Biodiversity credits provide measurable environmental benefits by incentivizing conservation projects that protect ecosystems and species diversity, playing a crucial role in addressing habitat loss and climate change. Sustainable supply chains focus on reducing environmental impact through responsible sourcing, waste reduction, and ethical labor practices across production and distribution networks. Explore how integrating biodiversity credits can enhance the effectiveness of sustainable supply chains and contribute to a regenerative economy.
Why it is important
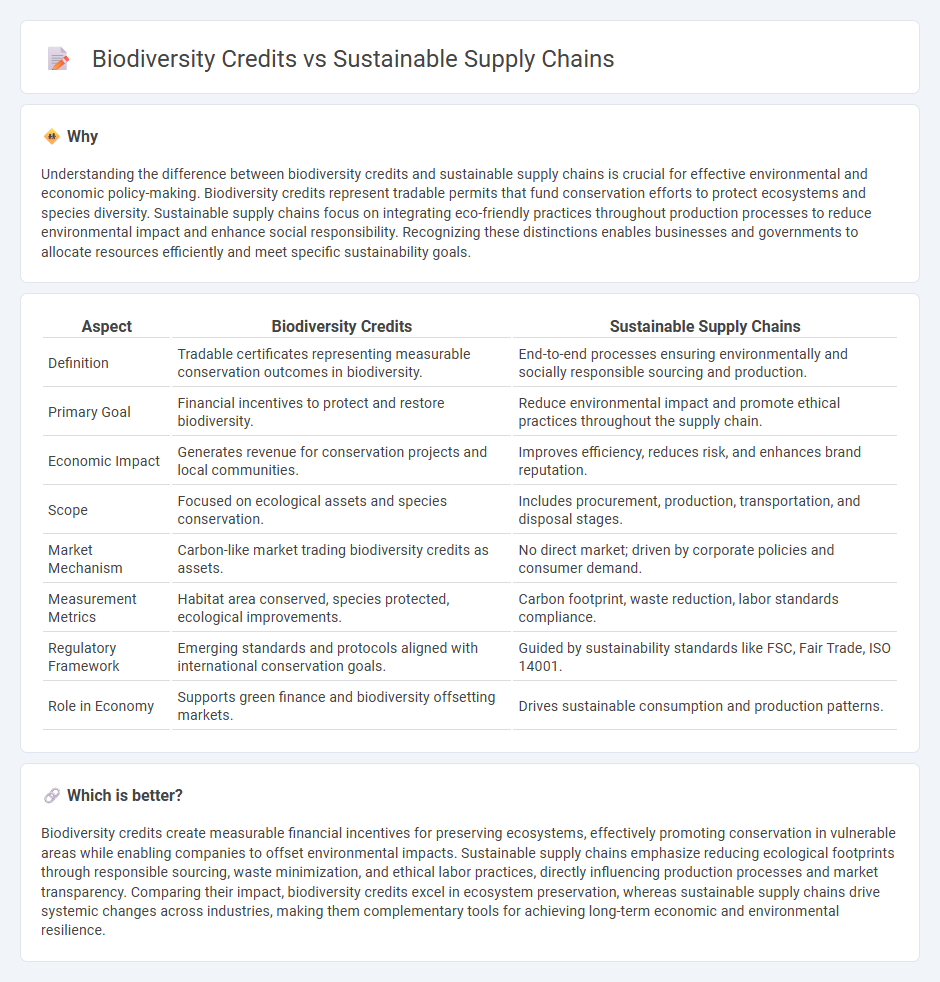
Understanding the difference between biodiversity credits and sustainable supply chains is crucial for effective environmental and economic policy-making. Biodiversity credits represent tradable permits that fund conservation efforts to protect ecosystems and species diversity. Sustainable supply chains focus on integrating eco-friendly practices throughout production processes to reduce environmental impact and enhance social responsibility. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses and governments to allocate resources efficiently and meet specific sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Biodiversity Credits | Sustainable Supply Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tradable certificates representing measurable conservation outcomes in biodiversity. | End-to-end processes ensuring environmentally and socially responsible sourcing and production. |
| Primary Goal | Financial incentives to protect and restore biodiversity. | Reduce environmental impact and promote ethical practices throughout the supply chain. |
| Economic Impact | Generates revenue for conservation projects and local communities. | Improves efficiency, reduces risk, and enhances brand reputation. |
| Scope | Focused on ecological assets and species conservation. | Includes procurement, production, transportation, and disposal stages. |
| Market Mechanism | Carbon-like market trading biodiversity credits as assets. | No direct market; driven by corporate policies and consumer demand. |
| Measurement Metrics | Habitat area conserved, species protected, ecological improvements. | Carbon footprint, waste reduction, labor standards compliance. |
| Regulatory Framework | Emerging standards and protocols aligned with international conservation goals. | Guided by sustainability standards like FSC, Fair Trade, ISO 14001. |
| Role in Economy | Supports green finance and biodiversity offsetting markets. | Drives sustainable consumption and production patterns. |
Which is better?
Biodiversity credits create measurable financial incentives for preserving ecosystems, effectively promoting conservation in vulnerable areas while enabling companies to offset environmental impacts. Sustainable supply chains emphasize reducing ecological footprints through responsible sourcing, waste minimization, and ethical labor practices, directly influencing production processes and market transparency. Comparing their impact, biodiversity credits excel in ecosystem preservation, whereas sustainable supply chains drive systemic changes across industries, making them complementary tools for achieving long-term economic and environmental resilience.
Connection
Biodiversity credits incentivize companies to preserve ecosystems, directly influencing sustainable supply chains by promoting responsible sourcing and reducing environmental impact. Integrating biodiversity credits into supply chain management enhances transparency and accountability, ensuring procurement practices support conservation goals. This alignment fosters long-term economic resilience while meeting regulatory requirements and consumer demand for sustainable products.
Key Terms
Circular Economy
Sustainable supply chains integrate circular economy principles by reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and promoting product lifecycle extension to minimize environmental impact. Biodiversity credits function as market-based incentives that reward businesses for conserving ecosystems and enhancing biodiversity while supporting circular economic activities. Explore how combining these strategies can drive innovative solutions for environmental sustainability and economic growth.
Ecosystem Services
Sustainable supply chains prioritize reducing environmental impact by integrating eco-friendly practices throughout production and distribution, directly supporting ecosystem services such as water purification and soil fertility. Biodiversity credits offer a market-based approach to conserving habitats by financially rewarding landowners for preserving or restoring ecosystems that provide essential services like carbon sequestration and pollination. Explore how combining these strategies can enhance ecosystem service conservation and promote long-term environmental resilience.
Environmental Accounting
Sustainable supply chains integrate environmental accounting to measure and reduce ecological impacts, ensuring resource efficiency and minimizing carbon footprints throughout product lifecycles. Biodiversity credits represent quantified ecosystem services, enabling companies to offset biodiversity loss by investing in conservation projects that align with global environmental standards. Explore how these approaches redefine corporate responsibility and drive innovation in environmental accounting.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Supply Chain Management? - IBM - Sustainable supply chain management integrates environmental, social, and financial considerations into sourcing, production, and logistics to reduce emissions, ensure ethical labor, and improve cost-efficiency using strategies like supplier audits and AI monitoring.
What Is Supply Chain Sustainability and Why Is It Important? - NetSuite - Supply chain sustainability focuses on reducing environmental impacts and promoting social equity through practices like using recycled materials, supporting artisan cooperatives, and sustainable food sourcing that empower communities and reduce waste.
Supply chain sustainability: what is it and why is it important? - Sedex - It encompasses environmentally and socially responsible practices across the supply chain, safeguarding ecosystems and labor conditions, emphasizing that true sustainability must balance ecological and human welfare, not just environmental factors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com