Gigification transforms the economy by increasing freelance and short-term contract work, challenging traditional job security models tied to permanent employment. This shift impacts income stability, benefits access, and workers' long-term financial planning. Discover more about how gigification reshapes economic landscapes and job market dynamics.
Why it is important
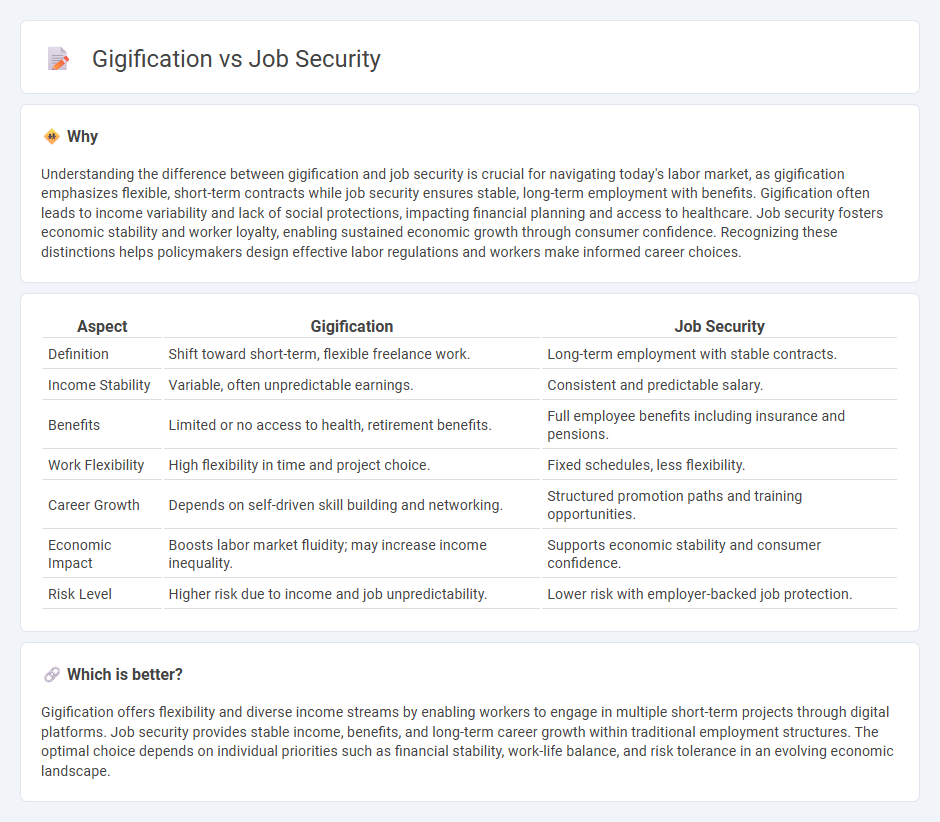
Understanding the difference between gigification and job security is crucial for navigating today's labor market, as gigification emphasizes flexible, short-term contracts while job security ensures stable, long-term employment with benefits. Gigification often leads to income variability and lack of social protections, impacting financial planning and access to healthcare. Job security fosters economic stability and worker loyalty, enabling sustained economic growth through consumer confidence. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers design effective labor regulations and workers make informed career choices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Job Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shift toward short-term, flexible freelance work. | Long-term employment with stable contracts. |
| Income Stability | Variable, often unpredictable earnings. | Consistent and predictable salary. |
| Benefits | Limited or no access to health, retirement benefits. | Full employee benefits including insurance and pensions. |
| Work Flexibility | High flexibility in time and project choice. | Fixed schedules, less flexibility. |
| Career Growth | Depends on self-driven skill building and networking. | Structured promotion paths and training opportunities. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts labor market fluidity; may increase income inequality. | Supports economic stability and consumer confidence. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to income and job unpredictability. | Lower risk with employer-backed job protection. |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexibility and diverse income streams by enabling workers to engage in multiple short-term projects through digital platforms. Job security provides stable income, benefits, and long-term career growth within traditional employment structures. The optimal choice depends on individual priorities such as financial stability, work-life balance, and risk tolerance in an evolving economic landscape.
Connection
Gigification reshapes traditional employment by increasing freelance, contract, and temporary work, which often lacks the stability of full-time jobs. Job security diminishes as workers face income volatility, limited benefits, and unpredictable schedules inherent in gig economy roles. This shift challenges economic frameworks by prioritizing flexibility over long-term employment guarantees, impacting overall workforce stability.
Key Terms
Employment Stability
Employment stability faces significant challenges as gigification reshapes traditional job security paradigms, with 70% of workers in gig roles reporting income unpredictability and limited benefits compared to conventional employment. The rise in freelance and contract positions lowers long-term job guarantees and access to employer-sponsored health insurance and retirement plans. Explore innovative strategies to enhance employment stability in the evolving gig economy.
Independent Contracting
Independent contracting offers flexible work arrangements but often lacks traditional job security benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and unemployment protection. The rise of gigification has shifted the labor market toward short-term contracts, impacting long-term financial stability for many workers. Explore how the balance between job security and gig economy opportunities affects your career choices.
Labor Protections
Labor protections play a crucial role in job security by ensuring workers receive stable wages, benefits, and safe working conditions. The rise of gigification often challenges these protections as gig workers typically lack access to traditional labor rights like minimum wage guarantees and health insurance. Explore how evolving policies can balance gig economy flexibility with essential labor protections to safeguard worker security.
Source and External Links
Job security - Wikipedia - Job security is the likelihood that an individual keeps their job, influenced by factors like globalization, downsizing, recessions, and technology; it is supported by laws, unions, skills, and career adaptability.
The Importance of Job Security in the Workplace (With Tips) - Indeed - Job security benefits employers by attracting and retaining talent, motivating employees, fostering loyalty, and maintaining positive morale, which supports productivity and company stability.
How to build a culture of job security in a changing workplace - Job security today faces threats from automation, economic instability, restructuring, and outsourcing, with HR addressing these via skills development, transparency, cross-training, and employee engagement programs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com