Global economies face challenges from a polycrisis--interconnected crises like climate change, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions--that intensify financial instability. Simultaneously, credit crunches occur when banks tighten lending standards, restricting access to capital for businesses and consumers, leading to slower economic growth. Explore how these overlapping pressures shape fiscal policy and market resilience today.
Why it is important
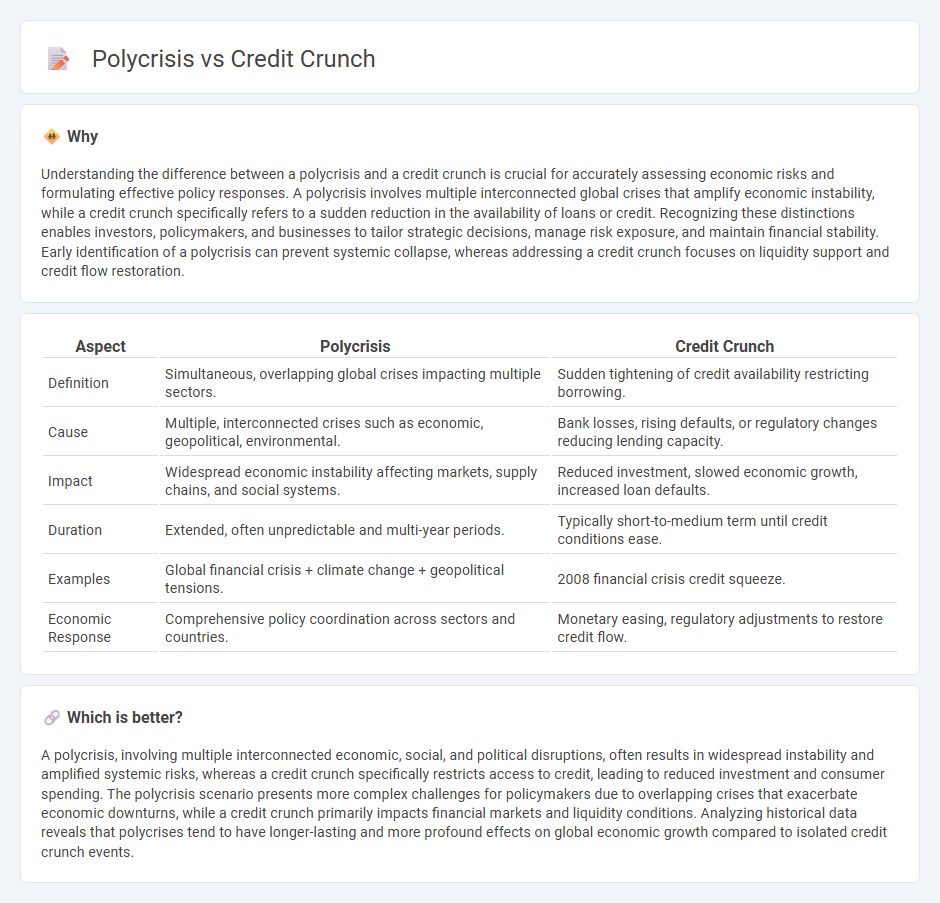
Understanding the difference between a polycrisis and a credit crunch is crucial for accurately assessing economic risks and formulating effective policy responses. A polycrisis involves multiple interconnected global crises that amplify economic instability, while a credit crunch specifically refers to a sudden reduction in the availability of loans or credit. Recognizing these distinctions enables investors, policymakers, and businesses to tailor strategic decisions, manage risk exposure, and maintain financial stability. Early identification of a polycrisis can prevent systemic collapse, whereas addressing a credit crunch focuses on liquidity support and credit flow restoration.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Polycrisis | Credit Crunch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous, overlapping global crises impacting multiple sectors. | Sudden tightening of credit availability restricting borrowing. |
| Cause | Multiple, interconnected crises such as economic, geopolitical, environmental. | Bank losses, rising defaults, or regulatory changes reducing lending capacity. |
| Impact | Widespread economic instability affecting markets, supply chains, and social systems. | Reduced investment, slowed economic growth, increased loan defaults. |
| Duration | Extended, often unpredictable and multi-year periods. | Typically short-to-medium term until credit conditions ease. |
| Examples | Global financial crisis + climate change + geopolitical tensions. | 2008 financial crisis credit squeeze. |
| Economic Response | Comprehensive policy coordination across sectors and countries. | Monetary easing, regulatory adjustments to restore credit flow. |
Which is better?
A polycrisis, involving multiple interconnected economic, social, and political disruptions, often results in widespread instability and amplified systemic risks, whereas a credit crunch specifically restricts access to credit, leading to reduced investment and consumer spending. The polycrisis scenario presents more complex challenges for policymakers due to overlapping crises that exacerbate economic downturns, while a credit crunch primarily impacts financial markets and liquidity conditions. Analyzing historical data reveals that polycrises tend to have longer-lasting and more profound effects on global economic growth compared to isolated credit crunch events.
Connection
Polycrisis, characterized by simultaneous global challenges such as climate change, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions, intensifies economic uncertainty, leading to tighter financial conditions. This heightened uncertainty increases the risk perception among lenders, triggering a credit crunch where banks reduce lending due to fears of default and economic instability. The interconnected nature of polycrisis exacerbates credit scarcity, impairing investment and slowing economic growth.
Key Terms
**Credit Crunch:**
A credit crunch occurs when banks and financial institutions severely reduce the availability of loans or credit, leading to tightened borrowing conditions and restricted access to capital in the economy. This contraction in credit supply can result in decreased consumer spending, slowed business investments, and a potential economic downturn. Explore the dynamics and consequences of credit crunches to understand their impact on financial markets and economic stability.
Liquidity shortage
A credit crunch is characterized by a sudden reduction in the availability of loans or credit, leading to a liquidity shortage that hampers business operations and consumer spending. In contrast, a polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises that collectively exacerbate liquidity issues across financial, economic, and social systems. Explore further to understand how liquidity shortages influence both credit crunches and polycrises in global markets.
Banking crisis
The credit crunch refers to a sudden reduction in the availability of loans or credit from banks, leading to tightened liquidity and increased borrowing costs, which can trigger a banking crisis as financial institutions face solvency challenges. A polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises occurring simultaneously, such as economic downturns, geopolitical tensions, and banking instability, compounding the risks and complexity within the financial sector. Explore more to understand how these phenomena impact global banking resilience and risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
Credit crunch - Wikipedia - A credit crunch is a sudden reduction in the general availability of loans or tightening of loan conditions by banks, often occurring independently of interest rate changes and leading to credit rationing.
Credit Crunch Definition, Causes & Consequences - Study.com - A credit crunch happens when banks reduce lending due to economic downturns, loss of confidence, or increased borrower defaults, causing tighter loan availability and often resulting in higher mortgage rates and unemployment.
Explaining the Credit Crunch | NBER - The 2007-2008 credit crunch was triggered by declining housing prices and mortgage defaults, which forced banks to write down bad loans leading to tightened credit and a severe economic downturn.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com