The gig economy thrives on flexible, short-term jobs driven by digital platforms, enabling freelancers and contractors to offer services across various industries. The knowledge economy, on the other hand, centers on intellectual capabilities, innovation, and information management, emphasizing education and expertise as key economic drivers. Explore the impact and future prospects of these evolving economic models to understand their roles in shaping modern work environments.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the gig economy and the knowledge economy is crucial for strategic workforce planning and economic policy development. The gig economy relies on short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms, impacting labor rights and income stability. In contrast, the knowledge economy is driven by intellectual capabilities and innovation, emphasizing education and skilled labor as key growth factors. Distinguishing these models helps businesses and governments adapt to evolving labor markets and foster sustainable economic growth.
Comparison Table
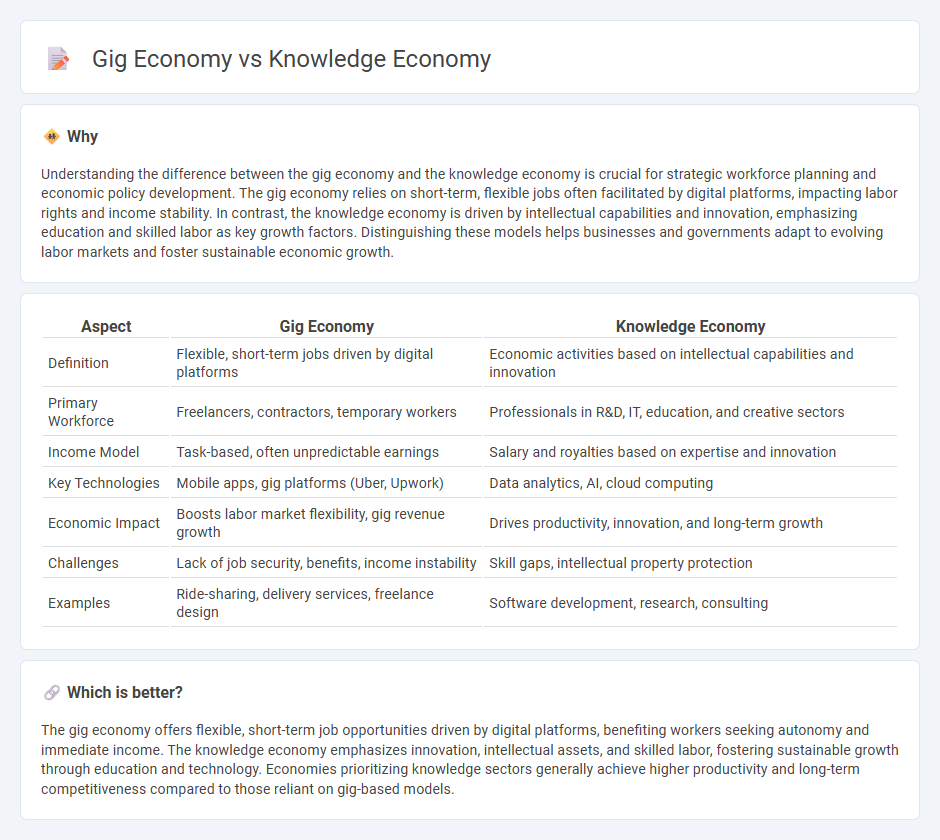
| Aspect | Gig Economy | Knowledge Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flexible, short-term jobs driven by digital platforms | Economic activities based on intellectual capabilities and innovation |
| Primary Workforce | Freelancers, contractors, temporary workers | Professionals in R&D, IT, education, and creative sectors |
| Income Model | Task-based, often unpredictable earnings | Salary and royalties based on expertise and innovation |
| Key Technologies | Mobile apps, gig platforms (Uber, Upwork) | Data analytics, AI, cloud computing |
| Economic Impact | Boosts labor market flexibility, gig revenue growth | Drives productivity, innovation, and long-term growth |
| Challenges | Lack of job security, benefits, income instability | Skill gaps, intellectual property protection |
| Examples | Ride-sharing, delivery services, freelance design | Software development, research, consulting |
Which is better?
The gig economy offers flexible, short-term job opportunities driven by digital platforms, benefiting workers seeking autonomy and immediate income. The knowledge economy emphasizes innovation, intellectual assets, and skilled labor, fostering sustainable growth through education and technology. Economies prioritizing knowledge sectors generally achieve higher productivity and long-term competitiveness compared to those reliant on gig-based models.
Connection
The gig economy thrives on flexible, project-based work often enabled by digital platforms, while the knowledge economy centers on the creation, distribution, and utilization of information and expertise. Both economies rely heavily on technology and skilled labor, with gig workers frequently providing specialized knowledge services such as consulting, software development, and creative content. This intersection enhances innovation, agility, and productivity in modern markets by leveraging expertise in a decentralized and dynamic labor environment.
Key Terms
Intellectual Capital
Intellectual capital drives the knowledge economy by emphasizing expertise, innovation, and intangible assets like human capital, structural capital, and relational capital. In contrast, the gig economy relies on flexible, task-based work arrangements, often prioritizing labor over continuous intellectual development. Explore how leveraging intellectual capital differentiates these economic models and influences future workforce strategies.
Flexibility
The knowledge economy thrives on intellectual capital and innovation, offering professionals the flexibility to engage in complex problem-solving and creative tasks often from remote or hybrid settings. Conversely, the gig economy emphasizes short-term, task-based work with high flexibility in work hours but less stability, catering primarily to service-oriented roles and freelance opportunities. Explore further to understand how flexibility shapes career choices and economic growth in these distinct economic models.
Innovation
The knowledge economy thrives on the creation, distribution, and application of information, driving innovation through research, intellectual capital, and advanced technology sectors like AI and biotechnology. The gig economy, characterized by freelance, temporary, and flexible work arrangements, fosters innovation primarily in digital platforms and service delivery models such as ride-sharing and on-demand services. Explore how these economic models uniquely influence innovative practices and economic growth.
Source and External Links
Knowledge Economy, The KAM Methodology And ... - This paper discusses the concept of the knowledge economy, which is driven by the creation and effective use of knowledge for economic growth.
Knowledge Economy - The knowledge economy is an economic system where production is based mainly on knowledge-intensive activities.
THE KNOWLEDGE ECONOMY by WW Powell - This publication defines the knowledge economy as a production system relying heavily on intellectual capabilities and technological advancements.
Knowledge Economy: Overview & Characteristics - The knowledge economy is characterized by its reliance on intellectual capabilities and intangible assets like big data and automation.
Knowledge Economy - Overview, Characteristics, Examples - This economy features a high percentage of skilled employees whose jobs require specialized knowledge.
Knowledge Economy - It emphasizes the importance of skills in service-oriented jobs and the value of intellectual property.
Knowledge Economy: Overview & Characteristics - The knowledge economy is more resilient and better equipped to handle economic challenges, with examples like Silicon Valley and Germany.
Knowledge Economy - Overview, Characteristics, Examples - It includes the growth of IT/ICT sectors, such as AI and robotics, contributing significantly to economic development.
Knowledge Economy, The KAM Methodology And ... - Successful transition to the knowledge economy involves investments in education and innovation, supported by conducive economic environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com