Price gouging occurs when sellers increase prices excessively during emergencies, exploiting supply shortages and urgent demand to maximize profits unfairly. Profiteering involves obtaining unreasonable financial gains by manipulating market conditions or exploiting vulnerabilities ethically or legally ambiguous, often during crises. Explore the key distinctions and economic impacts between price gouging and profiteering to understand regulation challenges and consumer protections.
Why it is important
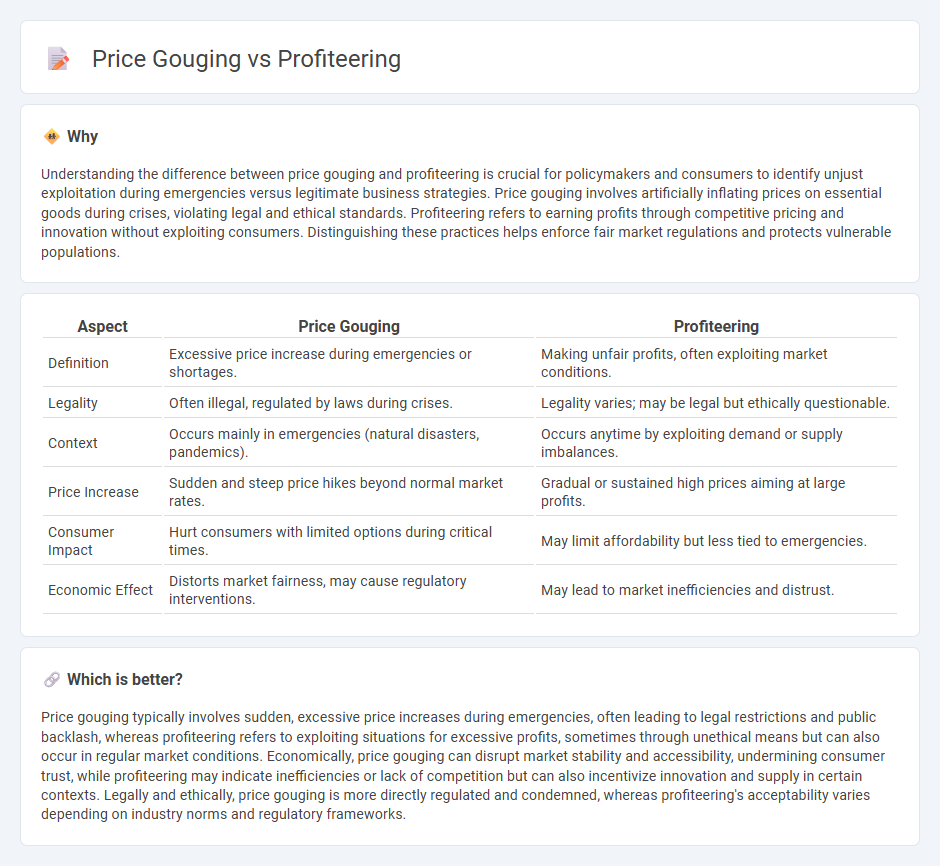
Understanding the difference between price gouging and profiteering is crucial for policymakers and consumers to identify unjust exploitation during emergencies versus legitimate business strategies. Price gouging involves artificially inflating prices on essential goods during crises, violating legal and ethical standards. Profiteering refers to earning profits through competitive pricing and innovation without exploiting consumers. Distinguishing these practices helps enforce fair market regulations and protects vulnerable populations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Price Gouging | Profiteering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive price increase during emergencies or shortages. | Making unfair profits, often exploiting market conditions. |
| Legality | Often illegal, regulated by laws during crises. | Legality varies; may be legal but ethically questionable. |
| Context | Occurs mainly in emergencies (natural disasters, pandemics). | Occurs anytime by exploiting demand or supply imbalances. |
| Price Increase | Sudden and steep price hikes beyond normal market rates. | Gradual or sustained high prices aiming at large profits. |
| Consumer Impact | Hurt consumers with limited options during critical times. | May limit affordability but less tied to emergencies. |
| Economic Effect | Distorts market fairness, may cause regulatory interventions. | May lead to market inefficiencies and distrust. |
Which is better?
Price gouging typically involves sudden, excessive price increases during emergencies, often leading to legal restrictions and public backlash, whereas profiteering refers to exploiting situations for excessive profits, sometimes through unethical means but can also occur in regular market conditions. Economically, price gouging can disrupt market stability and accessibility, undermining consumer trust, while profiteering may indicate inefficiencies or lack of competition but can also incentivize innovation and supply in certain contexts. Legally and ethically, price gouging is more directly regulated and condemned, whereas profiteering's acceptability varies depending on industry norms and regulatory frameworks.
Connection
Price gouging and profiteering are closely connected through the exploitation of market imbalances during crises or shortages, leading to exorbitant price increases on essential goods and services. Both practices result in unfair economic advantages by prioritizing excessive profit margins over consumer welfare and market stability. Regulatory bodies often target these behaviors to protect consumers and maintain competitive, transparent economic conditions.
Key Terms
Excessive Pricing
Profiteering involves charging excessively high prices to exploit consumers, often during periods of high demand or shortages, while price gouging specifically refers to the act of raising prices to unfair levels during emergencies or disasters. Both practices result in excessive pricing that harms consumers by limiting access to essential goods and services. Learn more about the legal implications and consumer protections against excessive pricing.
Market Manipulation
Profiteering and price gouging both involve exploiting market conditions, but profiteering refers to making excessive profits through unethical or manipulative strategies, often manipulating supply and demand to maximize gains. Price gouging specifically occurs when sellers increase prices significantly during emergencies or shortages, capitalizing on urgent consumer needs beyond reasonable market rates. Explore more on how regulatory frameworks address market manipulation and protect consumers.
Consumer Protection
Profiteering involves exploiting market conditions to earn excessive profits, often during emergencies, whereas price gouging specifically refers to raising prices unreasonably on essential goods and services during crises. Consumer protection laws aim to prevent both practices by ensuring fair pricing and safeguarding consumers from exploitative costs. Explore more to understand legal frameworks and how they protect your rights as a consumer.
Source and External Links
Profiteering - Wikipedia - Profiteering is the act of making a profit by methods considered unethical, such as raising prices during emergencies or exploiting political corruption, with some forms illegal in countries like the UK and Germany.
War profiteering - Wikipedia - War profiteering is when individuals or organizations make unreasonable profits from warfare, often with a negative connotation, exemplified by defense contractors benefiting significantly during wartime.
What is profiteering? Simple Definition & Meaning - Profiteering means taking advantage of a situation where goods are scarce or in high demand to charge excessively high prices, commonly seen during wars or disasters, and is generally viewed as unfair or unethical.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com