Supercore inflation measures the change in prices of goods and services excluding volatile sectors like food and energy, providing a clearer view of underlying inflation trends. Headline inflation captures the total inflation rate, including all categories, reflecting the overall cost of living changes experienced by consumers. Explore deeper insights into how these inflation measures impact economic policy and market expectations.
Why it is important
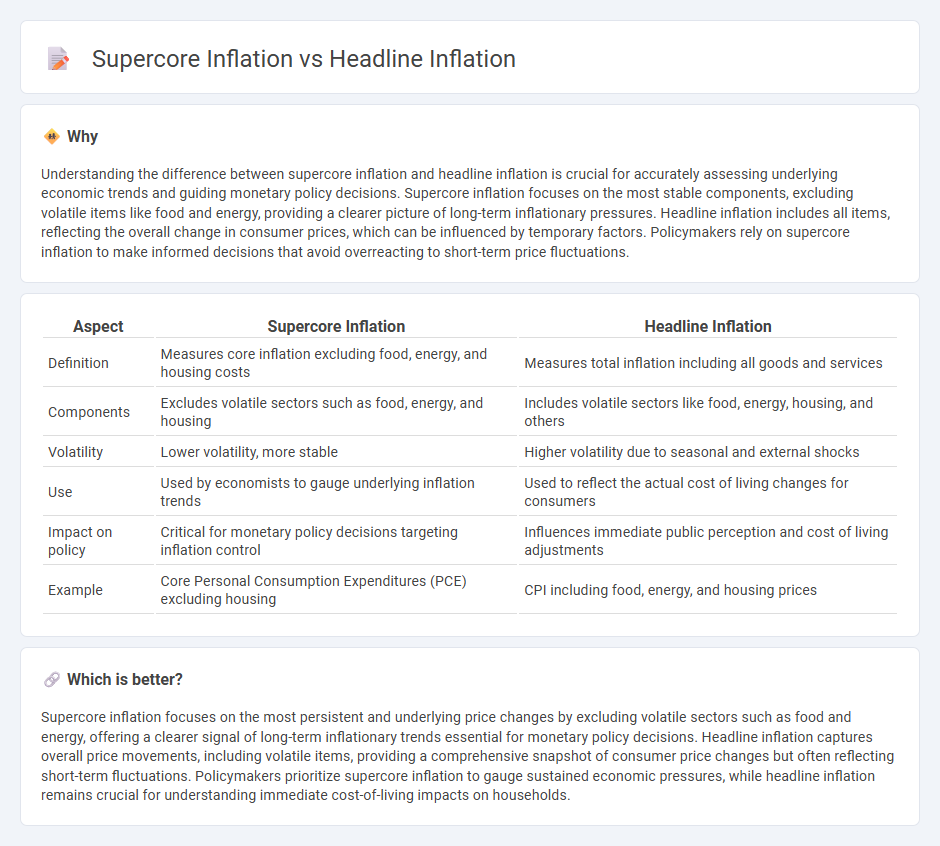
Understanding the difference between supercore inflation and headline inflation is crucial for accurately assessing underlying economic trends and guiding monetary policy decisions. Supercore inflation focuses on the most stable components, excluding volatile items like food and energy, providing a clearer picture of long-term inflationary pressures. Headline inflation includes all items, reflecting the overall change in consumer prices, which can be influenced by temporary factors. Policymakers rely on supercore inflation to make informed decisions that avoid overreacting to short-term price fluctuations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supercore Inflation | Headline Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures core inflation excluding food, energy, and housing costs | Measures total inflation including all goods and services |
| Components | Excludes volatile sectors such as food, energy, and housing | Includes volatile sectors like food, energy, housing, and others |
| Volatility | Lower volatility, more stable | Higher volatility due to seasonal and external shocks |
| Use | Used by economists to gauge underlying inflation trends | Used to reflect the actual cost of living changes for consumers |
| Impact on policy | Critical for monetary policy decisions targeting inflation control | Influences immediate public perception and cost of living adjustments |
| Example | Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) excluding housing | CPI including food, energy, and housing prices |
Which is better?
Supercore inflation focuses on the most persistent and underlying price changes by excluding volatile sectors such as food and energy, offering a clearer signal of long-term inflationary trends essential for monetary policy decisions. Headline inflation captures overall price movements, including volatile items, providing a comprehensive snapshot of consumer price changes but often reflecting short-term fluctuations. Policymakers prioritize supercore inflation to gauge sustained economic pressures, while headline inflation remains crucial for understanding immediate cost-of-living impacts on households.
Connection
Supercore inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, closely tracks underlying economic trends and wage growth, providing a stable measure of inflationary pressures. Headline inflation reflects the total change in consumer prices, including volatile categories, making it more susceptible to short-term shocks. The connection between the two lies in supercore inflation's ability to signal persistent inflation trends that eventually influence headline inflation movements.
Key Terms
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Headline inflation measures the overall change in the Consumer Price Index (CPI), including food and energy prices, which tend to be volatile. Supercore inflation excludes these volatile components, focusing on the underlying, persistent trends in core CPI to better gauge long-term inflationary pressures. Explore detailed CPI analyses to understand the nuances between headline and supercore inflation.
Core Inflation
Headline inflation measures the overall increase in prices, including volatile food and energy sectors, whereas supercore inflation zeros in on the most stable components of core inflation, excluding even shelter and other housing costs. Core inflation strips out food and energy to provide a clearer view of long-term trends, but supercore inflation refines this further to reveal underlying inflation pressures more accurately. Discover more about how these inflation measures impact economic policy and market forecasts.
Services Excluding Housing
Headline inflation measures the overall increase in prices across all goods and services, reflecting direct consumer costs, while supercore inflation zeroes in on the services sector excluding housing, highlighting underlying price trends unaffected by volatile housing markets. The services excluding housing component provides a clearer view of persistent inflationary pressures driven by labor costs and service demand dynamics. Explore how analyzing supercore inflation can offer deeper insights into economic conditions and policy decisions.
Source and External Links
Headline Inflation - Definition, Formula, Applications - Headline inflation is the total inflation in an economy measured by including all goods in a basket, such as food and energy prices, making it more volatile than core inflation which excludes these volatile components.
Headline inflation - Wikipedia - Headline inflation measures aggregate price movement in an economy using indexes like the Consumer Price Index, and includes food and energy prices which cause fluctuations, differing from core inflation that excludes these volatile items.
What's inflation - and how exactly do we measure it? - UNSW - Headline inflation is the inflation rate reflected in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) including all items, subject to volatile price changes in some goods like food and petrol, contrasting with underlying or core inflation measures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com