De-risking in the economy involves identifying and mitigating potential financial threats to ensure stability, while insulation focuses on creating barriers to protect economic sectors from external shocks. Strategies such as diversifying investments and enhancing regulatory frameworks play key roles in de-risking, whereas insulation may include tariffs and quarantine measures to shield domestic markets. Explore more to understand how these approaches shape economic resilience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between de-risking and insulation in the economy is crucial for effective risk management and financial stability. De-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk assets or markets to prevent potential losses, while insulation focuses on protecting economic systems or portfolios from external shocks. Accurate knowledge enables policymakers and investors to implement appropriate strategies that safeguard economic growth and resilience. This distinction helps balance risk mitigation and opportunity maximization in volatile economic environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-risking | Insulation |
|---|---|---|
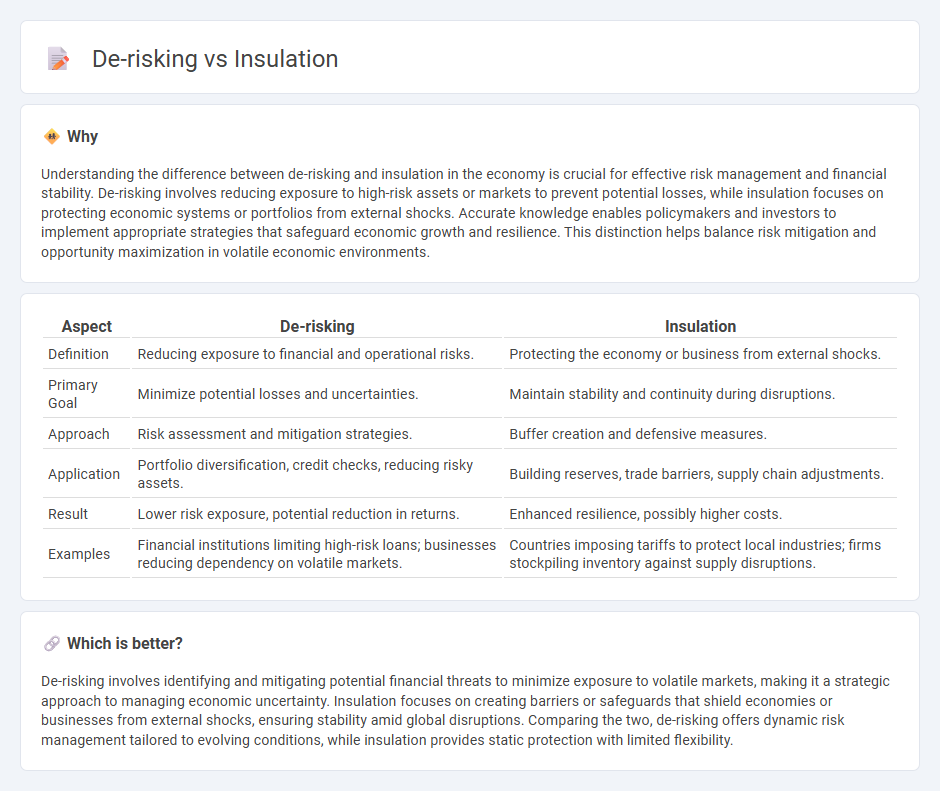
| Definition | Reducing exposure to financial and operational risks. | Protecting the economy or business from external shocks. |
| Primary Goal | Minimize potential losses and uncertainties. | Maintain stability and continuity during disruptions. |
| Approach | Risk assessment and mitigation strategies. | Buffer creation and defensive measures. |
| Application | Portfolio diversification, credit checks, reducing risky assets. | Building reserves, trade barriers, supply chain adjustments. |
| Result | Lower risk exposure, potential reduction in returns. | Enhanced resilience, possibly higher costs. |
| Examples | Financial institutions limiting high-risk loans; businesses reducing dependency on volatile markets. | Countries imposing tariffs to protect local industries; firms stockpiling inventory against supply disruptions. |
Which is better?
De-risking involves identifying and mitigating potential financial threats to minimize exposure to volatile markets, making it a strategic approach to managing economic uncertainty. Insulation focuses on creating barriers or safeguards that shield economies or businesses from external shocks, ensuring stability amid global disruptions. Comparing the two, de-risking offers dynamic risk management tailored to evolving conditions, while insulation provides static protection with limited flexibility.
Connection
De-risking and insulation are connected through their shared goal of protecting economies from external shocks and financial volatility. De-risking involves reducing exposure to high-risk markets or assets, thereby enhancing economic stability, while insulation refers to implementing policies that shield domestic economies from sudden global economic changes. Together, these strategies improve resilience by minimizing vulnerabilities and safeguarding economic growth.
Key Terms
Risk Management
Insulation in risk management involves creating barriers to prevent risk exposure, effectively isolating critical assets from potential threats. De-risking focuses on identifying, assessing, and reducing risks through strategic actions and controls to minimize impact and likelihood. Explore further to understand how these approaches optimize your organization's risk resilience.
Diversification
Insulation in investment refers to creating barriers that protect a portfolio from market volatility, often through hedging strategies or defensive assets, while de-risking focuses on gradually reducing exposure to high-risk investments to preserve capital. Diversification plays a critical role in both approaches by spreading assets across various sectors, geographies, and asset classes to minimize specific risks and enhance portfolio stability. Explore strategies to optimize diversification for effective insulation and de-risking in your investment portfolio.
Supply Chain Resilience
Insulation strategies in supply chain resilience involve creating buffers such as safety stocks and redundant suppliers to shield against disruptions, while de-risking focuses on identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities through diversification and supplier assessment. Effective supply chain resilience incorporates both approaches to ensure continuity and minimize impact from uncertainties like geopolitical risks or natural disasters. Explore deeper insights into optimizing supply chain resilience through strategic insulation and comprehensive de-risking methods.
Source and External Links
Types of Insulation - The most common types of insulation materials include cellulose, fiberglass, and mineral wool, with advanced options like structural insulated panels (SIPs) offering superior energy savings and airtightness when installed correctly.
Building insulation - Building insulation is material used in the building envelope to reduce heat transfer, improve thermal comfort, and lower energy consumption, with materials ranging from fiberglass and rock wool to plant-based and recycled options.
Insulation - Insulation resists heat flow through conduction, convection, and radiation, reducing heating and cooling costs by maintaining indoor temperature stability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com