Public shaming boycotts have emerged as powerful tools for consumers to hold brands accountable by leveraging social media exposure and collective financial pressure. Consumer advocacy, rooted in informed decision-making and organized campaigns, emphasizes long-term influence on corporate policies and ethical practices. Explore how these approaches shape economic dynamics and drive responsible consumer behavior.
Why it is important
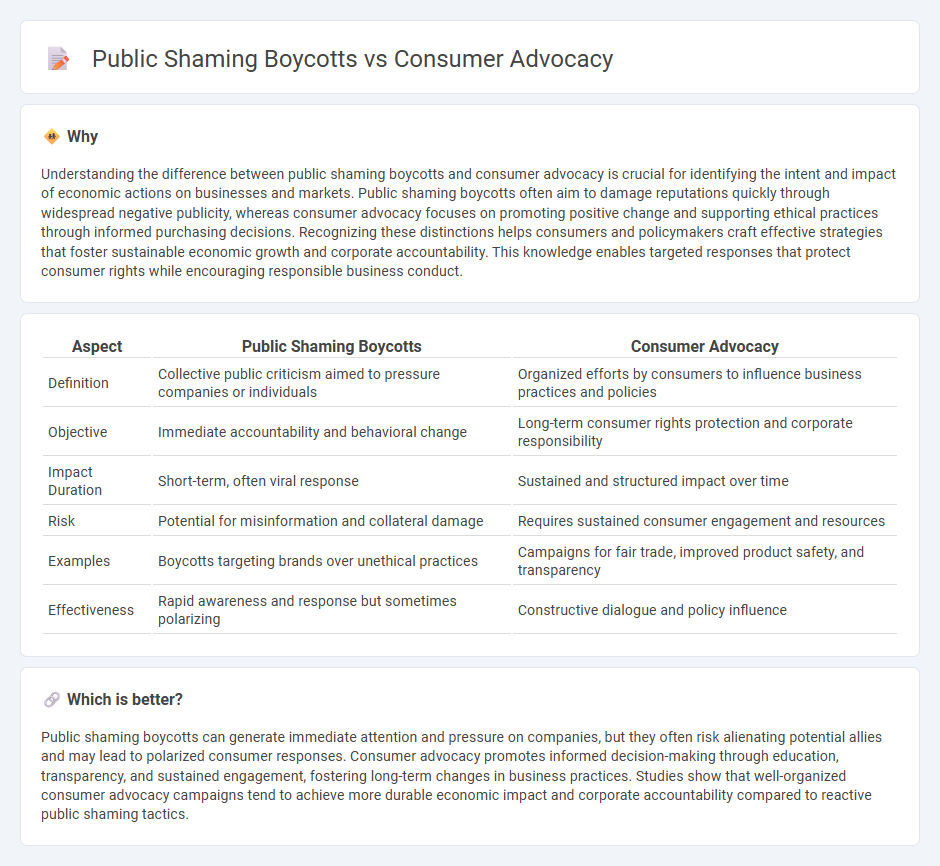
Understanding the difference between public shaming boycotts and consumer advocacy is crucial for identifying the intent and impact of economic actions on businesses and markets. Public shaming boycotts often aim to damage reputations quickly through widespread negative publicity, whereas consumer advocacy focuses on promoting positive change and supporting ethical practices through informed purchasing decisions. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers and policymakers craft effective strategies that foster sustainable economic growth and corporate accountability. This knowledge enables targeted responses that protect consumer rights while encouraging responsible business conduct.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Public Shaming Boycotts | Consumer Advocacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collective public criticism aimed to pressure companies or individuals | Organized efforts by consumers to influence business practices and policies |
| Objective | Immediate accountability and behavioral change | Long-term consumer rights protection and corporate responsibility |
| Impact Duration | Short-term, often viral response | Sustained and structured impact over time |
| Risk | Potential for misinformation and collateral damage | Requires sustained consumer engagement and resources |
| Examples | Boycotts targeting brands over unethical practices | Campaigns for fair trade, improved product safety, and transparency |
| Effectiveness | Rapid awareness and response but sometimes polarizing | Constructive dialogue and policy influence |
Which is better?
Public shaming boycotts can generate immediate attention and pressure on companies, but they often risk alienating potential allies and may lead to polarized consumer responses. Consumer advocacy promotes informed decision-making through education, transparency, and sustained engagement, fostering long-term changes in business practices. Studies show that well-organized consumer advocacy campaigns tend to achieve more durable economic impact and corporate accountability compared to reactive public shaming tactics.
Connection
Public shaming boycotts drive consumer advocacy by spotlighting unethical business practices and pressuring companies to adopt socially responsible policies. Consumer advocacy leverages these collective actions to influence market dynamics, encouraging transparency and accountability. This interconnected mechanism amplifies economic shifts by aligning consumer values with corporate behavior, reshaping industry standards.
Key Terms
Consumer Protection
Consumer advocacy actively promotes policies and practices that safeguard consumer rights and ensure fair treatment in the marketplace, employing legal channels and informed public campaigns. Public shaming boycotts leverage social pressure to hold companies accountable for unethical behavior but may lack structured regulatory enforcement and can sometimes lead to misinformation. Explore how both strategies impact consumer protection and shape corporate accountability.
Corporate Accountability
Consumer advocacy empowers individuals to influence corporate behavior through informed choices and collective action such as ethical purchasing and supporting transparent business practices. Public shaming boycotts leverage social media and public pressure to hold companies accountable for unethical actions, often resulting in swift reputational damage and operational changes. Explore the nuanced impacts of these approaches on corporate accountability to understand how consumers shape business ethics.
Ethical Consumption
Consumer advocacy promotes ethical consumption by encouraging informed purchasing decisions that support fair labor, environmental sustainability, and corporate responsibility. Public shaming boycotts aim to hold companies accountable through social pressure and widespread consumer action, often sparking rapid change but sometimes risking backlash or misinformation. Explore the effectiveness and impacts of these ethical consumption strategies to better understand their roles in fostering responsible markets.
Source and External Links
How We Work for Marketplace Change - Consumer Reports - Consumer advocacy is about ensuring companies prioritize safety, fairness, and honesty by influencing policies and empowering consumers to raise their voices for a fair marketplace.
Consumer protection - Wikipedia - Consumer advocacy involves safeguarding buyers against unfair market practices, supporting consumer rights like safety, information, and redress, often backed by laws and organizations that help consumers make better choices and pursue complaints.
Consumer advocacy : Insurance market regulation : State of Oregon - Consumer advocacy handles complaints from consumers about regulated entities, using expert knowledge to resolve issues and refer complaints to regulators when necessary, aiming to recover benefits and enforce laws.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com