Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on price differences of recyclable metals across regional markets, leveraging fluctuations in supply, demand, and transportation costs to generate profit. Currency arbitrage exploits discrepancies in foreign exchange rates between different currency pairs on separate platforms or geographic locations, enabling traders to buy low and sell high almost simultaneously. Explore deeper insights into how these arbitrage strategies impact global economic dynamics and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between scrap metal arbitrage and currency arbitrage is crucial for accurately assessing risk and profit margins in specific markets; scrap metal arbitrage involves price discrepancies in physical commodities across regions, while currency arbitrage exploits differences in exchange rates across forex markets. Knowledge of these distinctions helps investors and traders optimize strategies and avoid misleading assumptions in financial planning. Efficient arbitrage can lead to substantial cost savings or revenue generation by capitalizing on market inefficiencies. Mastery of each arbitrage type supports informed decision-making in global trade and finance sectors.
Comparison Table
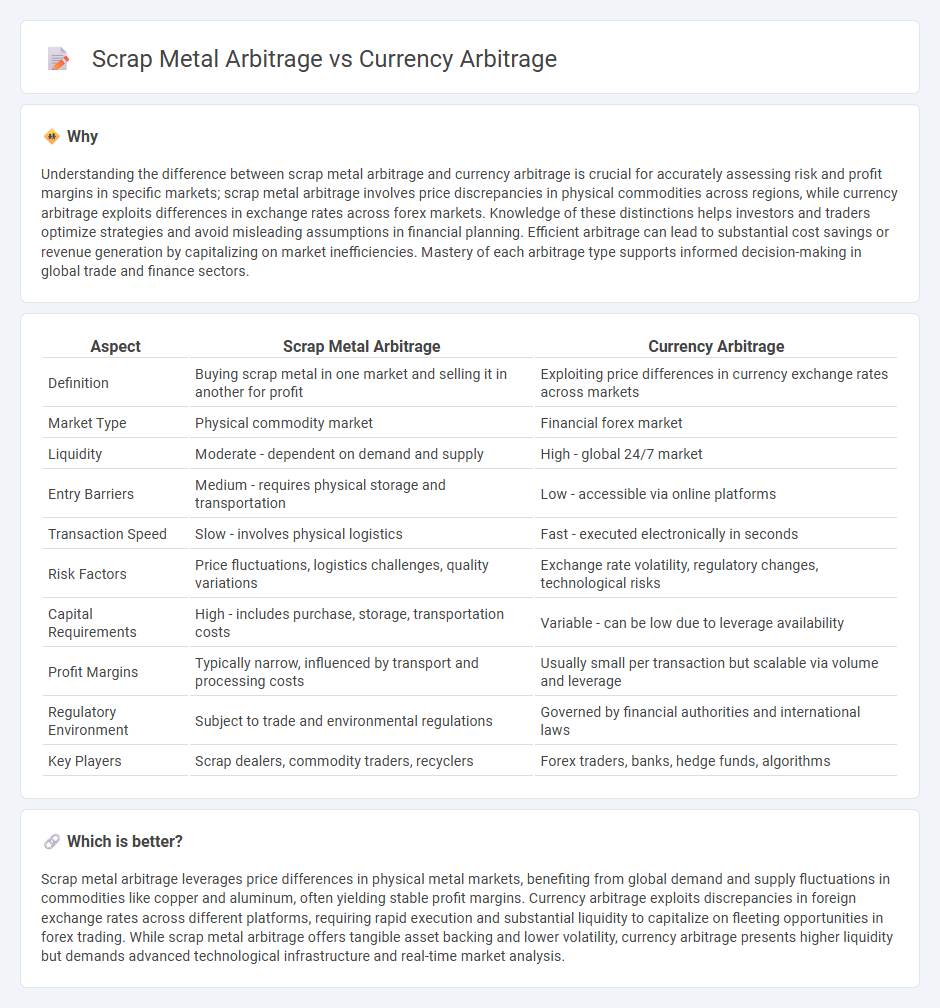
| Aspect | Scrap Metal Arbitrage | Currency Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying scrap metal in one market and selling it in another for profit | Exploiting price differences in currency exchange rates across markets |
| Market Type | Physical commodity market | Financial forex market |
| Liquidity | Moderate - dependent on demand and supply | High - global 24/7 market |
| Entry Barriers | Medium - requires physical storage and transportation | Low - accessible via online platforms |
| Transaction Speed | Slow - involves physical logistics | Fast - executed electronically in seconds |
| Risk Factors | Price fluctuations, logistics challenges, quality variations | Exchange rate volatility, regulatory changes, technological risks |
| Capital Requirements | High - includes purchase, storage, transportation costs | Variable - can be low due to leverage availability |
| Profit Margins | Typically narrow, influenced by transport and processing costs | Usually small per transaction but scalable via volume and leverage |
| Regulatory Environment | Subject to trade and environmental regulations | Governed by financial authorities and international laws |
| Key Players | Scrap dealers, commodity traders, recyclers | Forex traders, banks, hedge funds, algorithms |
Which is better?
Scrap metal arbitrage leverages price differences in physical metal markets, benefiting from global demand and supply fluctuations in commodities like copper and aluminum, often yielding stable profit margins. Currency arbitrage exploits discrepancies in foreign exchange rates across different platforms, requiring rapid execution and substantial liquidity to capitalize on fleeting opportunities in forex trading. While scrap metal arbitrage offers tangible asset backing and lower volatility, currency arbitrage presents higher liquidity but demands advanced technological infrastructure and real-time market analysis.
Connection
Scrap metal arbitrage and currency arbitrage are connected through their reliance on market inefficiencies to generate profit by exploiting price differences across regions and currencies. Both practices involve buying low and selling high simultaneously, with scrap metal arbitrage focusing on physical commodities while currency arbitrage operates in foreign exchange markets. Currency fluctuations directly impact the cost and profitability of cross-border scrap metal trades, linking the two arbitrage strategies within global economic dynamics.
Key Terms
Exchange rates
Currency arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies between different forex markets by simultaneously buying and selling currencies to profit from exchange rate discrepancies. Scrap metal arbitrage, however, hinges on regional price variations in metal markets, influenced indirectly by exchange rates, which affect import/export costs and global demand. Explore deeper insights into how exchange rates distinctly impact these two arbitrage strategies.
Price differentials
Currency arbitrage exploits price differentials in foreign exchange markets by simultaneously buying and selling currencies across different platforms to profit from fluctuating exchange rates. Scrap metal arbitrage, on the other hand, capitalizes on regional disparities in scrap metal prices, purchasing low-cost materials in one market and selling them in higher-priced areas. Explore further to understand how these arbitrage strategies optimize price gaps for maximum gain.
Market efficiency
Currency arbitrage exploits price discrepancies in global forex markets, where high liquidity and rapid information flow make inefficiencies rare and short-lived. Scrap metal arbitrage involves capitalizing on regional price variations due to supply-demand imbalances, logistical costs, and varying recycling regulations, often presenting more persistent market inefficiencies. Explore how these dynamics shape arbitrage strategies and market behavior in greater detail.
Source and External Links
Triangular arbitrage - Wikipedia - Currency arbitrage involves executing a series of trades among three different currencies to exploit discrepancies between quoted exchange rates and implicit cross exchange rates, allowing traders to make a risk-free profit before prices realign.
What is Currency Arbitrage and How Does it Work? - Benzinga - Currency arbitrage profits by exploiting temporary price differences for the same currency pairs across different markets or platforms, buying at a lower price in one market and simultaneously selling at a higher price in another, typically requiring swift action due to short-lived inefficiencies.
Triangular Arbitrage Opportunity - Definition and Example - Triangular arbitrage exploits inconsistencies among three currency exchange rates where the cross-exchange rate deviates from the quoted rates, involving large trades and often margin to amplify profits while managing transaction costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com