Regenerative agriculture and agroforestry are sustainable farming practices that boost soil health, increase biodiversity, and enhance carbon sequestration. Regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring soil organic matter and biodiversity through techniques like cover cropping and reduced tillage, while agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into crop and livestock systems to create multifunctional landscapes. Explore the economic benefits and environmental impacts of these methods to understand their potential in transforming agricultural economies.
Why it is important
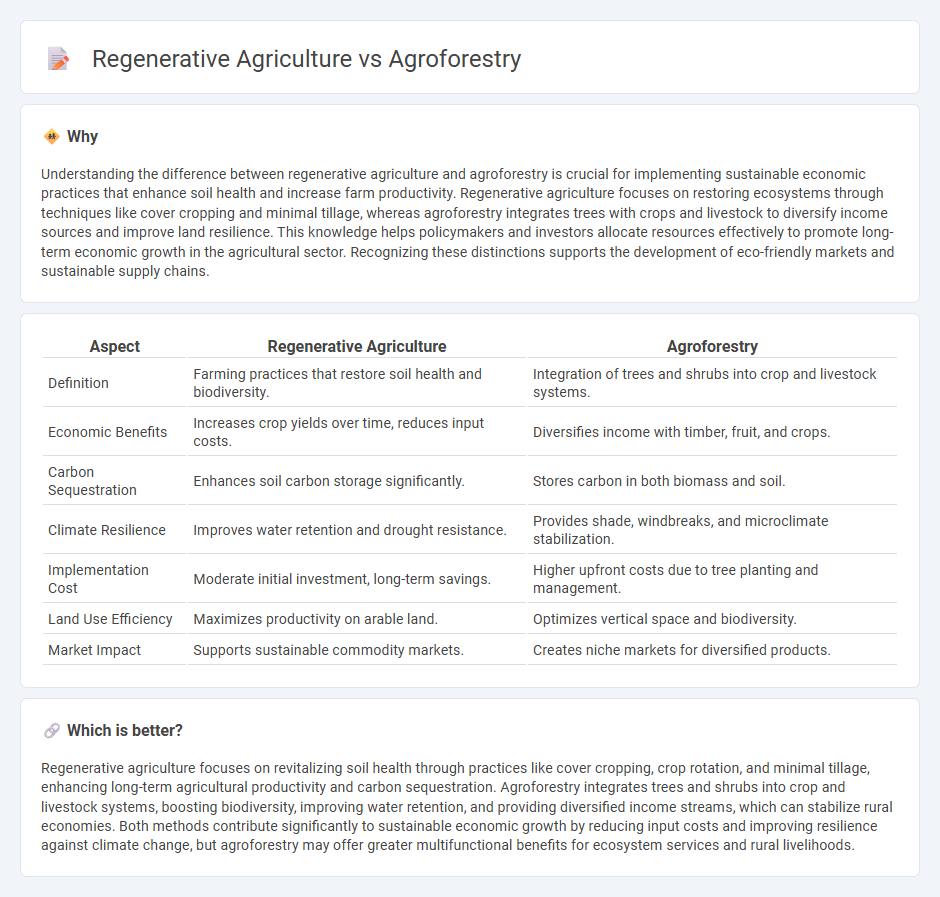
Understanding the difference between regenerative agriculture and agroforestry is crucial for implementing sustainable economic practices that enhance soil health and increase farm productivity. Regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring ecosystems through techniques like cover cropping and minimal tillage, whereas agroforestry integrates trees with crops and livestock to diversify income sources and improve land resilience. This knowledge helps policymakers and investors allocate resources effectively to promote long-term economic growth in the agricultural sector. Recognizing these distinctions supports the development of eco-friendly markets and sustainable supply chains.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Agriculture | Agroforestry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Farming practices that restore soil health and biodiversity. | Integration of trees and shrubs into crop and livestock systems. |
| Economic Benefits | Increases crop yields over time, reduces input costs. | Diversifies income with timber, fruit, and crops. |
| Carbon Sequestration | Enhances soil carbon storage significantly. | Stores carbon in both biomass and soil. |
| Climate Resilience | Improves water retention and drought resistance. | Provides shade, windbreaks, and microclimate stabilization. |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate initial investment, long-term savings. | Higher upfront costs due to tree planting and management. |
| Land Use Efficiency | Maximizes productivity on arable land. | Optimizes vertical space and biodiversity. |
| Market Impact | Supports sustainable commodity markets. | Creates niche markets for diversified products. |
Which is better?
Regenerative agriculture focuses on revitalizing soil health through practices like cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage, enhancing long-term agricultural productivity and carbon sequestration. Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into crop and livestock systems, boosting biodiversity, improving water retention, and providing diversified income streams, which can stabilize rural economies. Both methods contribute significantly to sustainable economic growth by reducing input costs and improving resilience against climate change, but agroforestry may offer greater multifunctional benefits for ecosystem services and rural livelihoods.
Connection
Regenerative agriculture and agroforestry are connected through their shared focus on sustainable land management that enhances soil health, increases biodiversity, and sequesters carbon. Agroforestry integrates trees into agricultural landscapes, promoting ecosystem services that complement regenerative practices like cover cropping and reduced tillage. These approaches collectively improve ecosystem resilience, boost crop yields, and contribute to climate change mitigation by restoring natural cycles and soil fertility.
Key Terms
Value Chains
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, enhancing biodiversity and creating diversified value chains through timber, fruits, and non-timber forest products. Regenerative agriculture emphasizes soil health improvement and ecosystem restoration, fostering value chains built on carbon sequestration, organic produce, and sustainable livestock systems. Explore detailed insights on how each practice transforms agricultural value chains and boosts environmental resilience.
Market Access
Agroforestry integrates trees with crops and livestock to enhance biodiversity and create diversified income streams, improving market resilience for farmers. Regenerative agriculture emphasizes soil health and ecosystem restoration, promoting sustainable production that appeals to eco-conscious consumers and niche markets. Explore deeper insights into how these practices impact market access and profitability.
Economic Resilience
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, enhancing soil health, increasing biodiversity, and providing diversified income streams, which contribute significantly to economic resilience by reducing dependency on single crops. Regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring soil fertility, improving water retention, and sequestering carbon through practices like cover cropping and minimal tillage, resulting in long-term productivity and lowered input costs that bolster farm profitability. Explore how these sustainable practices can revolutionize economic stability in farming communities.
Source and External Links
Agroforestry | Home - USDA - Agroforestry is the intentional integration of trees and shrubs into crop and animal farming systems to create environmental, economic, and social benefits, combining agriculture and forestry technologies for sustainable land-use systems in the U.S.
What are the benefits? | Agroforestry - Soil Association - Agroforestry increases productivity and sustainability by integrating trees with crops, reducing soil erosion, cycling nutrients efficiently, and protecting the environment from water pollution.
Agroforestry - Wikipedia - Agroforestry is a land use system that integrates trees with crops or pasture, enhancing soil stability, increasing crop resilience, improving ecosystem services, and contributing to sustainable agriculture by diversifying products and restoring land.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com