Just-in-time hiring allows companies to quickly adjust workforce levels based on immediate demand, reducing labor costs and increasing flexibility. The gig economy leverages freelance or short-term contracts, enabling businesses to tap into specialized skills without long-term commitments. Explore the impacts of these labor strategies on economic growth and workforce dynamics.
Why it is important
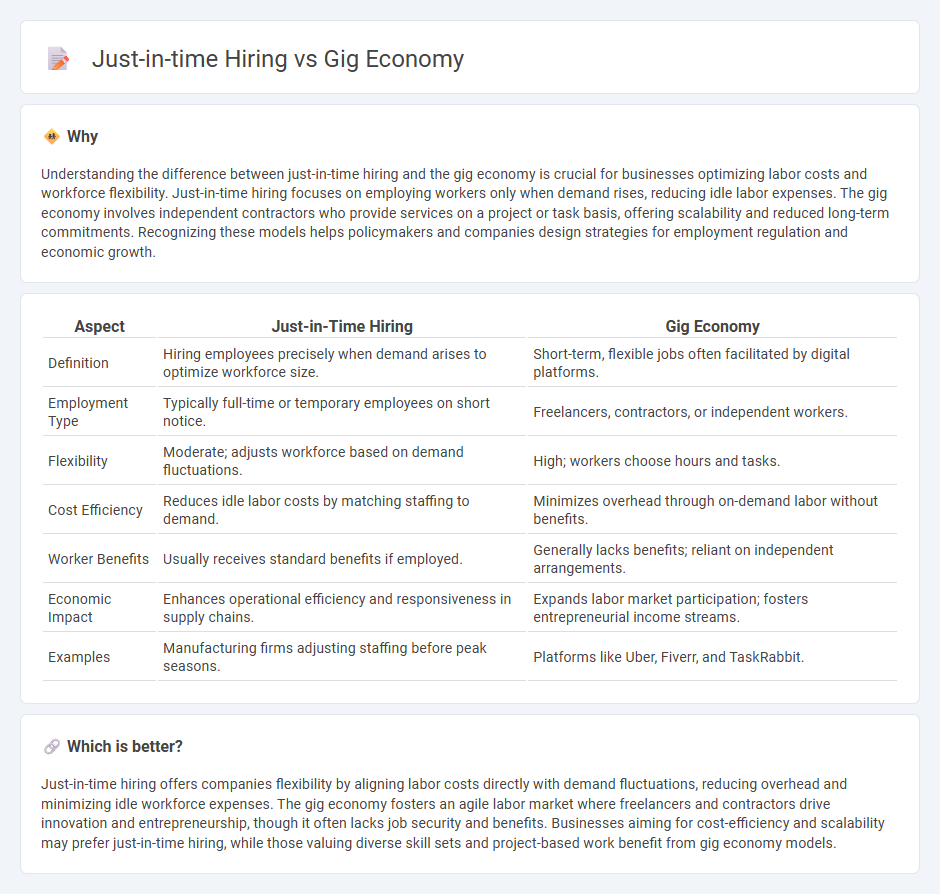
Understanding the difference between just-in-time hiring and the gig economy is crucial for businesses optimizing labor costs and workforce flexibility. Just-in-time hiring focuses on employing workers only when demand rises, reducing idle labor expenses. The gig economy involves independent contractors who provide services on a project or task basis, offering scalability and reduced long-term commitments. Recognizing these models helps policymakers and companies design strategies for employment regulation and economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Just-in-Time Hiring | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring employees precisely when demand arises to optimize workforce size. | Short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms. |
| Employment Type | Typically full-time or temporary employees on short notice. | Freelancers, contractors, or independent workers. |
| Flexibility | Moderate; adjusts workforce based on demand fluctuations. | High; workers choose hours and tasks. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces idle labor costs by matching staffing to demand. | Minimizes overhead through on-demand labor without benefits. |
| Worker Benefits | Usually receives standard benefits if employed. | Generally lacks benefits; reliant on independent arrangements. |
| Economic Impact | Enhances operational efficiency and responsiveness in supply chains. | Expands labor market participation; fosters entrepreneurial income streams. |
| Examples | Manufacturing firms adjusting staffing before peak seasons. | Platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and TaskRabbit. |
Which is better?
Just-in-time hiring offers companies flexibility by aligning labor costs directly with demand fluctuations, reducing overhead and minimizing idle workforce expenses. The gig economy fosters an agile labor market where freelancers and contractors drive innovation and entrepreneurship, though it often lacks job security and benefits. Businesses aiming for cost-efficiency and scalability may prefer just-in-time hiring, while those valuing diverse skill sets and project-based work benefit from gig economy models.
Connection
Just-in-time hiring aligns with the gig economy by enabling businesses to rapidly adjust workforce size based on immediate demand, minimizing labor costs and increasing operational agility. The gig economy's reliance on freelance, short-term contracts facilitates just-in-time recruitment through flexible, on-demand talent pools. This symbiotic relationship boosts economic efficiency by reducing hiring lead times and optimizing resource allocation.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig economy offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing workers to choose their projects and set their schedules, which contrasts with just-in-time hiring that provides employers the ability to rapidly adjust workforce size based on immediate demand. This flexibility in gig work supports diverse income streams and work-life balance, while just-in-time hiring often prioritizes operational efficiency over worker autonomy. Explore the nuances of flexibility in gig economy and just-in-time hiring to understand their distinct impacts on the modern labor market.
On-demand workforce
The gig economy leverages digital platforms to connect workers with short-term, flexible jobs, emphasizing autonomy and diverse income streams, while just-in-time hiring focuses on rapidly fulfilling specific labor needs to optimize operational efficiency. Both models rely on an on-demand workforce but differ in scope; gig work typically involves multiple clients or projects, whereas just-in-time hiring targets immediate, site-specific tasks. Explore how businesses balance these strategies to maximize productivity and workforce agility.
Cost efficiency
The gig economy leverages flexible, short-term contracts to reduce labor costs and minimize overhead by paying workers per task or project, enhancing cost efficiency for businesses. Just-in-time hiring focuses on aligning workforce availability precisely with demand peaks, minimizing idle labor expenses and improving cash flow management. Explore the distinct cost-saving strategies behind gig economy and just-in-time hiring models to optimize your workforce management.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - The gig economy is a flexible labor market where workers are hired as independent contractors for temporary, digitally mediated jobs, enabling cheaper and more efficient services while offering flexibility to workers and businesses alike.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - This model allows workers to engage in short-term projects or gigs rather than full-time roles, providing flexibility and autonomy, with over 70 million Americans participating and the global market expected to triple in value by 2033.
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - The gig economy is characterized by temporary jobs, enabled by digital platforms that connect freelancers with consumers worldwide, decoupling jobs from location and promoting workforce mobility and remote work.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com