Living wage represents the minimum income necessary for workers to meet basic needs, including housing, food, healthcare, and transportation, while prevailing wage reflects the standard wage paid to workers in a particular industry or region, often determined by market forces or government regulations. The distinction between these wages affects economic equity, labor market stability, and social welfare policies, influencing both employers' costs and employees' quality of life. Explore the detailed impacts of living wage versus prevailing wage on economic growth and workforce wellbeing.
Why it is important
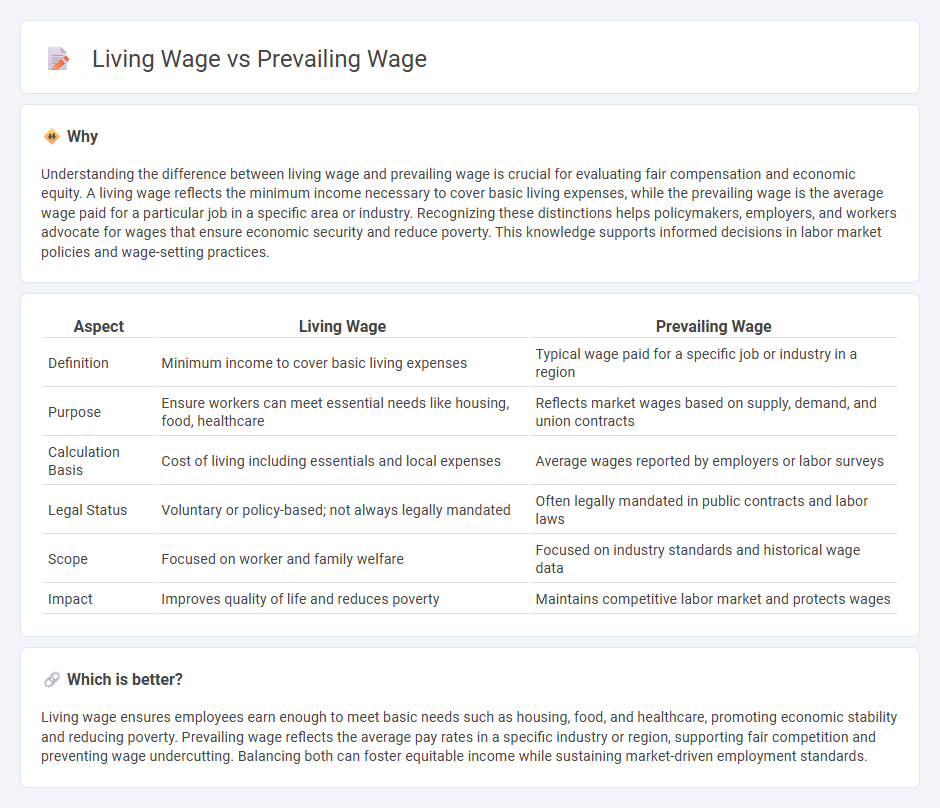
Understanding the difference between living wage and prevailing wage is crucial for evaluating fair compensation and economic equity. A living wage reflects the minimum income necessary to cover basic living expenses, while the prevailing wage is the average wage paid for a particular job in a specific area or industry. Recognizing these distinctions helps policymakers, employers, and workers advocate for wages that ensure economic security and reduce poverty. This knowledge supports informed decisions in labor market policies and wage-setting practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Living Wage | Prevailing Wage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimum income to cover basic living expenses | Typical wage paid for a specific job or industry in a region |
| Purpose | Ensure workers can meet essential needs like housing, food, healthcare | Reflects market wages based on supply, demand, and union contracts |
| Calculation Basis | Cost of living including essentials and local expenses | Average wages reported by employers or labor surveys |
| Legal Status | Voluntary or policy-based; not always legally mandated | Often legally mandated in public contracts and labor laws |
| Scope | Focused on worker and family welfare | Focused on industry standards and historical wage data |
| Impact | Improves quality of life and reduces poverty | Maintains competitive labor market and protects wages |
Which is better?
Living wage ensures employees earn enough to meet basic needs such as housing, food, and healthcare, promoting economic stability and reducing poverty. Prevailing wage reflects the average pay rates in a specific industry or region, supporting fair competition and preventing wage undercutting. Balancing both can foster equitable income while sustaining market-driven employment standards.
Connection
Living wage and prevailing wage are connected through their focus on fair employee compensation tied to local economic conditions. Living wage represents the minimum income necessary for workers to meet basic living costs, while prevailing wage reflects the standard wage rates established by local government or union contracts in specific industries or regions. Both concepts aim to ensure workers earn sufficient income to support a stable and productive workforce within an economy.
Key Terms
Wage Standards
Prevailing wage sets a legally mandated minimum pay rate based on unionized or local labor market standards, often applying to public works and government contracts to ensure fair compensation. Living wage measures the income necessary for workers to afford basic living expenses such as housing, food, healthcare, and transportation, reflecting a cost-of-living standard rather than market or union rates. Explore comprehensive wage standards to understand how these benchmarks impact labor policies and economic equity.
Cost of Living
Prevailing wage refers to the average wage paid to workers in a specific geographic area for a particular job, as determined by government standards, while living wage is the minimum income necessary for a worker to meet basic needs such as housing, food, healthcare, and transportation in that area. The cost of living significantly impacts the living wage, as higher expenses in urban centers require wages that adapt beyond prevailing wage minimums to ensure economic stability for workers. Explore how adjusting wages to reflect true living costs bridges income gaps and promotes equitable labor standards.
Labor Regulations
Prevailing wage laws mandate minimum pay rates based on local standards for specific jobs, ensuring workers receive fair compensation aligned with market conditions and union agreements. Living wage policies set higher payment thresholds to cover basic living expenses, aiming to improve quality of life by addressing cost of living discrepancies often overlooked by prevailing wage standards. Explore comprehensive labor regulations to understand how these wage standards impact worker rights and economic equity.
Source and External Links
Prevailing Wages | Flag.dol.gov - The prevailing wage rate is the average wage paid to similarly employed workers in a specific occupation in the area of intended employment and is used to ensure foreign workers are paid fairly without adversely affecting U.S. workers' wages and conditions.
Prevailing wages on federal contracts - Worker.gov - On federally funded or assisted construction projects, the Davis-Bacon Act requires payment of locally prevailing wages, including fringe benefits, to workers according to their classification and geographic area.
Prevailing Wage - City and County of Denver - Denver's Prevailing Wage Ordinance requires contractors and subcontractors on city contracts over $2,000 to pay workers the prevailing wage rates set for construction, maintenance, or janitorial work on public projects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com