De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade to strengthen domestic currencies and enhance economic sovereignty. Local currency settlement facilitates trade by using national currencies, minimizing exchange rate risks and promoting regional financial integration. Explore the impact of these strategies on global economic stability and trade dynamics.
Why it is important
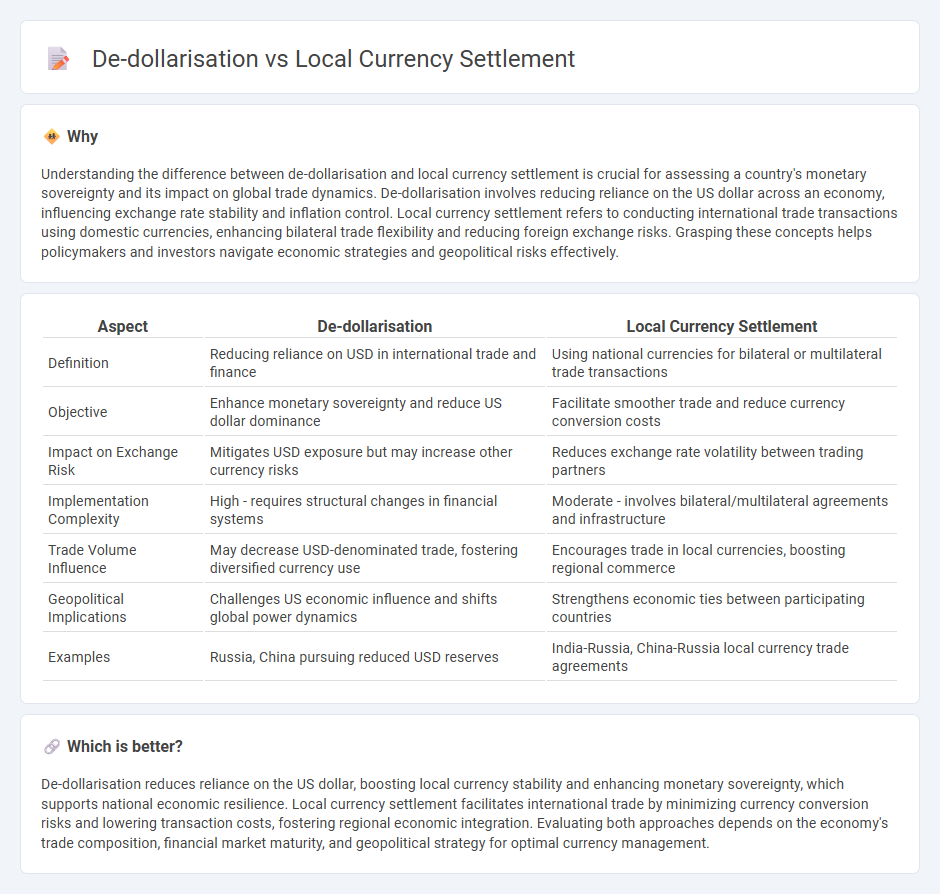
Understanding the difference between de-dollarisation and local currency settlement is crucial for assessing a country's monetary sovereignty and its impact on global trade dynamics. De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the US dollar across an economy, influencing exchange rate stability and inflation control. Local currency settlement refers to conducting international trade transactions using domestic currencies, enhancing bilateral trade flexibility and reducing foreign exchange risks. Grasping these concepts helps policymakers and investors navigate economic strategies and geopolitical risks effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-dollarisation | Local Currency Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing reliance on USD in international trade and finance | Using national currencies for bilateral or multilateral trade transactions |
| Objective | Enhance monetary sovereignty and reduce US dollar dominance | Facilitate smoother trade and reduce currency conversion costs |
| Impact on Exchange Risk | Mitigates USD exposure but may increase other currency risks | Reduces exchange rate volatility between trading partners |
| Implementation Complexity | High - requires structural changes in financial systems | Moderate - involves bilateral/multilateral agreements and infrastructure |
| Trade Volume Influence | May decrease USD-denominated trade, fostering diversified currency use | Encourages trade in local currencies, boosting regional commerce |
| Geopolitical Implications | Challenges US economic influence and shifts global power dynamics | Strengthens economic ties between participating countries |
| Examples | Russia, China pursuing reduced USD reserves | India-Russia, China-Russia local currency trade agreements |
Which is better?
De-dollarisation reduces reliance on the US dollar, boosting local currency stability and enhancing monetary sovereignty, which supports national economic resilience. Local currency settlement facilitates international trade by minimizing currency conversion risks and lowering transaction costs, fostering regional economic integration. Evaluating both approaches depends on the economy's trade composition, financial market maturity, and geopolitical strategy for optimal currency management.
Connection
De-dollarisation involves reducing reliance on the US dollar in international trade, promoting local currency settlement to facilitate direct transactions in native currencies. This shift enhances national monetary sovereignty and mitigates foreign exchange risks linked to dollar fluctuations. Countries adopting local currency settlements strengthen economic resilience and encourage regional financial integration.
Key Terms
Exchange Rate
Local currency settlement allows transactions between countries to bypass the US dollar, directly impacting exchange rate volatility by promoting bilateral trade in native currencies. De-dollarisation seeks to reduce global dependence on the US dollar, stabilizing exchange rates through the diversification of reserve currencies and increased use of alternative currencies in international trade. Explore how these mechanisms influence global currency dynamics and future economic stability.
Currency Sovereignty
Local currency settlement enhances currency sovereignty by reducing reliance on dominant foreign currencies like the US dollar, thereby strengthening national monetary control and financial stability. De-dollarisation strategies aim to shift trade and finance away from the dollar, promoting the use of local currencies in international transactions and mitigating exposure to dollar fluctuations and sanctions. Explore how these approaches impact economic independence and global trade dynamics for deeper insights.
Reserve Currency
Local currency settlement involves transacting in domestic currencies to reduce dependency on dominant foreign currencies, which supports efforts toward de-dollarisation by minimizing the role of the U.S. dollar as the global reserve currency. De-dollarisation strategies seek to diversify reserve currency holdings among alternatives like the euro, yuan, or gold to enhance financial sovereignty and mitigate exposure to dollar-related risks. Explore how emerging markets are adapting their reserve currency strategies to balance economic stability and geopolitical influences.
Source and External Links
Reducing Risk, Boosting Trade: The Case for Indonesia's Local Currency Settlement - Local currency settlement is a bilateral transaction procedure where countries use their own currencies for trade and investment, reducing reliance on the US dollar and mitigating risks from US monetary policies; Indonesia has agreements with Malaysia, Thailand, Japan, and China to facilitate this system via designated banks called Appointed Cross Currency Dealers (ACCD).
Ways to Promote Trade Settlement Denominated in Local Currencies - Promoting local currency trade settlement requires addressing firms' reluctance and negative attitudes, removing capital flow restrictions, developing sound financial markets, and encouraging bilateral and regional trade agreements to enable efficient, cost-effective foreign trade settlements in local currencies.
Understanding the growing use of local currencies in cross-border payments - ASEAN countries have launched frameworks such as the Local Currency Settlement Framework allowing bilateral trade in local currency, expanded to investment, and developed digital payment systems facilitating these transactions without USD or RMB intermediaries; similarly, BRICS countries are advancing local currency cross-border payments through mechanisms like BRICS Pay.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com