Funflation refers to rising prices driven by increased consumer spending on entertainment and leisure activities, reflecting a shift in demand patterns post-pandemic. Greedflation occurs when businesses raise prices beyond cost increases to maximize profits, contributing to inflationary pressures without corresponding economic fundamentals. Explore further to understand the impact of these trends on everyday costs and policy responses.
Why it is important
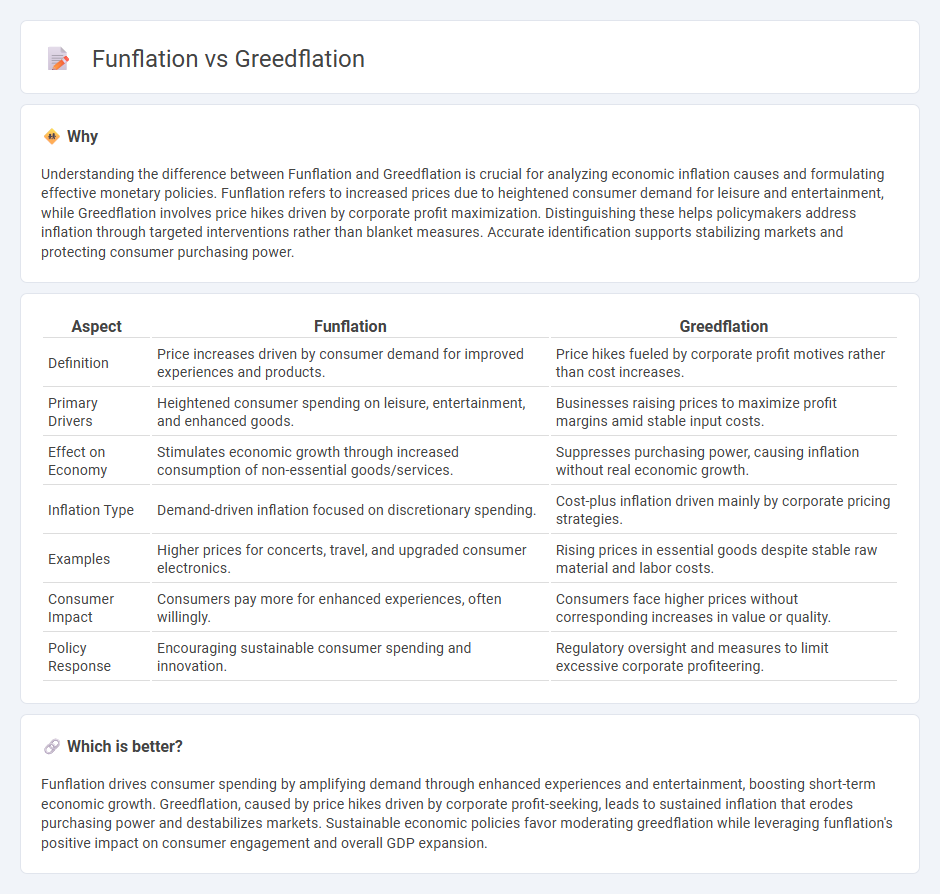
Understanding the difference between Funflation and Greedflation is crucial for analyzing economic inflation causes and formulating effective monetary policies. Funflation refers to increased prices due to heightened consumer demand for leisure and entertainment, while Greedflation involves price hikes driven by corporate profit maximization. Distinguishing these helps policymakers address inflation through targeted interventions rather than blanket measures. Accurate identification supports stabilizing markets and protecting consumer purchasing power.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Funflation | Greedflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Price increases driven by consumer demand for improved experiences and products. | Price hikes fueled by corporate profit motives rather than cost increases. |
| Primary Drivers | Heightened consumer spending on leisure, entertainment, and enhanced goods. | Businesses raising prices to maximize profit margins amid stable input costs. |
| Effect on Economy | Stimulates economic growth through increased consumption of non-essential goods/services. | Suppresses purchasing power, causing inflation without real economic growth. |
| Inflation Type | Demand-driven inflation focused on discretionary spending. | Cost-plus inflation driven mainly by corporate pricing strategies. |
| Examples | Higher prices for concerts, travel, and upgraded consumer electronics. | Rising prices in essential goods despite stable raw material and labor costs. |
| Consumer Impact | Consumers pay more for enhanced experiences, often willingly. | Consumers face higher prices without corresponding increases in value or quality. |
| Policy Response | Encouraging sustainable consumer spending and innovation. | Regulatory oversight and measures to limit excessive corporate profiteering. |
Which is better?
Funflation drives consumer spending by amplifying demand through enhanced experiences and entertainment, boosting short-term economic growth. Greedflation, caused by price hikes driven by corporate profit-seeking, leads to sustained inflation that erodes purchasing power and destabilizes markets. Sustainable economic policies favor moderating greedflation while leveraging funflation's positive impact on consumer engagement and overall GDP expansion.
Connection
Funflation and greedflation are interconnected economic phenomena driving recent inflation trends by altering consumer pricing strategies. Funflation occurs when companies increase prices by enhancing product experiences or adding entertainment value, appealing to consumer desire for enjoyment. Greedflation involves firms raising prices beyond cost increases to boost profit margins, often justified by market power or reduced competition, resulting in sustained inflation pressures.
Key Terms
Price Gouging
Greedflation occurs when companies increase prices beyond what rising costs justify, exploiting market conditions to maximize profits, whereas funflation involves price hikes driven by enhanced consumer experiences or added value. Price gouging is a critical concern in greedflation, reflecting unethical inflations during supply shortages or high demand. Explore these concepts further to understand their impact on consumer behavior and market fairness.
Consumer Demand
Greedflation describes inflation driven primarily by corporate profit margins rather than cost increases, impacting consumer prices independently of demand fluctuations. Funflation, on the other hand, refers to rising prices in entertainment and leisure due to growing consumer demand and evolving consumption patterns. Explore how these distinct inflation types influence market dynamics and shape spending behavior.
Profit Margins
Greedflation occurs when companies raise prices beyond increased costs to boost profit margins, often during periods of high demand or supply constraints. Funflation refers to price hikes in entertainment and leisure sectors driven by consumers' willingness to pay more for unique experiences rather than increased costs. Explore how these dynamics impact market behavior and profitability in diverse industries for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
What is greedflation - and is it driving higher prices? - Greedflation refers to the idea that businesses exploit inflation conditions to generate excessive profits by raising prices beyond what supply shortages would justify, but many economists argue that inflation is primarily caused by supply shortages rather than corporate greed.
Greedflation in the US and UK | NEB Digest - The term "greedflation" has become a political focus, with leaders like President Biden highlighting corporate price gouging as a driver of inflation in the US and UK, where research shows some large companies have increased profit margins contributing to higher consumer prices.
Last Word: Busting the "Greedflation" Myth - Critics of the greedflation theory argue that widespread corporate collusion to raise prices is unlikely due to competitive pressures, and that both inflation and higher profits have more to do with excess macroeconomic stimulus than with firms intentionally keeping prices high.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com