Ghost kitchen expansion drives cost efficiency and scalability by eliminating traditional dine-in expenses and focusing solely on delivery operations, appealing to restaurateurs aiming to optimize overhead. Third-party aggregators offer extensive customer reach and streamlined order management but impose high commission fees that can erode profit margins for restaurants. Explore how businesses balance these strategies to maximize revenue and operational efficiency in the evolving food delivery economy.
Why it is important
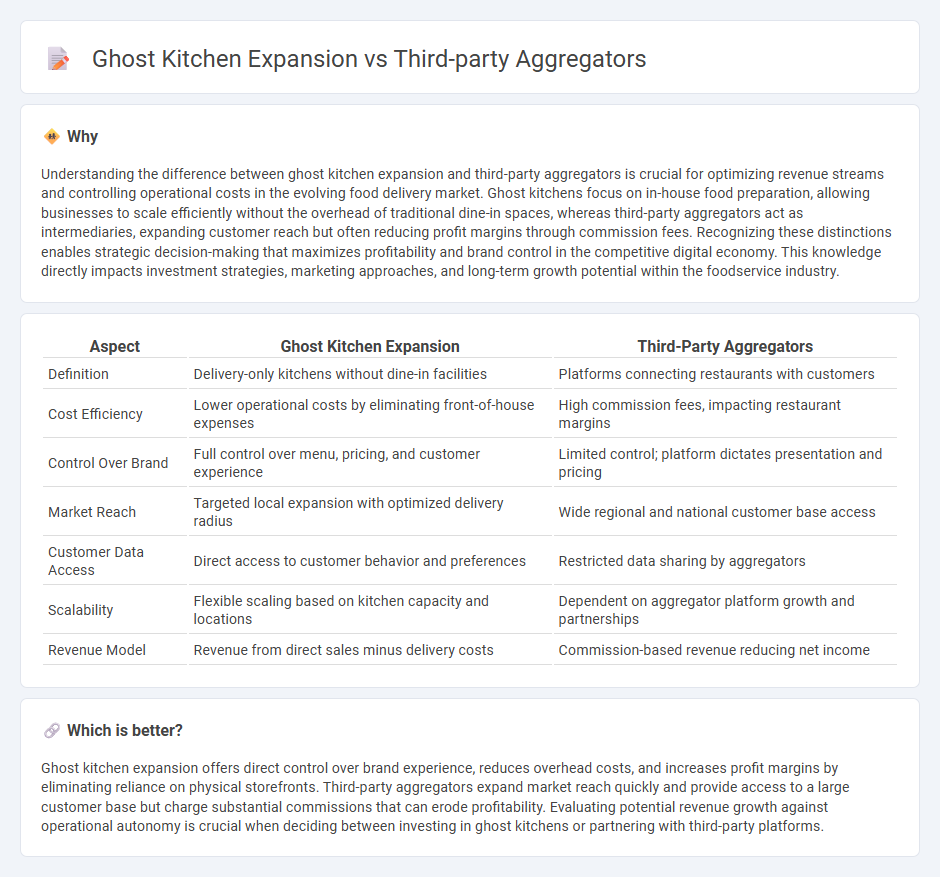
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchen expansion and third-party aggregators is crucial for optimizing revenue streams and controlling operational costs in the evolving food delivery market. Ghost kitchens focus on in-house food preparation, allowing businesses to scale efficiently without the overhead of traditional dine-in spaces, whereas third-party aggregators act as intermediaries, expanding customer reach but often reducing profit margins through commission fees. Recognizing these distinctions enables strategic decision-making that maximizes profitability and brand control in the competitive digital economy. This knowledge directly impacts investment strategies, marketing approaches, and long-term growth potential within the foodservice industry.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Kitchen Expansion | Third-Party Aggregators |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery-only kitchens without dine-in facilities | Platforms connecting restaurants with customers |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs by eliminating front-of-house expenses | High commission fees, impacting restaurant margins |
| Control Over Brand | Full control over menu, pricing, and customer experience | Limited control; platform dictates presentation and pricing |
| Market Reach | Targeted local expansion with optimized delivery radius | Wide regional and national customer base access |
| Customer Data Access | Direct access to customer behavior and preferences | Restricted data sharing by aggregators |
| Scalability | Flexible scaling based on kitchen capacity and locations | Dependent on aggregator platform growth and partnerships |
| Revenue Model | Revenue from direct sales minus delivery costs | Commission-based revenue reducing net income |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchen expansion offers direct control over brand experience, reduces overhead costs, and increases profit margins by eliminating reliance on physical storefronts. Third-party aggregators expand market reach quickly and provide access to a large customer base but charge substantial commissions that can erode profitability. Evaluating potential revenue growth against operational autonomy is crucial when deciding between investing in ghost kitchens or partnering with third-party platforms.
Connection
Ghost kitchen expansion thrives on the widespread use of third-party aggregators, which drive demand by offering consumers seamless access to diverse virtual dining options. Third-party platforms facilitate order distribution and delivery logistics, enabling ghost kitchens to scale efficiently without traditional storefront constraints. This symbiotic relationship accelerates market growth, reduces overhead costs, and reshapes the foodservice economy.
Key Terms
Platform Intermediation
Third-party aggregators serve as key platform intermediaries by connecting customers with a variety of food vendors through a single digital interface, enhancing market accessibility and order convenience. Ghost kitchens, by operating as centralized food production facilities without dine-in options, leverage platform intermediation to optimize delivery efficiency and expand culinary brands rapidly. Explore in-depth insights on how platform intermediation shapes the competitive landscape between third-party aggregators and ghost kitchen growth.
Asset-Light Model
Third-party aggregators leverage an asset-light model by providing digital platforms for food delivery without owning physical kitchens, enabling rapid scalability and reduced capital investment. Ghost kitchens, while also asset-light, focus on optimizing kitchen space and operations solely for delivery, enhancing efficiency and menu flexibility without front-of-house costs. Explore deeper insights into how these models revolutionize the food service industry's growth strategies and operational dynamics.
Market Penetration
Third-party aggregators boost market penetration by leveraging established delivery platforms and vast customer bases, enabling restaurants to reach wider audiences without significant upfront investment. Ghost kitchen expansion focuses on creating dedicated delivery-only facilities, reducing operational costs and enhancing scalability in high-demand locations to capture new market segments efficiently. Explore how these strategies can redefine your growth approach in the food delivery market.
Source and External Links
Third-Party Aggregator Data - Third-party aggregators collect, clean, and normalize data from multiple sources, providing centralized analytics platforms for industries like travel management.
Third-Party Aggregators: Friend or Foe? - Platforms like UberEats, DoorDash, and Grubhub act as third-party aggregators, connecting retailers (or restaurants) with customers by consolidating offerings on a single digital marketplace.
How to Choose a Third-Party Aggregator? - Third-party payment aggregators enable merchants to accept various payment methods online without needing to set up their own bank merchant accounts, streamlining transaction processes for e-commerce businesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com