Slowbalisation reflects a deceleration in globalization characterized by reduced cross-border trade growth and increased supply chain localization. Nearshoring shifts production closer to consumer markets, enhancing efficiency and reducing risks linked to long-distance logistics. Explore the impacts of these trends on global economic strategies and supply chain management.
Why it is important
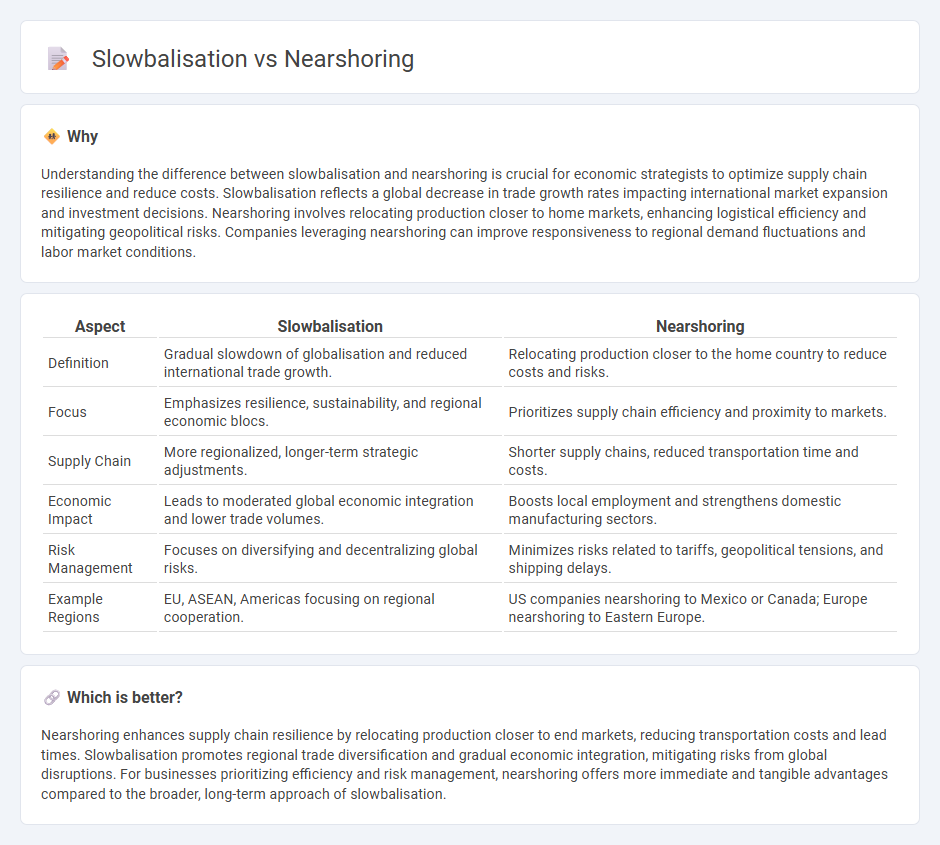
Understanding the difference between slowbalisation and nearshoring is crucial for economic strategists to optimize supply chain resilience and reduce costs. Slowbalisation reflects a global decrease in trade growth rates impacting international market expansion and investment decisions. Nearshoring involves relocating production closer to home markets, enhancing logistical efficiency and mitigating geopolitical risks. Companies leveraging nearshoring can improve responsiveness to regional demand fluctuations and labor market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalisation | Nearshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual slowdown of globalisation and reduced international trade growth. | Relocating production closer to the home country to reduce costs and risks. |
| Focus | Emphasizes resilience, sustainability, and regional economic blocs. | Prioritizes supply chain efficiency and proximity to markets. |
| Supply Chain | More regionalized, longer-term strategic adjustments. | Shorter supply chains, reduced transportation time and costs. |
| Economic Impact | Leads to moderated global economic integration and lower trade volumes. | Boosts local employment and strengthens domestic manufacturing sectors. |
| Risk Management | Focuses on diversifying and decentralizing global risks. | Minimizes risks related to tariffs, geopolitical tensions, and shipping delays. |
| Example Regions | EU, ASEAN, Americas focusing on regional cooperation. | US companies nearshoring to Mexico or Canada; Europe nearshoring to Eastern Europe. |
Which is better?
Nearshoring enhances supply chain resilience by relocating production closer to end markets, reducing transportation costs and lead times. Slowbalisation promotes regional trade diversification and gradual economic integration, mitigating risks from global disruptions. For businesses prioritizing efficiency and risk management, nearshoring offers more immediate and tangible advantages compared to the broader, long-term approach of slowbalisation.
Connection
Slowbalisation, characterized by reduced global trade growth and supply chain diversification, drives companies to prioritize nearshoring as a strategic response. Nearshoring helps mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and long-distance logistics by relocating production closer to end markets. This shift supports regional economic resilience and reshapes global supply chain dynamics.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Nearshoring enhances supply chain efficiency by relocating production closer to the consumer market, reducing transportation costs and lead times. Slowbalisation reflects a trend towards cautious globalization, emphasizing supply chain resilience and diversification amid geopolitical risks. Explore how these dynamics reshape modern supply chain strategies and operational decisions.
Tariffs
Nearshoring reduces exposure to tariffs by relocating production closer to target markets, minimizing cross-border trade costs. Slowbalisation leads to more regional trade agreements, stabilizing tariff policies while balancing global supply chain dependencies. Explore how tariff dynamics shape strategic decisions in nearshoring and slowbalisation for deeper insights.
Trade Flows
Nearshoring accelerates trade flows by relocating manufacturing closer to consumer markets, reducing shipping times and logistical complexities. Slowbalisation reflects a gradual slowdown in global trade growth due to rising protectionism and supply chain diversification, impacting long-term trade volume expansion. Explore how these contrasting trends reshape global trade dynamics and supply chain strategies.
Source and External Links
Nearshoring - Nearshoring is the outsourcing of business processes, especially information technology, to companies in a nearby country, often sharing a border with the outsourcing firm.
Nearshoring in Mexico | Deloitte Insights - Nearshoring is a strategy where companies move production closer to the final consumer to reduce costs and supply chain risks, with Mexico emerging as a key beneficiary due to trade agreements and global disruptions impacting logistics.
What is Nearshoring? Definition and Benefits - TTEC - Nearshoring offers cultural alignment, geographic proximity, and cost advantages by recruiting employees from neighboring countries, making it a hybrid between onshore and offshore outsourcing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com