Workation merges remote work with travel, boosting productivity and well-being by allowing employees to work from diverse locations. The gig economy relies on flexible, short-term jobs, empowering individuals to freelance or contract across various industries. Explore how these evolving work models reshape economic landscapes and career opportunities.
Why it is important
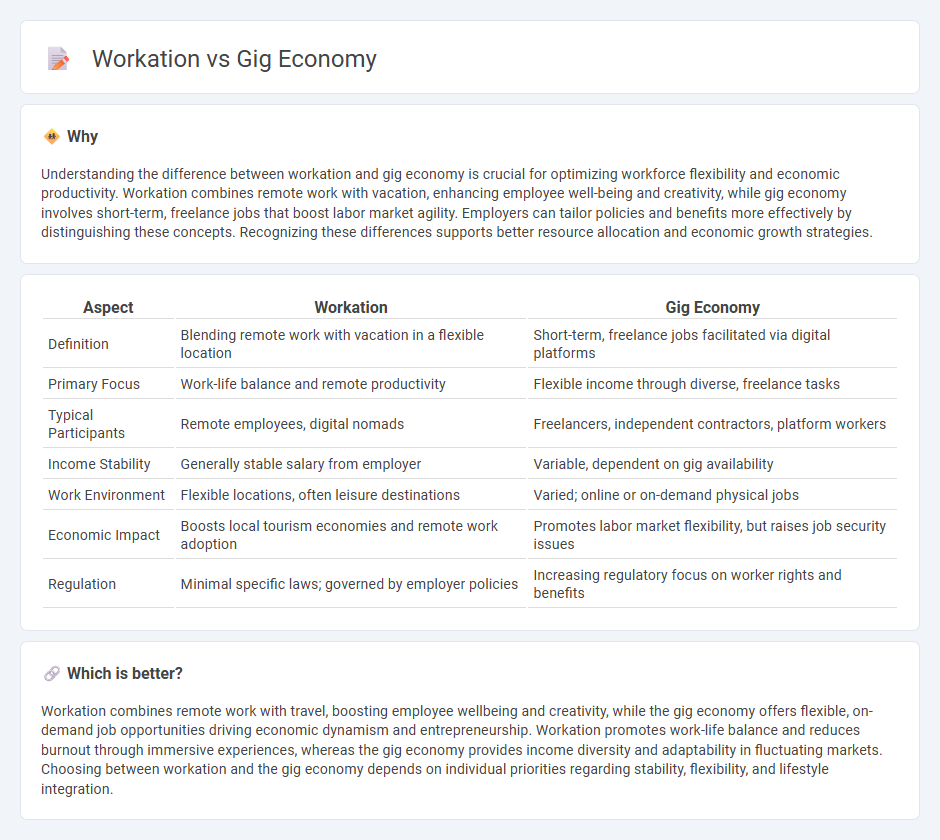
Understanding the difference between workation and gig economy is crucial for optimizing workforce flexibility and economic productivity. Workation combines remote work with vacation, enhancing employee well-being and creativity, while gig economy involves short-term, freelance jobs that boost labor market agility. Employers can tailor policies and benefits more effectively by distinguishing these concepts. Recognizing these differences supports better resource allocation and economic growth strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Workation | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blending remote work with vacation in a flexible location | Short-term, freelance jobs facilitated via digital platforms |
| Primary Focus | Work-life balance and remote productivity | Flexible income through diverse, freelance tasks |
| Typical Participants | Remote employees, digital nomads | Freelancers, independent contractors, platform workers |
| Income Stability | Generally stable salary from employer | Variable, dependent on gig availability |
| Work Environment | Flexible locations, often leisure destinations | Varied; online or on-demand physical jobs |
| Economic Impact | Boosts local tourism economies and remote work adoption | Promotes labor market flexibility, but raises job security issues |
| Regulation | Minimal specific laws; governed by employer policies | Increasing regulatory focus on worker rights and benefits |
Which is better?
Workation combines remote work with travel, boosting employee wellbeing and creativity, while the gig economy offers flexible, on-demand job opportunities driving economic dynamism and entrepreneurship. Workation promotes work-life balance and reduces burnout through immersive experiences, whereas the gig economy provides income diversity and adaptability in fluctuating markets. Choosing between workation and the gig economy depends on individual priorities regarding stability, flexibility, and lifestyle integration.
Connection
Workation and the gig economy are interconnected through their emphasis on flexibility and remote work opportunities. Gig economy platforms enable professionals to engage in short-term, project-based tasks while enjoying workation benefits such as traveling to different locations. This synergy supports a modern workforce that values mobility, autonomy, and diverse income streams.
Key Terms
Flexible Employment
Flexible employment in the gig economy offers on-demand, project-based work with autonomous schedules, enabling workers to monetize skills across multiple platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit. Workations combine remote work with travel, allowing employees to maintain productivity while exploring new environments, supported by companies embracing hybrid and location-independent policies. Explore more about how these flexible employment trends are reshaping modern work-life balance and career choices.
Remote Work
The gig economy thrives on short-term, flexible tasks, often completed remotely, whereas workations blend work with travel, enabling employees to perform their duties from vacation-like settings. Remote work acts as the bridge, facilitating both gig workers who manage multiple projects independently and professionals seeking productivity outside traditional offices. Explore how remote work reshapes job flexibility and work-life balance in evolving career models.
Digital Platforms
Digital platforms play a pivotal role in the gig economy by connecting freelancers and clients globally, enabling task-based or project-based work flexibility. Workations leverage digital tools to facilitate remote work from exotic or unconventional locations without disrupting productivity, blending leisure with business effectively. Explore how digital platforms transform traditional work models and empower modern workforce dynamics.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - The gig economy is a flexible labor market facilitated by digital platforms where organizations hire independent contractors and freelancers for temporary, task-based work, enabling cheaper, efficient services and a growing share of the workforce globally.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy redefines employment by enabling short-term project work instead of full-time roles, connecting workers and businesses through digital platforms and growing rapidly with an expected market size reaching $2.15 trillion by 2033.
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - The gig economy is a free market system characterized by temporary jobs and short-term contracts accessible globally via digital platforms, supporting a decoupling of jobs and locations, and including freelancers, contractors, and part-time hires.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com