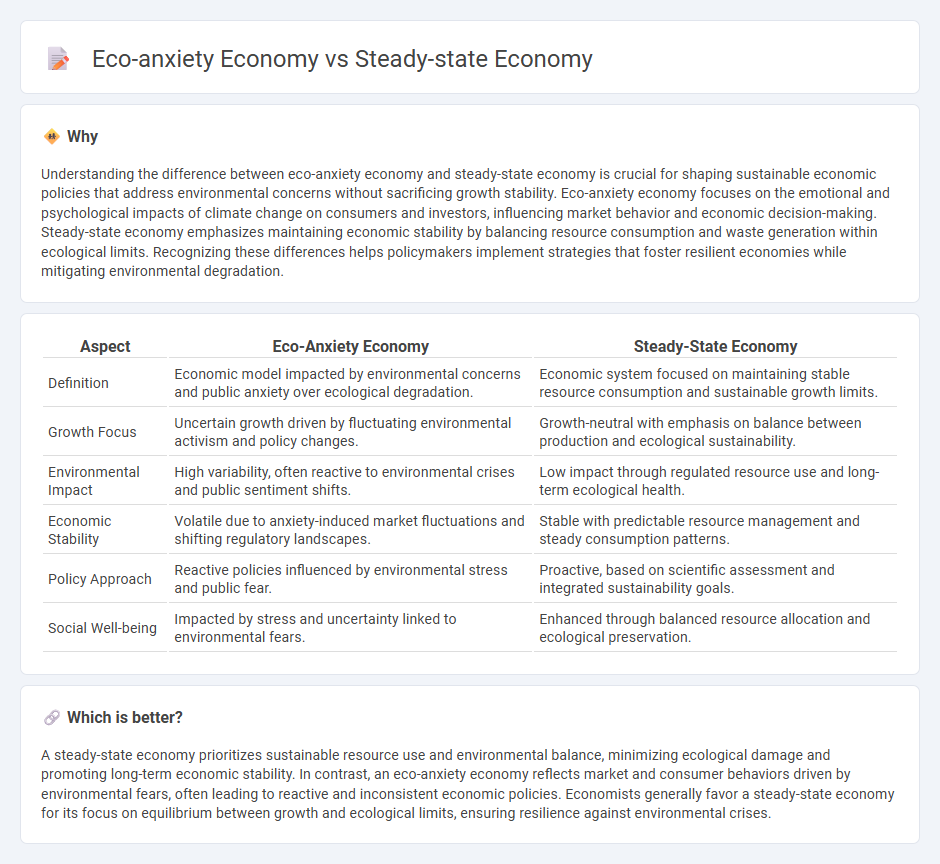
| Aspect | Eco-Anxiety Economy | Steady-State Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic model impacted by environmental concerns and public anxiety over ecological degradation. | Economic system focused on maintaining stable resource consumption and sustainable growth limits. |
| Growth Focus | Uncertain growth driven by fluctuating environmental activism and policy changes. | Growth-neutral with emphasis on balance between production and ecological sustainability. |
| Environmental Impact | High variability, often reactive to environmental crises and public sentiment shifts. | Low impact through regulated resource use and long-term ecological health. |
| Economic Stability | Volatile due to anxiety-induced market fluctuations and shifting regulatory landscapes. | Stable with predictable resource management and steady consumption patterns. |
| Policy Approach | Reactive policies influenced by environmental stress and public fear. | Proactive, based on scientific assessment and integrated sustainability goals. |
| Social Well-being | Impacted by stress and uncertainty linked to environmental fears. | Enhanced through balanced resource allocation and ecological preservation. |
Which is better?
A steady-state economy prioritizes sustainable resource use and environmental balance, minimizing ecological damage and promoting long-term economic stability. In contrast, an eco-anxiety economy reflects market and consumer behaviors driven by environmental fears, often leading to reactive and inconsistent economic policies. Economists generally favor a steady-state economy for its focus on equilibrium between growth and ecological limits, ensuring resilience against environmental crises.
Connection
The rise of eco-anxiety reflects growing public concern about environmental degradation and climate change, which pressures economies to rethink traditional growth models. This psychological stress accelerates interest in steady-state economy principles, emphasizing sustainable resource use and ecological balance without continuous expansion. By addressing eco-anxiety, steady-state economy strategies promote long-term economic resilience aligned with environmental limits.
Key Terms
**Steady-State Economy:**
A steady-state economy emphasizes sustainable development by maintaining stable population and resource consumption levels to achieve long-term ecological balance. It prioritizes low environmental impact, renewable resource use, and equitable wealth distribution while minimizing economic growth pressures. Explore how adopting a steady-state economy can mitigate eco-anxiety and foster planetary health.
Sustainable Yield
A steady-state economy emphasizes maintaining sustainable yield by balancing resource consumption with natural regeneration rates, ensuring long-term ecological stability. In contrast, an eco-anxiety economy grapples with psychological stress from environmental degradation and unsustainable practices, often prompting urgent but sometimes fragmented responses. Explore the dynamics between these economic models and their approaches to sustainable yield for a deeper understanding of environmental resilience.
Resource Limits
A steady-state economy prioritizes maintaining consistent resource consumption levels within ecological limits to ensure long-term sustainability. In contrast, an eco-anxiety economy reflects societal stress driven by perceived resource scarcity and environmental degradation, often resulting in erratic consumption patterns. Explore how integrating steady-state principles can alleviate eco-anxiety and promote resilient resource management.
Source and External Links
The Steady State Economy: Limits to Economic Growth? - A Steady State Economy (SSE) is a stable, sustainable economy at equilibrium with constant demand, supply, production, and population size, designed to live within Earth's resource limits while promoting social cohesion and economic stability by limiting growth and minimizing waste.
Balancing Act: How the Steady-State Economy Seeks Equilibrium - The steady-state economy prioritizes ecological balance over continuous growth by stabilizing population and consumption to ensure sustainability, focusing on quality of life and ecological health rather than GDP growth.
Steady-state economy - Wikipedia - A steady-state economy maintains constant physical wealth and population through institutions that limit income inequality, stabilize population growth with reproduction licensing, and regulate resource throughput via depletion quotas to politically enforce ecological sustainability and equity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com