Greenflation refers to rising prices driven by the costs of implementing environmentally friendly policies and transitioning to sustainable energy sources. Greedflation describes inflation fueled by firms increasing prices to boost profit margins rather than reflecting increased costs. Explore the dynamics behind these inflation types and their impact on the economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between greenflation and greedflation is crucial for accurate economic analysis and effective policy-making. Greenflation refers to price increases driven by the costs of transitioning to environmentally sustainable technologies and practices. Greedflation describes inflation caused by excessive corporate profit-seeking and price manipulation. Differentiating these helps target inflation control measures appropriately, balancing ecological goals with economic fairness.
Comparison Table
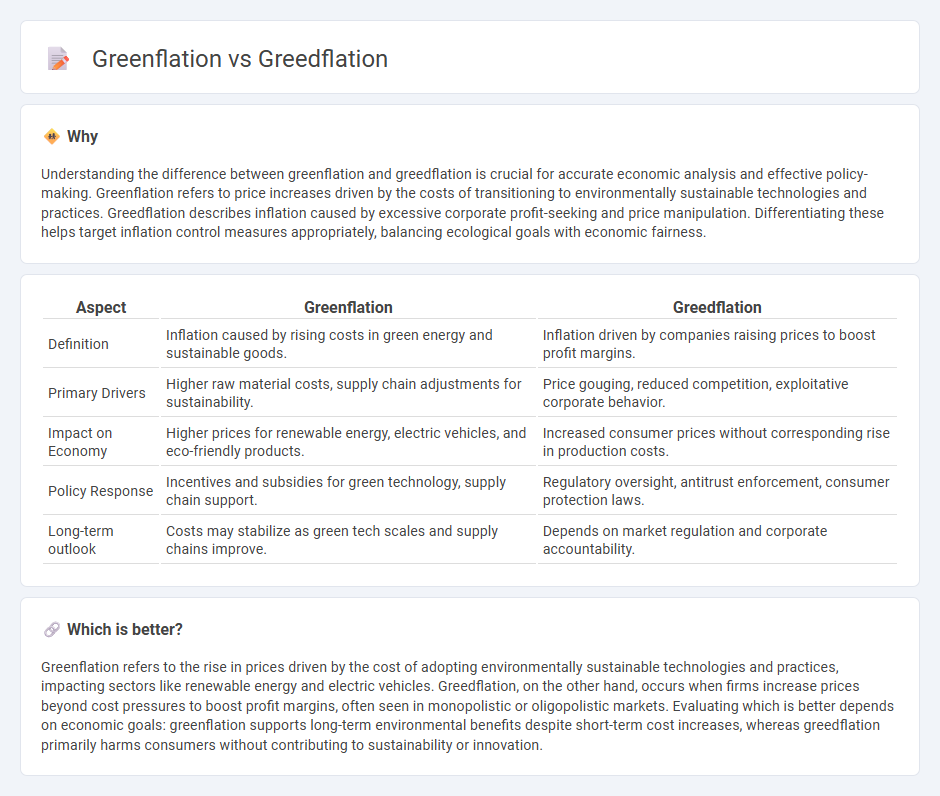
| Aspect | Greenflation | Greedflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation caused by rising costs in green energy and sustainable goods. | Inflation driven by companies raising prices to boost profit margins. |
| Primary Drivers | Higher raw material costs, supply chain adjustments for sustainability. | Price gouging, reduced competition, exploitative corporate behavior. |
| Impact on Economy | Higher prices for renewable energy, electric vehicles, and eco-friendly products. | Increased consumer prices without corresponding rise in production costs. |
| Policy Response | Incentives and subsidies for green technology, supply chain support. | Regulatory oversight, antitrust enforcement, consumer protection laws. |
| Long-term outlook | Costs may stabilize as green tech scales and supply chains improve. | Depends on market regulation and corporate accountability. |
Which is better?
Greenflation refers to the rise in prices driven by the cost of adopting environmentally sustainable technologies and practices, impacting sectors like renewable energy and electric vehicles. Greedflation, on the other hand, occurs when firms increase prices beyond cost pressures to boost profit margins, often seen in monopolistic or oligopolistic markets. Evaluating which is better depends on economic goals: greenflation supports long-term environmental benefits despite short-term cost increases, whereas greedflation primarily harms consumers without contributing to sustainability or innovation.
Connection
Greenflation and greedflation both drive inflation through distinct but interconnected mechanisms affecting the economy. Greenflation results from increased costs linked to sustainable energy transitions and environmental regulations, causing higher prices for raw materials and energy. Greedflation arises when corporations exploit inflationary environments to raise prices beyond cost increases, amplifying the overall inflationary pressures on consumers.
Key Terms
Profit Margins
Greedflation describes rising profit margins driven by excessive corporate pricing power during inflation, whereas greenflation refers to cost increases linked to environmental regulations and sustainable investment. Companies experiencing greedflation often prioritize short-term profit maximization over efficiency gains, while greenflation reflects structural shifts toward cleaner production that may temporarily compress margins. Explore how these distinct inflation types influence profitability and strategic decisions in various industries.
Carbon Pricing
Carbon pricing plays a pivotal role in both greedflation and greenflation, influencing the cost dynamics of goods and services by internalizing environmental externalities. Greedflation refers to price increases driven by corporate profit-seeking under the guise of scarcity, while greenflation stems from higher production costs linked to sustainable practices and carbon regulations. Explore the detailed impacts of carbon pricing on economic inflation patterns and sustainability efforts.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Greedflation refers to inflation driven by excessive corporate profiteering, while greenflation stems from increased costs due to the transition to environmentally sustainable practices. Supply chain disruptions exacerbate both phenomena by inflating production costs, with greedflation capitalizing on scarcity and greenflation reflecting investment in green technologies and materials. Explore deeper insights into how supply chain dynamics shape the distinct impacts of greedflation and greenflation.
Source and External Links
What is greedflation - and is it driving higher prices? - Greedflation refers to corporations exploiting inflation to create excessive profits by raising prices beyond cost increases, although some economists argue inflation's main driver is supply shortages rather than corporate greed.
What is greedflation: The viral financial term explained - Greedflation is when companies intentionally raise prices to increase profits, contributing to inflation, benefiting shareholders, and making essentials more expensive for consumers worldwide.
Greedflation in the US and UK | NEB Digest - New Economy Brief - Greedflation is a key political issue where rising corporate profits are linked to inflation in the US, UK, and EU, with government actions aiming to curb corporate price gouging and address monopoly power boosting prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com