Friendshoring involves relocating supply chains to allied countries to enhance security and reduce geopolitical risks, whereas offshoring typically shifts production to lower-cost nations without prioritizing political alignment. This strategic economic decision affects global trade dynamics, labor markets, and corporate risk management. Explore the implications of friendshoring versus offshoring to understand its impact on future economic stability and business operations.
Why it is important
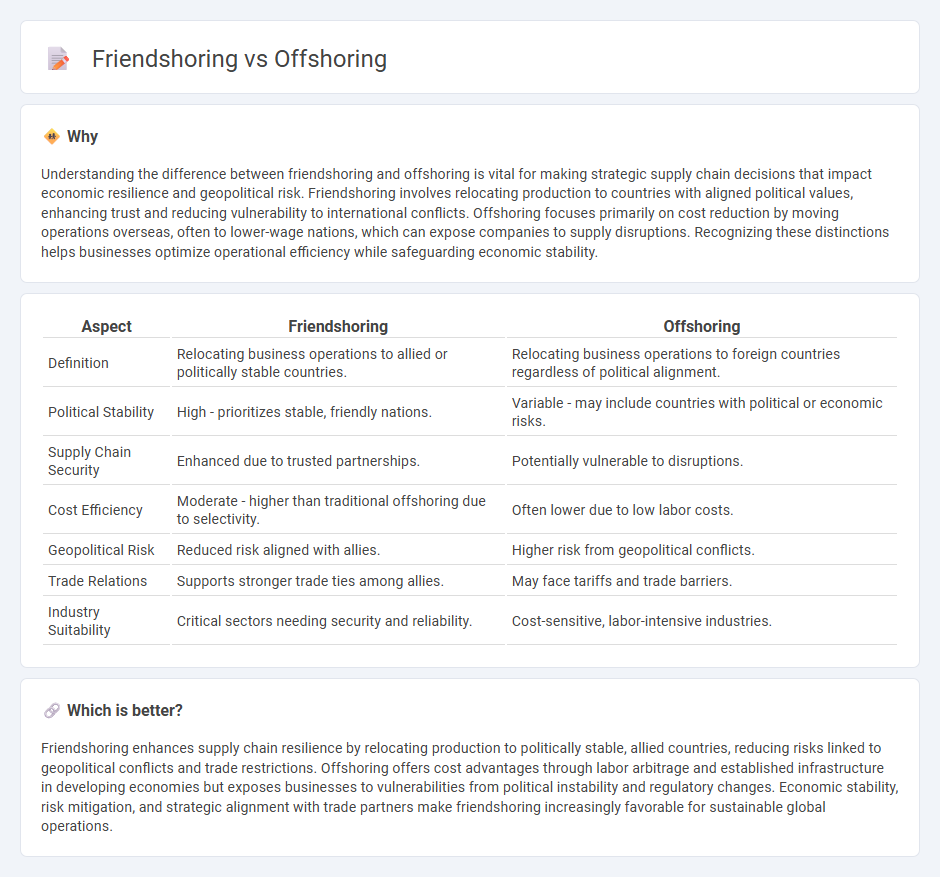
Understanding the difference between friendshoring and offshoring is vital for making strategic supply chain decisions that impact economic resilience and geopolitical risk. Friendshoring involves relocating production to countries with aligned political values, enhancing trust and reducing vulnerability to international conflicts. Offshoring focuses primarily on cost reduction by moving operations overseas, often to lower-wage nations, which can expose companies to supply disruptions. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses optimize operational efficiency while safeguarding economic stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Friendshoring | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business operations to allied or politically stable countries. | Relocating business operations to foreign countries regardless of political alignment. |
| Political Stability | High - prioritizes stable, friendly nations. | Variable - may include countries with political or economic risks. |
| Supply Chain Security | Enhanced due to trusted partnerships. | Potentially vulnerable to disruptions. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate - higher than traditional offshoring due to selectivity. | Often lower due to low labor costs. |
| Geopolitical Risk | Reduced risk aligned with allies. | Higher risk from geopolitical conflicts. |
| Trade Relations | Supports stronger trade ties among allies. | May face tariffs and trade barriers. |
| Industry Suitability | Critical sectors needing security and reliability. | Cost-sensitive, labor-intensive industries. |
Which is better?
Friendshoring enhances supply chain resilience by relocating production to politically stable, allied countries, reducing risks linked to geopolitical conflicts and trade restrictions. Offshoring offers cost advantages through labor arbitrage and established infrastructure in developing economies but exposes businesses to vulnerabilities from political instability and regulatory changes. Economic stability, risk mitigation, and strategic alignment with trade partners make friendshoring increasingly favorable for sustainable global operations.
Connection
Friendshoring and offshoring both involve relocating business processes or production to foreign countries to optimize costs and access resources. Friendshoring focuses on transferring operations to politically stable, allied nations to reduce geopolitical risks, while offshoring broadly targets cost savings without prioritizing political alignment. This strategic shift in global supply chains enhances economic resilience by balancing efficiency and security.
Key Terms
Labor Costs
Offshoring often prioritizes minimizing labor costs by relocating production to countries with lower wages, which can significantly reduce operational expenses for companies. Friendshoring, however, emphasizes shifting supply chains to politically stable, allied nations, balancing moderate labor costs with reduced geopolitical risk. Explore the implications of these strategies on global labor markets and economic resilience to better understand their impact.
Supply Chain
Offshoring shifts supply chain operations to distant countries to reduce costs but often risks disruption due to geopolitical tensions or long transit times. Friendshoring prioritizes partners in allied or politically stable nations, enhancing supply chain resilience and security while balancing cost-efficiency. Explore in-depth strategies and impacts of offshoring vs. friendshoring on global supply chains.
Geopolitical Risk
Offshoring involves relocating business processes to distant countries to capitalize on lower costs but often exposes companies to heightened geopolitical risks such as trade wars, regulatory changes, and political instability. Friendshoring mitigates these risks by shifting operations to politically aligned or allied nations, ensuring more stable supply chains and reducing the impact of geopolitical disruptions. Explore how businesses strategically balance cost-efficiency and geopolitical safety by diving deeper into offshoring versus friendshoring dynamics.
Source and External Links
Offshoring - Wikipedia - Offshoring is the relocation of a business process, such as manufacturing or supporting services, from one country to another, typically to lower costs or access qualified personnel.
Offshoring: Definition, Overview, Pros and Cons - Velocity Global - Offshoring involves moving business operations or services to a different country, often to reduce labor costs, tap into specialized talent, or expand into new markets.
Offshoring - Everything Policy - Briefs - Offshoring allows companies to lower expenses by transferring operations abroad, which can result in job shifts from higher-cost to lower-cost countries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com