Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to a company's original country to reduce supply chain risks and increase domestic job opportunities. Localization focuses on tailoring products and operations to meet the specific needs and preferences of local markets, enhancing customer satisfaction and market responsiveness. Explore the key differences and strategic benefits of reshoring versus localization in today's dynamic economy.
Why it is important
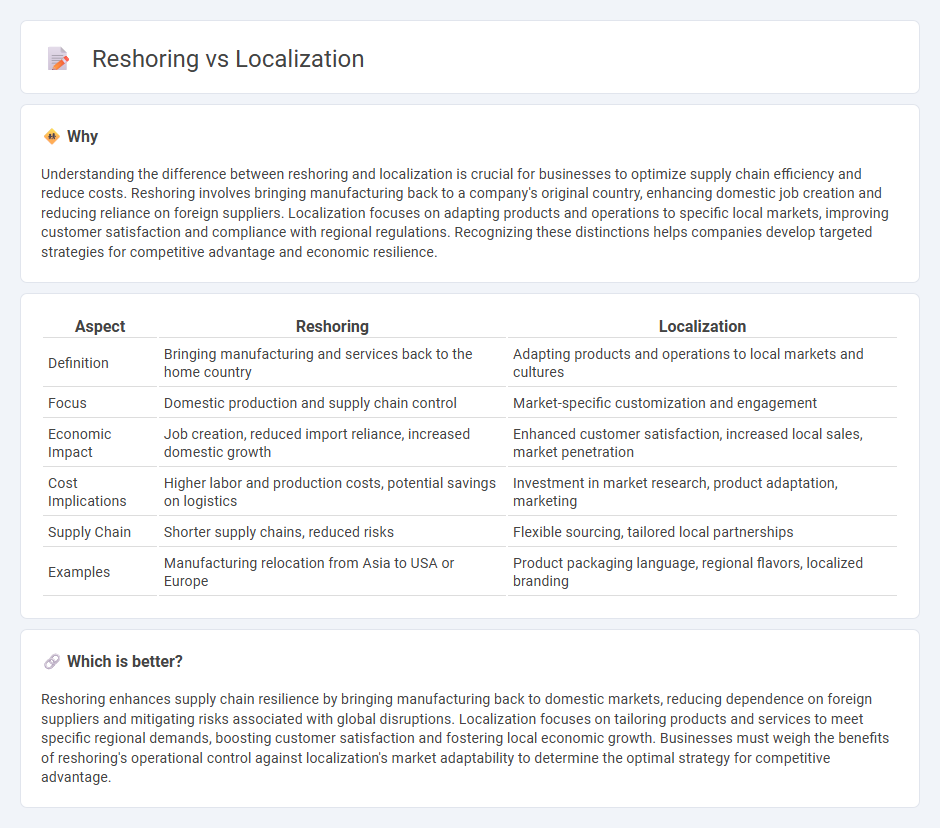
Understanding the difference between reshoring and localization is crucial for businesses to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce costs. Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to a company's original country, enhancing domestic job creation and reducing reliance on foreign suppliers. Localization focuses on adapting products and operations to specific local markets, improving customer satisfaction and compliance with regional regulations. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies develop targeted strategies for competitive advantage and economic resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reshoring | Localization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country | Adapting products and operations to local markets and cultures |
| Focus | Domestic production and supply chain control | Market-specific customization and engagement |
| Economic Impact | Job creation, reduced import reliance, increased domestic growth | Enhanced customer satisfaction, increased local sales, market penetration |
| Cost Implications | Higher labor and production costs, potential savings on logistics | Investment in market research, product adaptation, marketing |
| Supply Chain | Shorter supply chains, reduced risks | Flexible sourcing, tailored local partnerships |
| Examples | Manufacturing relocation from Asia to USA or Europe | Product packaging language, regional flavors, localized branding |
Which is better?
Reshoring enhances supply chain resilience by bringing manufacturing back to domestic markets, reducing dependence on foreign suppliers and mitigating risks associated with global disruptions. Localization focuses on tailoring products and services to meet specific regional demands, boosting customer satisfaction and fostering local economic growth. Businesses must weigh the benefits of reshoring's operational control against localization's market adaptability to determine the optimal strategy for competitive advantage.
Connection
Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and production back to a company's home country, boosting local employment and supply chain resilience. Localization emphasizes tailoring products and services to meet regional demand, encouraging investment in local resources and infrastructure. Together, reshoring and localization strengthen domestic economies by reducing reliance on global supply chains and fostering sustainable growth within local markets.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Localization enhances supply chain resilience by sourcing materials and manufacturing closer to end markets, reducing lead times and transportation costs while improving responsiveness to local demand. Reshoring relocates production back to the company's home country, addressing risks from global disruptions, increasing control over quality, and supporting domestic job growth. Explore the strategic benefits and challenges of both approaches for optimizing your supply chain.
Production Costs
Localization reduces production costs by minimizing tariffs, shipping fees, and import duties through manufacturing near target markets. Reshoring focuses on cutting labor expenses and improving supply chain efficiency by relocating production back to the company's home country. Explore detailed cost comparisons and strategic benefits to optimize your manufacturing decisions.
Trade Policy
Trade policy plays a crucial role in shaping decisions between localization and reshoring by influencing tariffs, import restrictions, and trade agreements that affect supply chain costs. Localization reduces reliance on international trade by producing goods closer to the end market, while reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the home country, often driven by incentives like tax breaks and reduced regulatory burdens. Explore further how evolving trade policies impact strategic manufacturing choices.
Source and External Links
LOCALIZATION definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Localization is the process of organizing a business or industry so that its main activities happen in local areas rather than nationally or internationally.
Localization (l10n): What It Is, and How to Build a Strategy? - Phrase - Localization is the process of adapting a product to meet the cultural, linguistic, legal, and other requirements of a target market, involving stages of analysis, choice, and execution to create an effective strategy.
What is Localization? All you Need to Know - Localization is converting content into something more suitable for another country or target audience, including adapting websites for different languages and cultures to reach global users.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com