Polycrisis refers to the simultaneous occurrence of multiple, interconnected economic, social, and environmental crises that amplify overall instability. Stagflation, characterized by stagnant economic growth combined with high inflation and unemployment, presents a unique challenge to traditional monetary policies. Explore the nuances and impacts of both phenomena to better understand current global economic dynamics.
Why it is important
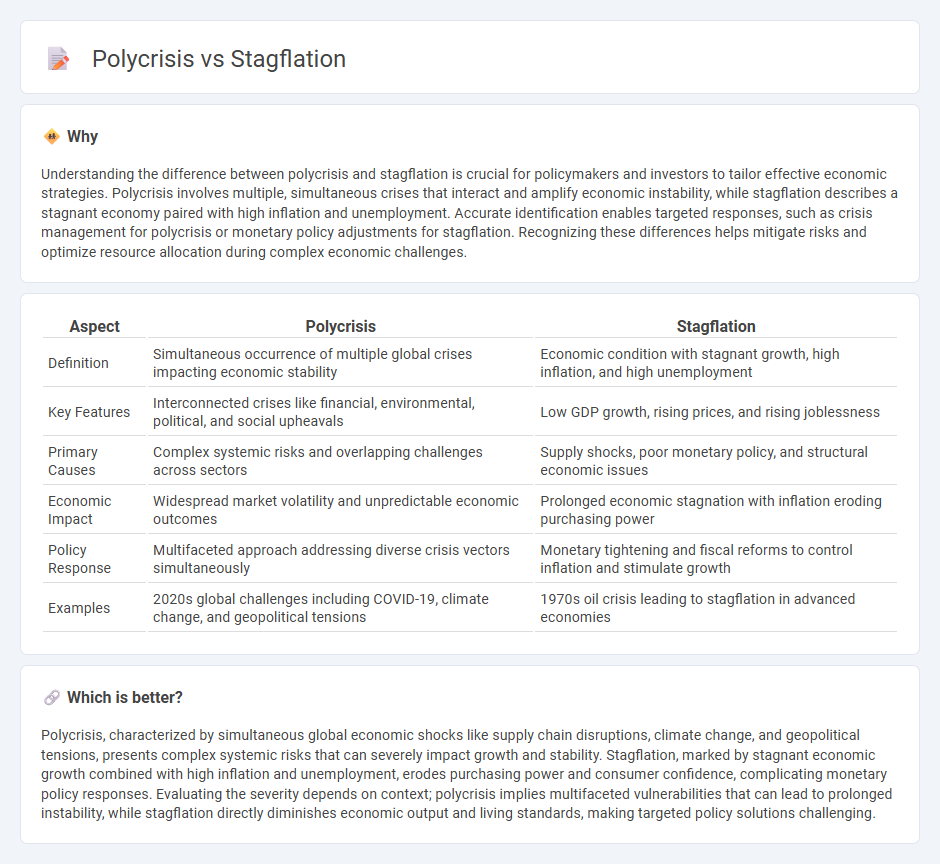
Understanding the difference between polycrisis and stagflation is crucial for policymakers and investors to tailor effective economic strategies. Polycrisis involves multiple, simultaneous crises that interact and amplify economic instability, while stagflation describes a stagnant economy paired with high inflation and unemployment. Accurate identification enables targeted responses, such as crisis management for polycrisis or monetary policy adjustments for stagflation. Recognizing these differences helps mitigate risks and optimize resource allocation during complex economic challenges.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Polycrisis | Stagflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous occurrence of multiple global crises impacting economic stability | Economic condition with stagnant growth, high inflation, and high unemployment |
| Key Features | Interconnected crises like financial, environmental, political, and social upheavals | Low GDP growth, rising prices, and rising joblessness |
| Primary Causes | Complex systemic risks and overlapping challenges across sectors | Supply shocks, poor monetary policy, and structural economic issues |
| Economic Impact | Widespread market volatility and unpredictable economic outcomes | Prolonged economic stagnation with inflation eroding purchasing power |
| Policy Response | Multifaceted approach addressing diverse crisis vectors simultaneously | Monetary tightening and fiscal reforms to control inflation and stimulate growth |
| Examples | 2020s global challenges including COVID-19, climate change, and geopolitical tensions | 1970s oil crisis leading to stagflation in advanced economies |
Which is better?
Polycrisis, characterized by simultaneous global economic shocks like supply chain disruptions, climate change, and geopolitical tensions, presents complex systemic risks that can severely impact growth and stability. Stagflation, marked by stagnant economic growth combined with high inflation and unemployment, erodes purchasing power and consumer confidence, complicating monetary policy responses. Evaluating the severity depends on context; polycrisis implies multifaceted vulnerabilities that can lead to prolonged instability, while stagflation directly diminishes economic output and living standards, making targeted policy solutions challenging.
Connection
Polycrisis, characterized by simultaneous global challenges such as supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and climate change, intensifies stagflation by exacerbating inflation and economic stagnation concurrently. Supply bottlenecks and energy price shocks driven by polycrisis factors reduce productivity and increase production costs, fueling persistent inflation while hindering economic growth. Central banks face constrained monetary policy options during stagflation, as tightening to control inflation may further suppress growth amid complex, overlapping crises.
Key Terms
Stagflation:
Stagflation refers to an economic condition characterized by stagnant growth, high unemployment, and rising inflation occurring simultaneously, challenging traditional monetary policy responses. This phenomenon was notably experienced during the 1970s oil crisis when supply shocks led to persistent inflation despite economic slowdown. Explore the underlying causes and implications of stagflation to understand its impact on modern economic strategies.
Inflation
Stagflation, characterized by persistent high inflation combined with stagnating economic growth and rising unemployment, contrasts sharply with a polycrisis that involves multiple simultaneous systemic risks, including inflation, climate change, geopolitical tensions, and financial instability. Inflation in stagflation erodes purchasing power while economic stagnation limits recovery options, whereas inflation within a polycrisis is compounded by overlapping crises affecting supply chains, energy prices, and global markets. To explore the complex interplay between inflation dynamics in stagflation and polycrisis scenarios, delve deeper into current economic analyses and risk assessments.
Unemployment
Stagflation is characterized by high unemployment combined with stagnant economic growth and rising inflation, creating a challenging environment for job seekers and policymakers. Polycrisis involves multiple interconnected crises, such as financial instability, climate change, and geopolitical tensions, which together exacerbate unemployment by disrupting markets and labor demand. Explore further insights on how unemployment trends evolve amid stagflation and polycrisis conditions.
Source and External Links
Overview, Examples, Why Stagflation is Feared - Stagflation is an economic event marked by high inflation, slow economic growth, and steady high unemployment, making it difficult for governments to address due to conflicting policy effects; key causes include supply shocks like oil price surges and poor economic policies, with the 1970s U.S. stagflation being the most notable example.
Is the worst of both worlds returning? Understanding stagflation risk - Stagflation combines high inflation with stagnant or declining GDP growth and rising unemployment, creating a "misery index" that reflects the painful simultaneous rise of inflation and joblessness, contrasting typical economic patterns.
Stagflation - Wikipedia - Stagflation is the coexistence of high inflation, stagnant economic growth, and elevated unemployment, first identified in the 1960s UK and highlighted after the 1973 oil crisis, challenging traditional economic views and leading to new economic theories due to its policy dilemmas.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com