De-risking involves systematically reducing economic exposures to potential threats by diversifying investments and enhancing regulatory frameworks, while containment focuses on mitigating the impact of crises through immediate control measures and policy interventions. Both strategies play crucial roles in maintaining financial stability and safeguarding economic growth during uncertain times. Explore more to understand how de-risking and containment shape resilient economies.
Why it is important
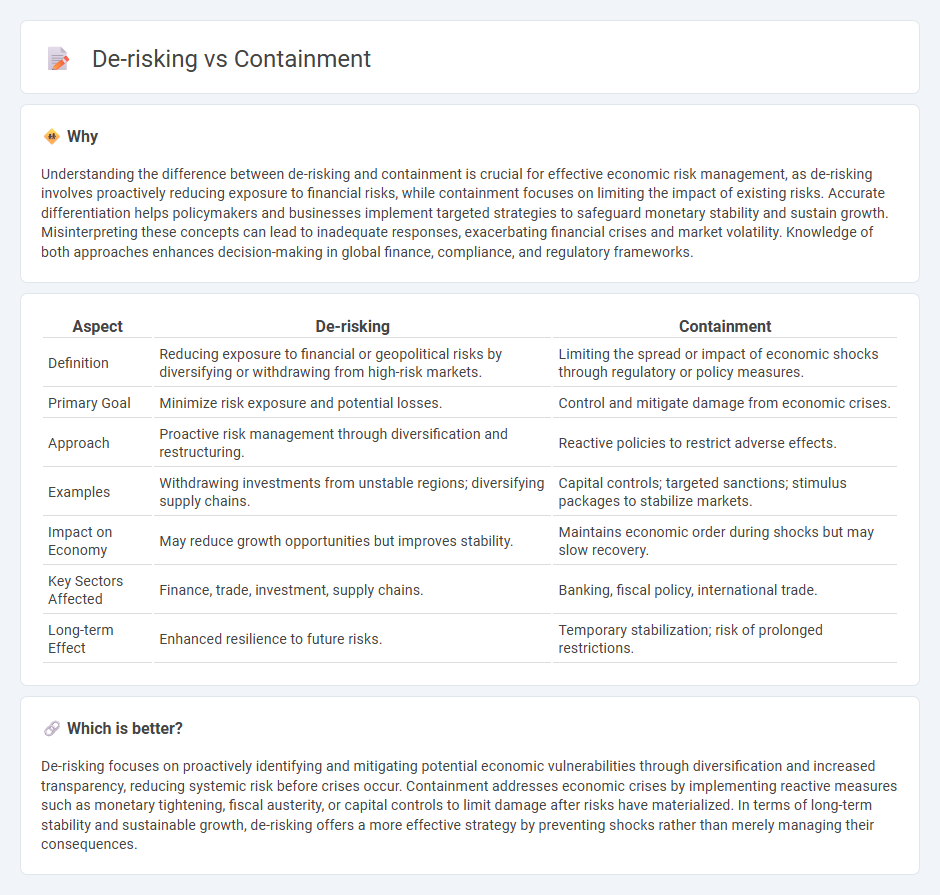
Understanding the difference between de-risking and containment is crucial for effective economic risk management, as de-risking involves proactively reducing exposure to financial risks, while containment focuses on limiting the impact of existing risks. Accurate differentiation helps policymakers and businesses implement targeted strategies to safeguard monetary stability and sustain growth. Misinterpreting these concepts can lead to inadequate responses, exacerbating financial crises and market volatility. Knowledge of both approaches enhances decision-making in global finance, compliance, and regulatory frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | De-risking | Containment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reducing exposure to financial or geopolitical risks by diversifying or withdrawing from high-risk markets. | Limiting the spread or impact of economic shocks through regulatory or policy measures. |
| Primary Goal | Minimize risk exposure and potential losses. | Control and mitigate damage from economic crises. |
| Approach | Proactive risk management through diversification and restructuring. | Reactive policies to restrict adverse effects. |
| Examples | Withdrawing investments from unstable regions; diversifying supply chains. | Capital controls; targeted sanctions; stimulus packages to stabilize markets. |
| Impact on Economy | May reduce growth opportunities but improves stability. | Maintains economic order during shocks but may slow recovery. |
| Key Sectors Affected | Finance, trade, investment, supply chains. | Banking, fiscal policy, international trade. |
| Long-term Effect | Enhanced resilience to future risks. | Temporary stabilization; risk of prolonged restrictions. |
Which is better?
De-risking focuses on proactively identifying and mitigating potential economic vulnerabilities through diversification and increased transparency, reducing systemic risk before crises occur. Containment addresses economic crises by implementing reactive measures such as monetary tightening, fiscal austerity, or capital controls to limit damage after risks have materialized. In terms of long-term stability and sustainable growth, de-risking offers a more effective strategy by preventing shocks rather than merely managing their consequences.
Connection
De-risking and containment in the economy are interconnected strategies aimed at minimizing financial system vulnerabilities by identifying and reducing exposure to high-risk assets and counterparties. Effective de-risking involves tightening regulatory oversight and improving risk assessment models, which in turn supports containment by preventing the spread of economic shocks across sectors. This synergy enhances economic stability by limiting systemic risks and promoting resilient financial markets.
Key Terms
Trade Restrictions
Trade restrictions impose limits on the flow of goods, services, and investments between countries to mitigate security risks or protect economic interests. Containment strategies aim to isolate and limit the influence of target nations through comprehensive trade barriers, while de-risking focuses on reducing dependency by diversifying supply chains and regulatory compliance without fully cutting ties. Explore the implications of trade restrictions in containment and de-risking to understand their impact on global commerce.
Supply Chain Diversification
Supply chain diversification mitigates risks by spreading sourcing across multiple regions, reducing dependency on a single market. Containment strategies prioritize limiting exposure to geopolitical tensions through selective vendor and country choices. Explore detailed approaches to supply chain diversification and risk management for resilient operations.
Economic Sanctions
Economic sanctions serve as containment by restricting targeted countries' access to global markets and financial systems, aiming to limit their geopolitical influence. De-risking involves businesses and financial institutions minimizing exposure to sanctioned entities to avoid regulatory penalties and reputational damage, often leading to reduced economic engagement beyond direct sanction targets. Explore the nuances of how containment strategies and de-risking policies shape international trade and diplomatic relations.
Source and External Links
Containment - Wikipedia - Containment was a U.S. foreign policy strategy during the Cold War aimed at preventing the spread of communism, first articulated by George F. Kennan in 1946.
Containment | Horror Thriller Sci-Fi | Full Movie - YouTube - In the 2015 film "Containment," residents of an apartment block find themselves sealed in by authorities, forced to uncover the truth behind their quarantine while fear and distrust escalate among them.
CONTAINMENT Definition & Meaning - Dictionary.com - Containment refers to the act or policy of restricting the territorial growth or ideological influence of another, especially a hostile nation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com