De-risking focuses on proactively identifying and eliminating potential economic vulnerabilities before they materialize into crises, emphasizing prevention and strategic foresight. Mitigation involves implementing measures to lessen the impact of economic shocks after they occur, aiming to stabilize and recover affected systems. Explore the nuances between de-risking and mitigation to enhance economic resilience strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-risking and mitigation is essential for effective economic strategy because de-risking involves eliminating or avoiding high-risk activities entirely, while mitigation focuses on reducing the impact of risks that cannot be avoided. De-risking protects financial institutions from exposure to potential losses by cutting ties with risky clients or sectors, often seen in banking and compliance contexts. Mitigation strategies include diversification, insurance, and hedging techniques that aim to minimize adverse economic effects without abandoning the risk source. Clear differentiation enables policymakers and businesses to allocate resources efficiently and maintain economic stability.
Comparison Table
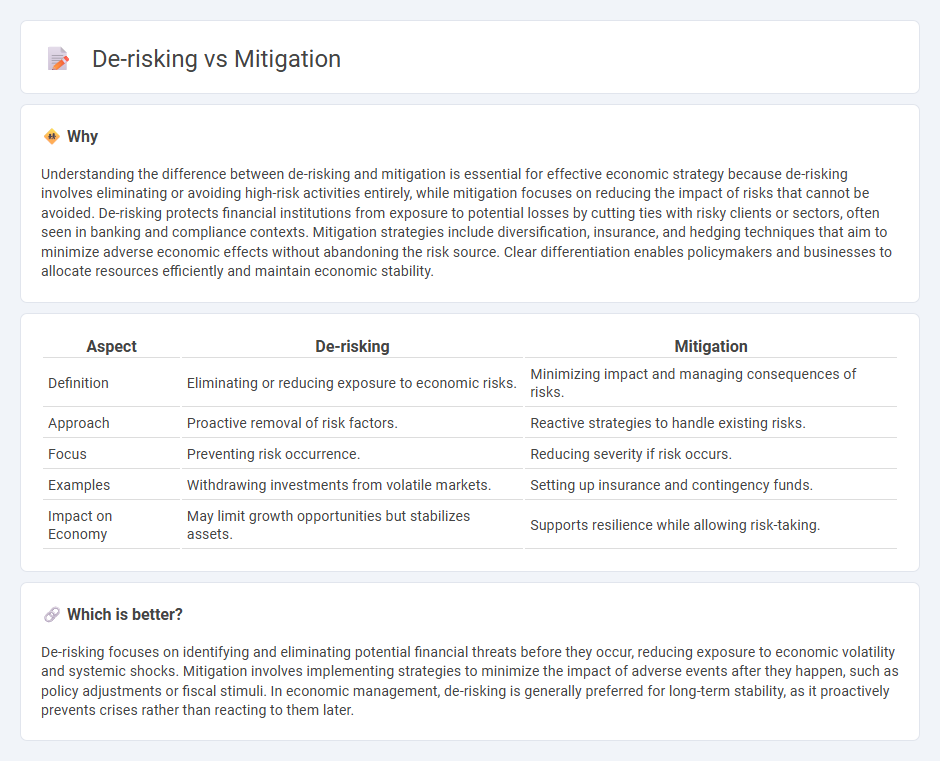
| Aspect | De-risking | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eliminating or reducing exposure to economic risks. | Minimizing impact and managing consequences of risks. |
| Approach | Proactive removal of risk factors. | Reactive strategies to handle existing risks. |
| Focus | Preventing risk occurrence. | Reducing severity if risk occurs. |
| Examples | Withdrawing investments from volatile markets. | Setting up insurance and contingency funds. |
| Impact on Economy | May limit growth opportunities but stabilizes assets. | Supports resilience while allowing risk-taking. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on identifying and eliminating potential financial threats before they occur, reducing exposure to economic volatility and systemic shocks. Mitigation involves implementing strategies to minimize the impact of adverse events after they happen, such as policy adjustments or fiscal stimuli. In economic management, de-risking is generally preferred for long-term stability, as it proactively prevents crises rather than reacting to them later.
Connection
De-risking and mitigation are interconnected processes essential in managing economic uncertainties and protecting financial stability. De-risking involves reducing exposure to potential economic threats by adjusting investment strategies or withdrawing from high-risk markets, while mitigation encompasses the implementation of measures such as diversification, hedging, and contingency planning to lessen the impact of adverse events. Together, these strategies enable businesses and economies to enhance resilience against volatility and safeguard long-term growth.
Key Terms
Risk Management
Mitigation in risk management involves implementing strategies to reduce the impact or likelihood of identified risks, such as developing contingency plans and safety protocols. De-risking focuses on eliminating or transferring risks altogether, often through diversification, insurance, or contractual agreements. Explore detailed approaches to optimize your risk management strategy effectively.
Diversification
Mitigation in finance involves reducing potential losses through strategies like diversification, which spreads investments across various asset classes to minimize risk exposure. De-risking focuses on eliminating or significantly reducing risk by withdrawing from high-risk activities or sectors, often resulting in a more conservative portfolio. Discover how diversification can balance mitigation and de-risking approaches to optimize your investment strategy.
Resilience
Mitigation targets reducing the severity and impact of risks by implementing protective measures and contingency plans to ensure business continuity. De-risking emphasizes eliminating or transferring risk exposure, often through strategic decisions such as diversification or insurance, enhancing overall resilience. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these strategies uniquely contribute to organizational strength and sustainability.
Source and External Links
Mitigation - DOE Directives - Mitigation involves activities that prevent emergencies, reduce their likelihood, or lessen the damaging effects of unavoidable incidents to reduce loss of life and property.
Hazard Mitigation Assistance Grants | FEMA.gov - Hazard mitigation refers to sustainable actions and funding aimed at minimizing long-term risks to people and property from future disasters.
Mitigation - Wikipedia - Mitigation is the reduction of harmful effects across various fields such as environment, financial risk, law, and occupational safety, involving measures to decrease or compensate for damage or risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com