Neobank stacking offers users integrated digital banking services with lower fees and enhanced user experience compared to traditional banks, leveraging cloud infrastructure and open APIs. Fintech platforms focus on specialized financial solutions such as lending, payments, or wealth management, often partnering with banks to deliver tailored products. Explore how these innovative models are reshaping the economy and financial accessibility.
Why it is important
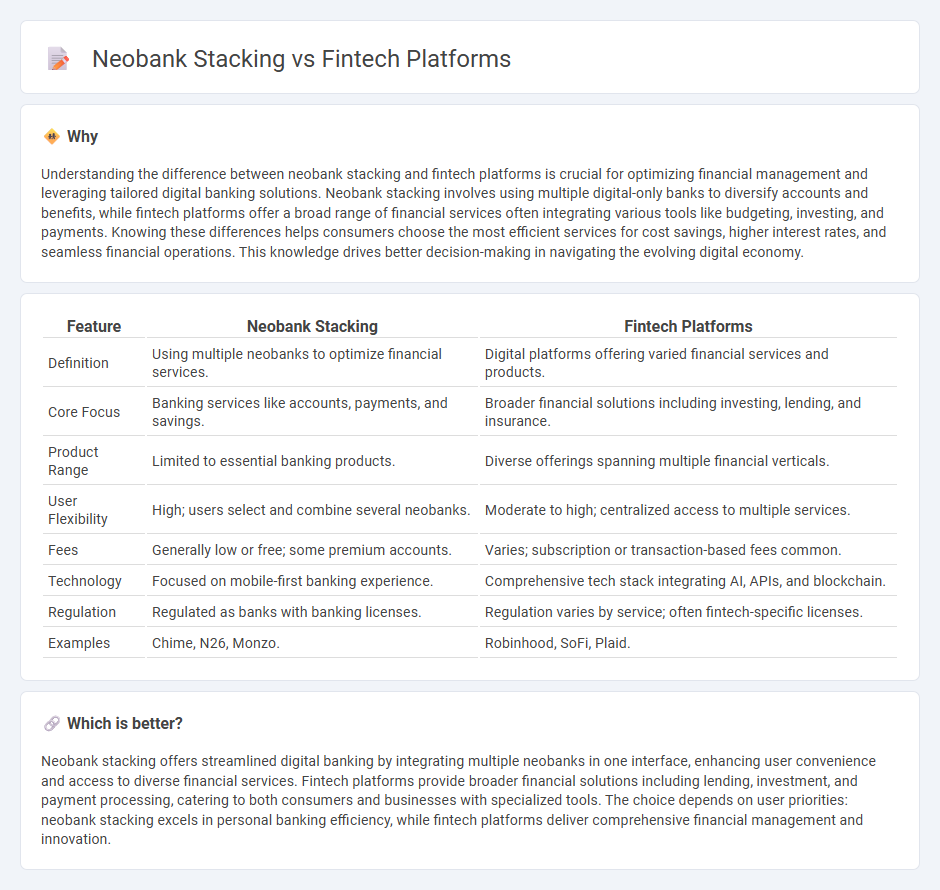
Understanding the difference between neobank stacking and fintech platforms is crucial for optimizing financial management and leveraging tailored digital banking solutions. Neobank stacking involves using multiple digital-only banks to diversify accounts and benefits, while fintech platforms offer a broad range of financial services often integrating various tools like budgeting, investing, and payments. Knowing these differences helps consumers choose the most efficient services for cost savings, higher interest rates, and seamless financial operations. This knowledge drives better decision-making in navigating the evolving digital economy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobank Stacking | Fintech Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using multiple neobanks to optimize financial services. | Digital platforms offering varied financial services and products. |
| Core Focus | Banking services like accounts, payments, and savings. | Broader financial solutions including investing, lending, and insurance. |
| Product Range | Limited to essential banking products. | Diverse offerings spanning multiple financial verticals. |
| User Flexibility | High; users select and combine several neobanks. | Moderate to high; centralized access to multiple services. |
| Fees | Generally low or free; some premium accounts. | Varies; subscription or transaction-based fees common. |
| Technology | Focused on mobile-first banking experience. | Comprehensive tech stack integrating AI, APIs, and blockchain. |
| Regulation | Regulated as banks with banking licenses. | Regulation varies by service; often fintech-specific licenses. |
| Examples | Chime, N26, Monzo. | Robinhood, SoFi, Plaid. |
Which is better?
Neobank stacking offers streamlined digital banking by integrating multiple neobanks in one interface, enhancing user convenience and access to diverse financial services. Fintech platforms provide broader financial solutions including lending, investment, and payment processing, catering to both consumers and businesses with specialized tools. The choice depends on user priorities: neobank stacking excels in personal banking efficiency, while fintech platforms deliver comprehensive financial management and innovation.
Connection
Neobank stacking leverages multiple digital banking services, enabling users to optimize financial management through seamless integration with fintech platforms. Fintech platforms provide advanced APIs and innovative tools that facilitate neobanks in offering personalized, real-time financial solutions, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. This synergy drives increased adoption of digital banking solutions and supports the broader digital transformation of the economy.
Key Terms
Digital Banking
Fintech platforms and neobank stacking represent pivotal innovations in digital banking, with fintech platforms offering diverse financial services through API integrations and neobank stacking allowing customers to manage multiple digital bank accounts seamlessly. Neobank stacking enhances liquidity management and user convenience by consolidating accounts from various neobanks, while fintech platforms focus on delivering specialized financial solutions such as lending, payments, and investment tools. Explore deeper insights into how these models transform the digital banking landscape and empower consumers to optimize their financial management.
API Integration
Fintech platforms rely heavily on robust API integration to connect diverse financial services, enabling seamless user experiences and real-time data exchange. Neobank stacking leverages multiple specialized APIs to combine banking functionalities, enhancing flexibility and customization for customers. Explore how advanced API strategies drive innovation in fintech and neobanking ecosystems.
Financial Intermediation
Fintech platforms leverage advanced algorithms and data analytics to streamline financial intermediation by connecting borrowers and lenders directly, reducing transaction costs and increasing accessibility. Neobank stacking enhances this process by integrating multiple digital banking services within a single ecosystem, offering seamless account management, payments, and lending solutions with lower operational overhead. Explore how these innovative models are transforming traditional financial intermediation and shaping the future of banking.
Source and External Links
113 Fintech Companies and Startups to Know - Profiles leading fintech platforms like iCapital (alternative asset investing), Trumid (fixed income trading), and Forward Financing (small business working capital), highlighting their specialized digital solutions and industry impact.
What is fintech? 6 main types of fintech and how they work - Showcases mainstream fintech platforms such as PayPal and Square (payments), Robinhood (investing), Chime (no-fee banking), and Prosper (peer-to-peer lending), illustrating the diversity of services modern fintech offers to consumers and businesses.
10 Examples of Fintech Solutions Reshaping Industries - Outlines key fintech platform categories including mobile banking, digital lending, automated advisors, and portfolio management, emphasizing how technology streamlines access to financial services and investment tools.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com