Grey market imports bypass official distribution channels, often involving genuine products sold through unauthorized dealers, impacting pricing and brand reputation. Informal trade encompasses a broader range of unregulated economic activities, including unregistered businesses and street vendors, contributing significantly to local economies while posing regulatory challenges. Explore how these distinct sectors influence market dynamics and economic policies.
Why it is important
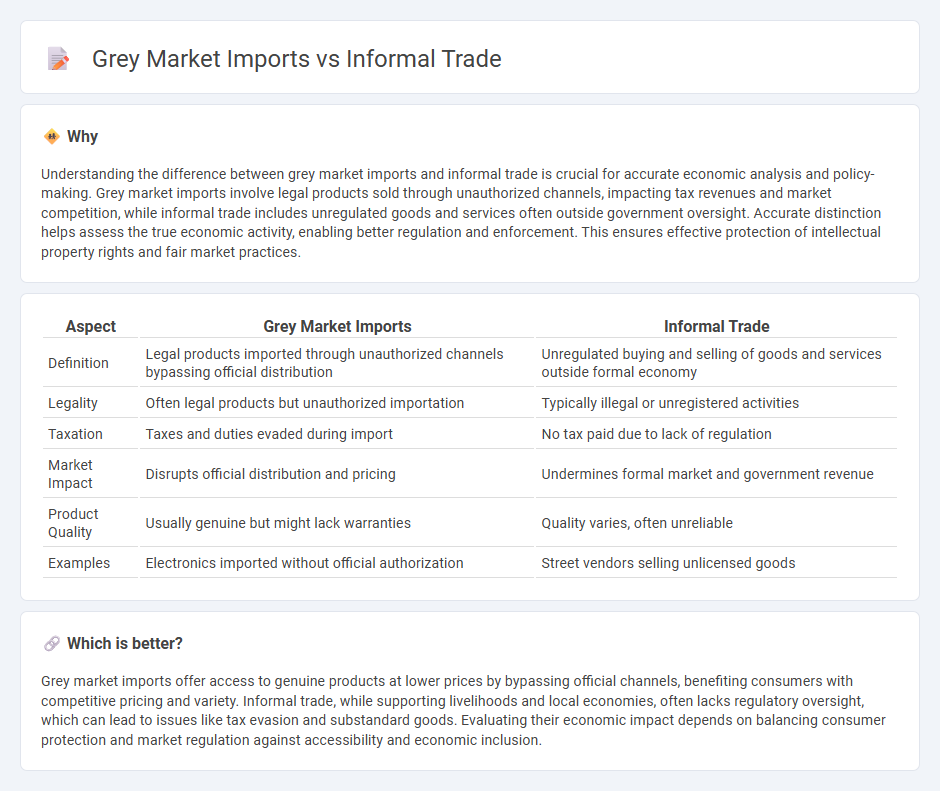
Understanding the difference between grey market imports and informal trade is crucial for accurate economic analysis and policy-making. Grey market imports involve legal products sold through unauthorized channels, impacting tax revenues and market competition, while informal trade includes unregulated goods and services often outside government oversight. Accurate distinction helps assess the true economic activity, enabling better regulation and enforcement. This ensures effective protection of intellectual property rights and fair market practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grey Market Imports | Informal Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal products imported through unauthorized channels bypassing official distribution | Unregulated buying and selling of goods and services outside formal economy |
| Legality | Often legal products but unauthorized importation | Typically illegal or unregistered activities |
| Taxation | Taxes and duties evaded during import | No tax paid due to lack of regulation |
| Market Impact | Disrupts official distribution and pricing | Undermines formal market and government revenue |
| Product Quality | Usually genuine but might lack warranties | Quality varies, often unreliable |
| Examples | Electronics imported without official authorization | Street vendors selling unlicensed goods |
Which is better?
Grey market imports offer access to genuine products at lower prices by bypassing official channels, benefiting consumers with competitive pricing and variety. Informal trade, while supporting livelihoods and local economies, often lacks regulatory oversight, which can lead to issues like tax evasion and substandard goods. Evaluating their economic impact depends on balancing consumer protection and market regulation against accessibility and economic inclusion.
Connection
Grey market imports and informal trade are closely linked through their mutual reliance on bypassing official regulations and customs duties, leading to unrecorded economic activities. Grey market goods, often imported without proper authorization, enter informal trade channels, affecting government tax revenues and market competition. This interconnectedness undermines legal businesses and complicates economic policy enforcement aimed at regulating trade flows.
Key Terms
Regulatory Evasion
Informal trade involves the exchange of goods outside official channels without proper documentation or regulatory compliance, often bypassing taxes and customs duties. Grey market imports consist of genuine products purchased through unauthorized distributors or markets, circumventing official distribution rights but typically not violating safety standards. Explore more to understand the regulatory distinctions and economic impacts of both trade types.
Parallel Importation
Informal trade represents unregulated commerce often outside formal channels, whereas grey market imports involve genuine products imported through unauthorized distribution channels, both impacting official market dynamics differently. Parallel importation specifically refers to the legal yet unofficial import of branded goods, enabling competitive pricing but challenging authorized distributors and intellectual property rights. Explore more about how parallel importation shapes market competition and regulatory strategies.
Tax Revenue Loss
Informal trade involves the unregistered sale of goods, often bypassing official customs and tax regulations, leading to significant tax revenue loss for governments. Grey market imports consist of genuine products imported through unauthorized channels, avoiding import duties and regulatory oversight, further reducing tax collections and distorting local markets. Explore our detailed analysis to understand the fiscal impact of these practices on government tax revenue.
Source and External Links
Informal Cross-Border Trade for Empowerment of Women - This project focuses on informal cross-border trade as a means to empower women economically, particularly in regions like Malawi, Tanzania, and Zambia.
TRADE AND THE INFORMAL ECONOMY - Discusses how globalization can lead to increased informality in work, highlighting the different theoretical models that explain the informal economy's connection to the formal economy.
Informal Trading - Defines informal trading as the economic activity of entrepreneurs selling legal goods and services in public spaces, often contributing to job creation in micro business sectors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com