Quiet vacationing focuses on taking restful breaks to recharge productivity and mental well-being, leading to sustained economic engagement and reduced burnout rates. Loud quitting, characterized by abrupt job resignations or disengagement without notice, often disrupts organizational efficiency and increases turnover costs, impacting overall economic stability. Discover how these contrasting workplace behaviors influence economic trends and individual career outcomes.
Why it is important
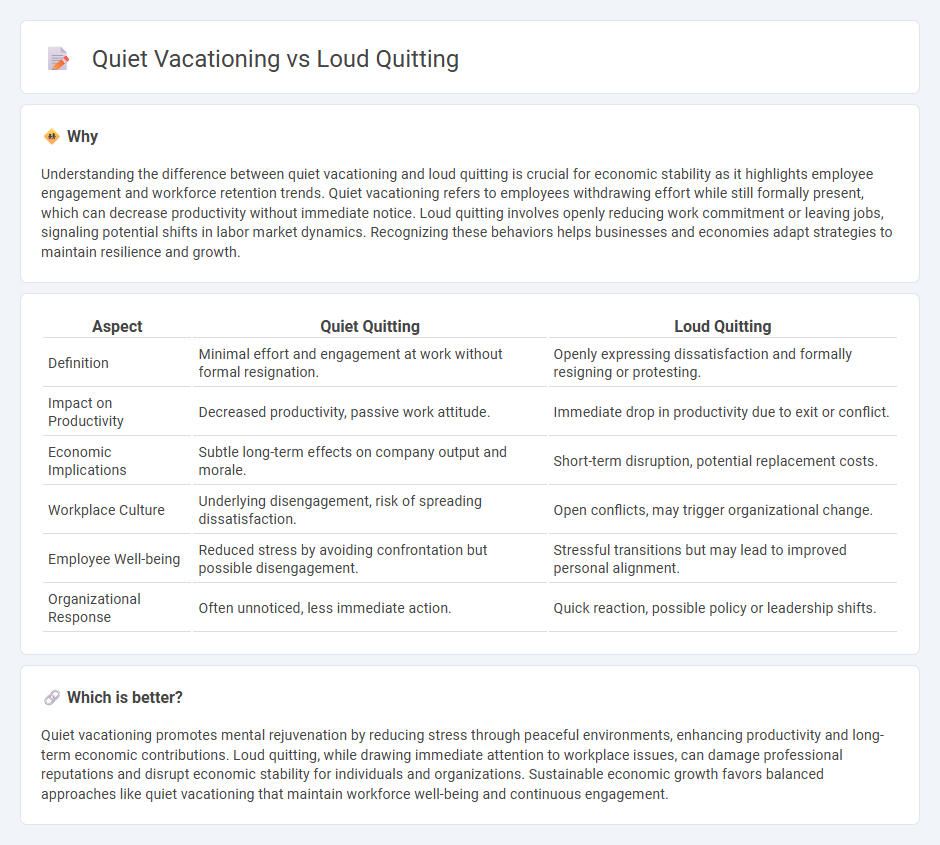
Understanding the difference between quiet vacationing and loud quitting is crucial for economic stability as it highlights employee engagement and workforce retention trends. Quiet vacationing refers to employees withdrawing effort while still formally present, which can decrease productivity without immediate notice. Loud quitting involves openly reducing work commitment or leaving jobs, signaling potential shifts in labor market dynamics. Recognizing these behaviors helps businesses and economies adapt strategies to maintain resilience and growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Quitting | Loud Quitting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimal effort and engagement at work without formal resignation. | Openly expressing dissatisfaction and formally resigning or protesting. |
| Impact on Productivity | Decreased productivity, passive work attitude. | Immediate drop in productivity due to exit or conflict. |
| Economic Implications | Subtle long-term effects on company output and morale. | Short-term disruption, potential replacement costs. |
| Workplace Culture | Underlying disengagement, risk of spreading dissatisfaction. | Open conflicts, may trigger organizational change. |
| Employee Well-being | Reduced stress by avoiding confrontation but possible disengagement. | Stressful transitions but may lead to improved personal alignment. |
| Organizational Response | Often unnoticed, less immediate action. | Quick reaction, possible policy or leadership shifts. |
Which is better?
Quiet vacationing promotes mental rejuvenation by reducing stress through peaceful environments, enhancing productivity and long-term economic contributions. Loud quitting, while drawing immediate attention to workplace issues, can damage professional reputations and disrupt economic stability for individuals and organizations. Sustainable economic growth favors balanced approaches like quiet vacationing that maintain workforce well-being and continuous engagement.
Connection
Quiet vacationing boosts employee well-being by promoting mental rest and reducing burnout, which can increase productivity and job satisfaction. Loud quitting, or openly expressing dissatisfaction while leaving a job, often arises from unresolved stress or lack of work-life balance. Both trends highlight a shifting economy where workers prioritize mental health and personal boundaries, influencing labor market dynamics and corporate culture.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Loud quitting, where employees openly express dissatisfaction and disengage, contrasts with quiet vacationing, characterized by silently withdrawing while maintaining appearances at work. Both behaviors significantly impact employee engagement and organizational productivity, reflecting underlying issues in workplace culture and management practices. Explore strategies to foster genuine engagement and address these challenges effectively.
Productivity
Loud quitting involves openly expressing dissatisfaction and reducing work effort as a form of protest, often leading to noticeable dips in productivity and team morale. Quiet vacationing, characterized by discreetly disengaging while maintaining basic job responsibilities, tends to have a subtler but consistent impact on overall output and workplace dynamics. Discover strategies to balance engagement and well-being for sustained productivity by exploring detailed analyses on these workforce behaviors.
Workplace Culture
Loud quitting involves openly expressing dissatisfaction and disengagement from work, often sparking conversations about workplace conditions and management practices. Quiet vacationing, in contrast, entails employees silently reducing effort and presence without explicit communication, impacting productivity and team dynamics subtly but significantly. Explore deeper insights on how these behaviors reflect and reshape workplace culture.
Source and External Links
Loud Quitting: What It Is and How To Address It - This article explains loud quitting as a form of employee disengagement where workers openly express dissatisfaction and undermine organizational morale and goals.
Loud quitting - Loud quitting refers to when employees openly share their discontent and intention to leave, often using public platforms like social media to express their grievances.
What is Loud Quitting: Causes, Effects & How to Deal With It - This piece discusses loud quitting as a form of attention-grabbing resignation where employees express frustration publicly, and provides strategies for employers to address such situations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com