Economic deglobalization involves the reduction of global trade and investment flows, emphasizing self-reliance and national production. Liberalization promotes the removal of trade barriers, encouraging open markets, foreign investment, and increased global economic integration. Explore the contrasting impacts of deglobalization and liberalization on global economic stability and growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between deglobalization and liberalization is crucial for analyzing global economic trends and policy impacts. Deglobalization refers to the reduction of cross-border trade, investment, and cooperation, often driven by protectionism or geopolitical tensions. Liberalization involves the removal of trade barriers, promoting open markets and economic integration. Recognizing these concepts helps businesses and policymakers adapt strategies to shifting economic landscapes and optimize growth opportunities.
Comparison Table
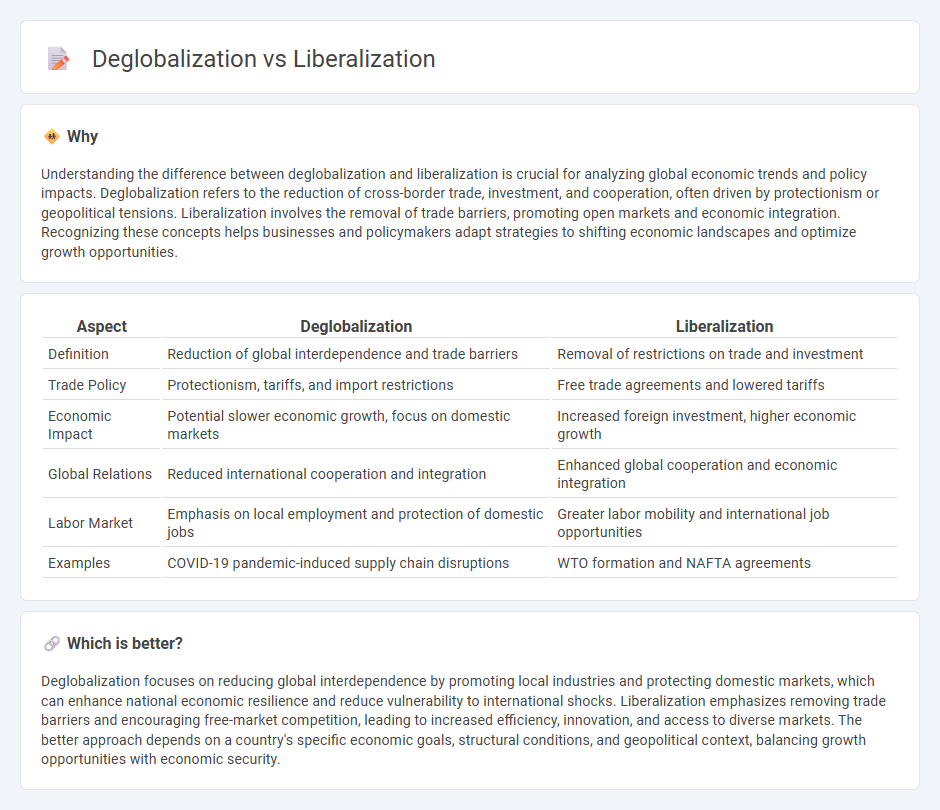
| Aspect | Deglobalization | Liberalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction of global interdependence and trade barriers | Removal of restrictions on trade and investment |
| Trade Policy | Protectionism, tariffs, and import restrictions | Free trade agreements and lowered tariffs |
| Economic Impact | Potential slower economic growth, focus on domestic markets | Increased foreign investment, higher economic growth |
| Global Relations | Reduced international cooperation and integration | Enhanced global cooperation and economic integration |
| Labor Market | Emphasis on local employment and protection of domestic jobs | Greater labor mobility and international job opportunities |
| Examples | COVID-19 pandemic-induced supply chain disruptions | WTO formation and NAFTA agreements |
Which is better?
Deglobalization focuses on reducing global interdependence by promoting local industries and protecting domestic markets, which can enhance national economic resilience and reduce vulnerability to international shocks. Liberalization emphasizes removing trade barriers and encouraging free-market competition, leading to increased efficiency, innovation, and access to diverse markets. The better approach depends on a country's specific economic goals, structural conditions, and geopolitical context, balancing growth opportunities with economic security.
Connection
Deglobalization and liberalization are interconnected through their contrasting impacts on trade and market access. While deglobalization involves reducing global interdependence by imposing tariffs, trade barriers, and localizing supply chains, liberalization promotes opening markets by removing restrictions and encouraging free trade. The balance between these forces shapes economic policies, influencing international investment flows and competitive dynamics.
Key Terms
Trade Barriers
Trade liberalization reduces tariffs, quotas, and non-tariff barriers, enhancing global market access and fostering economic integration. Deglobalization increases trade barriers to protect domestic industries, leading to reduced cross-border trade and potential supply chain disruptions. Explore the impacts of these contrasting approaches on global commerce and economic growth.
Capital Flows
Liberalization in capital flows involves reducing regulatory barriers, allowing for freer movement of investment across borders and fostering economic integration. Deglobalization, contrastingly, signifies a retreat from open capital markets, reflecting increased controls and restrictions aimed at protecting domestic economies from external shocks. Explore detailed implications of these contrasting trends on global investment patterns and economic stability.
Protectionism
Protectionism involves government policies that impose tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, contrasting with liberalization's emphasis on reducing such restrictions to promote free trade. During periods of deglobalization, protectionist measures often intensify as countries seek economic self-sufficiency and mitigate vulnerabilities exposed by global supply chain disruptions. Explore further to understand how these contrasting economic strategies impact global markets and national economies.
Source and External Links
Economic liberalization - Economic liberalization is the reduction of government regulations and restrictions in an economy to encourage greater private sector participation and economic development, often involving privatization, open markets, and less foreign capital restrictions.
Liberalization | Political Science, Economic Reforms & ... - Liberalization mainly refers to the easing of government controls, especially in economics, including reductions in restrictions on trade, capital, and deregulation of markets to enable freer market operations globally.
Liberalization - Liberalization involves removing barriers to cross-border movements of capital, goods, and people, and is analyzed based on who benefits, who supports it, and how governments implement market liberalization policies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com