Slowbalisation describes the gradual reduction of global trade growth and integration, reflecting shifting geopolitical tensions and rising protectionism. Decoupling refers to the deliberate separation of interconnected economies, particularly between major powers, to reduce dependency on each other's technology, supply chains, and markets. Explore how these trends reshape global economic strategies and influence future trade policies.
Why it is important
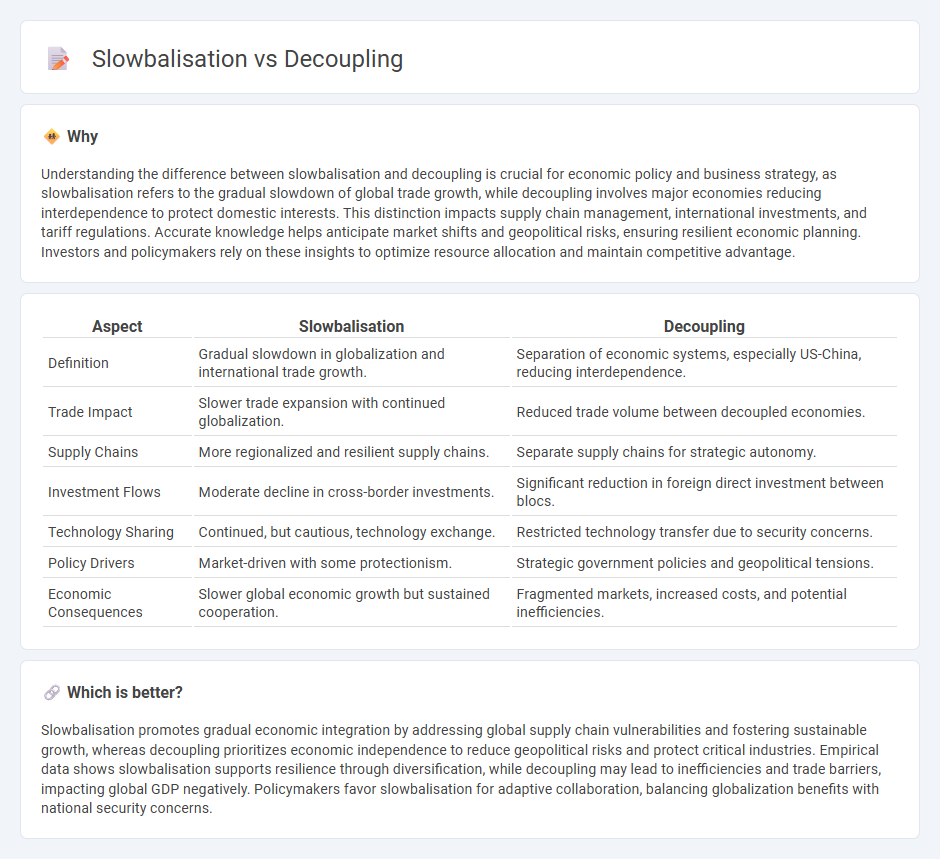
Understanding the difference between slowbalisation and decoupling is crucial for economic policy and business strategy, as slowbalisation refers to the gradual slowdown of global trade growth, while decoupling involves major economies reducing interdependence to protect domestic interests. This distinction impacts supply chain management, international investments, and tariff regulations. Accurate knowledge helps anticipate market shifts and geopolitical risks, ensuring resilient economic planning. Investors and policymakers rely on these insights to optimize resource allocation and maintain competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalisation | Decoupling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual slowdown in globalization and international trade growth. | Separation of economic systems, especially US-China, reducing interdependence. |
| Trade Impact | Slower trade expansion with continued globalization. | Reduced trade volume between decoupled economies. |
| Supply Chains | More regionalized and resilient supply chains. | Separate supply chains for strategic autonomy. |
| Investment Flows | Moderate decline in cross-border investments. | Significant reduction in foreign direct investment between blocs. |
| Technology Sharing | Continued, but cautious, technology exchange. | Restricted technology transfer due to security concerns. |
| Policy Drivers | Market-driven with some protectionism. | Strategic government policies and geopolitical tensions. |
| Economic Consequences | Slower global economic growth but sustained cooperation. | Fragmented markets, increased costs, and potential inefficiencies. |
Which is better?
Slowbalisation promotes gradual economic integration by addressing global supply chain vulnerabilities and fostering sustainable growth, whereas decoupling prioritizes economic independence to reduce geopolitical risks and protect critical industries. Empirical data shows slowbalisation supports resilience through diversification, while decoupling may lead to inefficiencies and trade barriers, impacting global GDP negatively. Policymakers favor slowbalisation for adaptive collaboration, balancing globalization benefits with national security concerns.
Connection
Slowbalisation, characterized by a gradual reduction in global trade growth, intensifies the trend of decoupling as countries seek to reduce economic dependencies and enhance self-sufficiency. Decoupling involves the strategic separation of supply chains and financial systems, promoting regionalization over globalization in response to geopolitical tensions and trade uncertainties. This interconnected dynamic reshapes the global economy by prioritizing resilience and localized economic ecosystems over deep, integrated international trade networks.
Key Terms
Globalization
Decoupling refers to the deliberate disentanglement of economic ties between major powers, primarily between the U.S. and China, to reduce dependency in supply chains and technology sectors. Slowbalisation denotes a deceleration in globalization's pace, marked by reduced cross-border investments and trade growth, reflecting geopolitical tensions and pandemic aftermath. Explore the evolving dynamics shaping the future of global interconnectedness.
Supply Chains
Decoupling involves the strategic separation of supply chains to reduce dependence on global partners, enhancing resilience and security in critical industries. Slowbalisation refers to the gradual slowdown and regionalization of global supply chains, driven by geopolitical tensions, rising costs, and a shift towards localization. Explore the evolving dynamics of supply chains to understand the implications of decoupling and slowbalisation on global trade and production efficiency.
Trade Flows
Decoupling refers to the strategic reduction of economic interdependence between major global powers, particularly in trade flows, often driven by geopolitical tensions and national security concerns. Slowbalisation describes the gradual slowdown in the growth of global trade integration due to factors such as increased protectionism, supply chain disruptions, and shifts in consumer demand. Explore the detailed impacts of decoupling and slowbalisation on international trade dynamics and their future implications.
Source and External Links
Decoupling - Decoupling generally refers to the ending or removal of coupling and can be applied in various fields such as economics (separation of economies), cosmology (particles falling out of equilibrium), engineering, and more, where it means reducing interaction or dependence between components or systems.
DECOUPLING | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - Decoupling is defined as a situation where two or more activities or entities are separated or do not develop in the same way, emphasizing the independence or separation of components previously linked.
Decoupling (cosmology) - In cosmology, decoupling describes the period when different types of particles fall out of thermal equilibrium due to the universe's expansion, leading for example to photon decoupling that enables the cosmic microwave background radiation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com