Public shaming boycotts influence corporate behavior by leveraging consumer power to enforce ethical standards without formal legal frameworks. Regulation imposes binding rules on businesses, ensuring compliance through government oversight and penalties. Explore the economic impact and effectiveness of these approaches in shaping market practices.
Why it is important
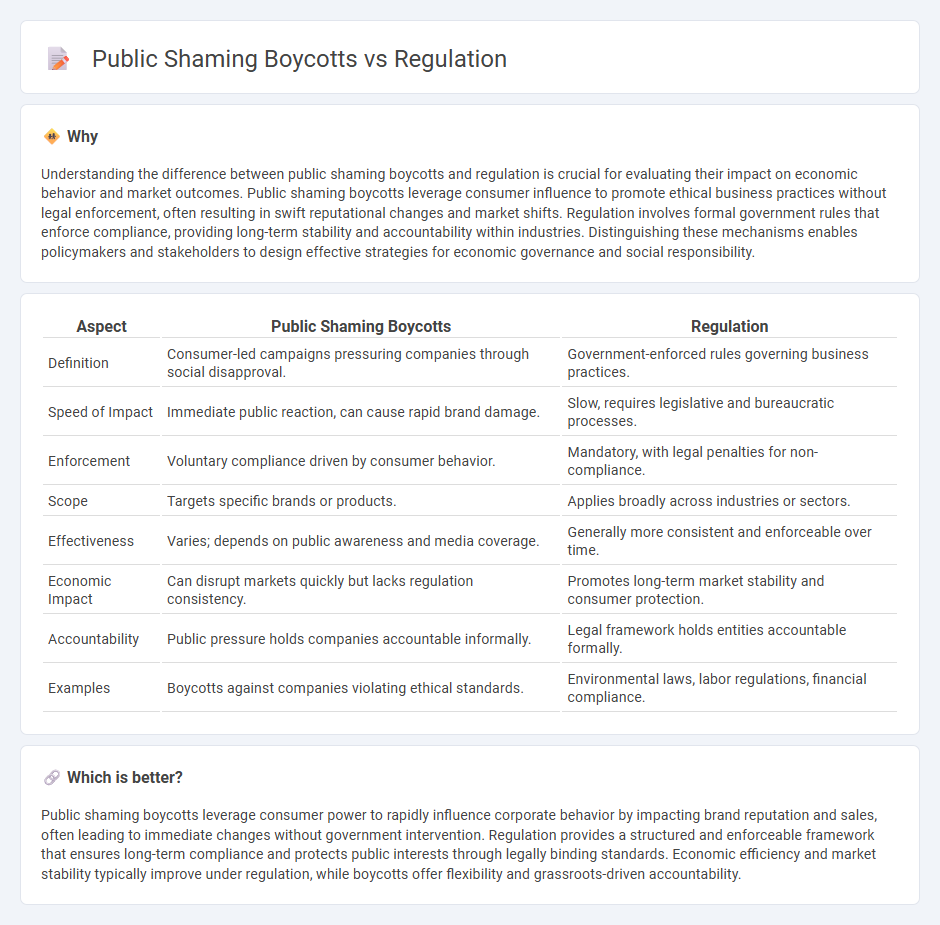
Understanding the difference between public shaming boycotts and regulation is crucial for evaluating their impact on economic behavior and market outcomes. Public shaming boycotts leverage consumer influence to promote ethical business practices without legal enforcement, often resulting in swift reputational changes and market shifts. Regulation involves formal government rules that enforce compliance, providing long-term stability and accountability within industries. Distinguishing these mechanisms enables policymakers and stakeholders to design effective strategies for economic governance and social responsibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Public Shaming Boycotts | Regulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consumer-led campaigns pressuring companies through social disapproval. | Government-enforced rules governing business practices. |
| Speed of Impact | Immediate public reaction, can cause rapid brand damage. | Slow, requires legislative and bureaucratic processes. |
| Enforcement | Voluntary compliance driven by consumer behavior. | Mandatory, with legal penalties for non-compliance. |
| Scope | Targets specific brands or products. | Applies broadly across industries or sectors. |
| Effectiveness | Varies; depends on public awareness and media coverage. | Generally more consistent and enforceable over time. |
| Economic Impact | Can disrupt markets quickly but lacks regulation consistency. | Promotes long-term market stability and consumer protection. |
| Accountability | Public pressure holds companies accountable informally. | Legal framework holds entities accountable formally. |
| Examples | Boycotts against companies violating ethical standards. | Environmental laws, labor regulations, financial compliance. |
Which is better?
Public shaming boycotts leverage consumer power to rapidly influence corporate behavior by impacting brand reputation and sales, often leading to immediate changes without government intervention. Regulation provides a structured and enforceable framework that ensures long-term compliance and protects public interests through legally binding standards. Economic efficiency and market stability typically improve under regulation, while boycotts offer flexibility and grassroots-driven accountability.
Connection
Public shaming, boycotts, and regulation intersect as mechanisms influencing corporate behavior and economic markets. Public shaming galvanizes consumer boycotts targeting companies, pressuring them to alter practices and uphold ethical standards, while regulatory frameworks institutionalize these demands through legal mandates and compliance requirements. Together, these forces shape market dynamics, enforce accountability, and drive sustainable economic policies.
Key Terms
Government Intervention
Government intervention in regulating public shaming boycotts often involves creating legal frameworks to prevent harassment and protect individual rights while balancing freedom of expression. Policies may include restrictions on defamation, cyberbullying laws, or guidelines for responsible social media conduct to mitigate the negative impacts of boycott-driven public shaming. Explore how different countries approach regulation to understand the evolving role of government in managing these social phenomena.
Social Accountability
Regulation enforces legal standards and compliance mechanisms to ensure corporate social responsibility, while public shaming boycotts leverage social accountability by mobilizing consumer activism to pressure companies into ethical behavior. Social accountability through boycotts highlights transparency and community-driven demands, influencing reputational risk and market performance more dynamically than static regulations. Discover how these approaches shape the future of corporate ethics and stakeholder engagement.
Market Discipline
Market discipline leverages regulation and public shaming boycotts as mechanisms to influence firm behavior and maintain market integrity. While regulation imposes formal rules and penalties to correct market failures, public shaming boycotts serve as informal tools that harness consumer power to enforce ethical standards. Explore how these approaches complement each other in promoting corporate accountability and shaping market dynamics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com