Reshoring involves relocating manufacturing and services back to a company's home country to reduce supply chain risks and support local economies, while globalization emphasizes expanding operations internationally to maximize efficiency and access larger markets. Countries like the United States and Germany have seen increased reshoring trends driven by rising labor costs abroad and geopolitical tensions. Explore the dynamic interplay between reshoring and globalization to understand their impact on the global economy.
Why it is important
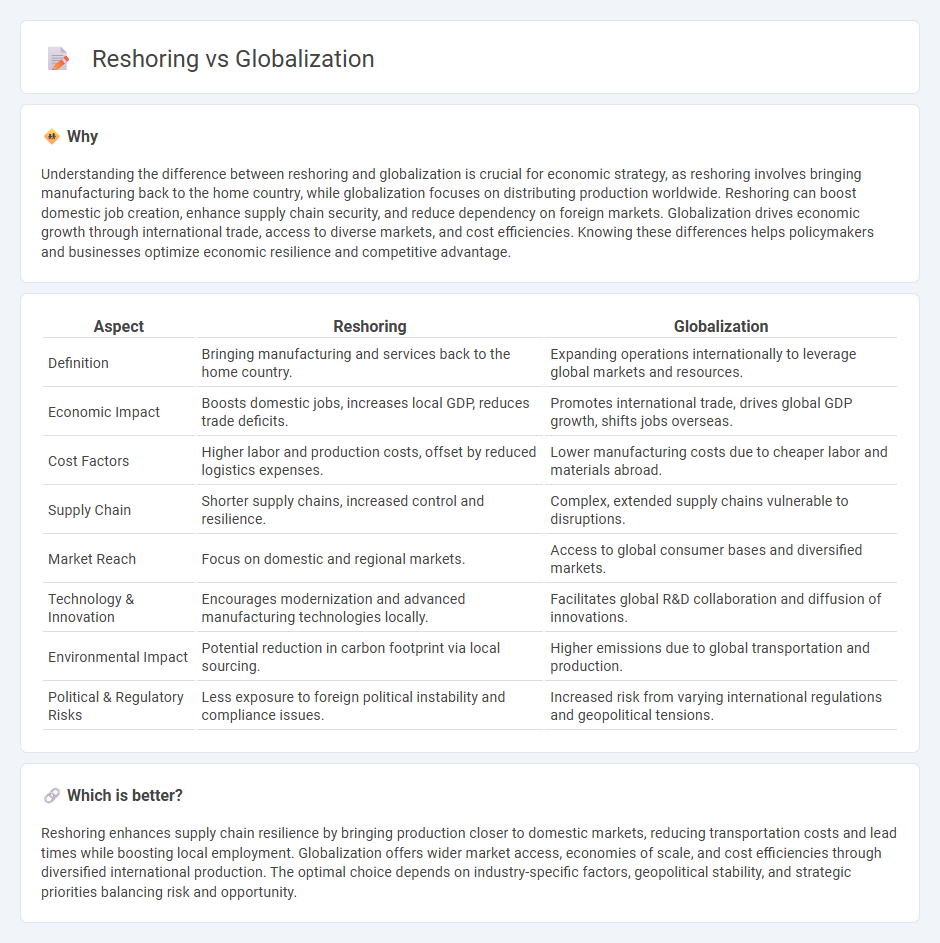
Understanding the difference between reshoring and globalization is crucial for economic strategy, as reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the home country, while globalization focuses on distributing production worldwide. Reshoring can boost domestic job creation, enhance supply chain security, and reduce dependency on foreign markets. Globalization drives economic growth through international trade, access to diverse markets, and cost efficiencies. Knowing these differences helps policymakers and businesses optimize economic resilience and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reshoring | Globalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing and services back to the home country. | Expanding operations internationally to leverage global markets and resources. |
| Economic Impact | Boosts domestic jobs, increases local GDP, reduces trade deficits. | Promotes international trade, drives global GDP growth, shifts jobs overseas. |
| Cost Factors | Higher labor and production costs, offset by reduced logistics expenses. | Lower manufacturing costs due to cheaper labor and materials abroad. |
| Supply Chain | Shorter supply chains, increased control and resilience. | Complex, extended supply chains vulnerable to disruptions. |
| Market Reach | Focus on domestic and regional markets. | Access to global consumer bases and diversified markets. |
| Technology & Innovation | Encourages modernization and advanced manufacturing technologies locally. | Facilitates global R&D collaboration and diffusion of innovations. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential reduction in carbon footprint via local sourcing. | Higher emissions due to global transportation and production. |
| Political & Regulatory Risks | Less exposure to foreign political instability and compliance issues. | Increased risk from varying international regulations and geopolitical tensions. |
Which is better?
Reshoring enhances supply chain resilience by bringing production closer to domestic markets, reducing transportation costs and lead times while boosting local employment. Globalization offers wider market access, economies of scale, and cost efficiencies through diversified international production. The optimal choice depends on industry-specific factors, geopolitical stability, and strategic priorities balancing risk and opportunity.
Connection
Reshoring and globalization are interconnected as reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and services back to domestic markets that were previously outsourced due to globalization. This shift impacts global supply chains by reducing dependency on foreign suppliers and increasing local production capacities, which can lead to changes in trade balances and labor markets. The dynamic interaction between reshoring trends and globalization shapes economic policies focused on national competitiveness and sustainable growth.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Globalization has expanded supply chains across continents, leveraging cost efficiencies and diverse sourcing options, while reshoring emphasizes bringing production closer to demand markets to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce lead times. Companies pursuing reshoring often aim to mitigate risks related to geopolitical tensions, transportation disruptions, and fluctuating tariffs. Discover how balancing globalization and reshoring strategies can optimize your supply chain's agility and sustainability.
Trade Balance
Globalization enhances trade balance by expanding export markets and enabling cost-efficient offshore production, which can improve a country's trade deficit. Reshoring aims to strengthen trade balance by reducing reliance on imports and boosting domestic manufacturing, potentially increasing exports and jobs at home. Explore how shifting strategies between globalization and reshoring impact national trade balances and economic stability.
Labor Costs
Labor costs significantly influence decisions between globalization and reshoring strategies for manufacturing companies. Globalization often offers access to lower wages in emerging markets, reducing production expenses, while reshoring can increase labor costs but improve quality control and reduce lead times. Explore how businesses balance these factors to optimize supply chain efficiency and competitiveness.
Source and External Links
Globalization - Wikipedia - Globalization is the increasing interdependence and integration among economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries, driven by technology, trade liberalization, and shifts in manufacturing, with major aspects including economic, cultural, and political globalization.
What is Globalization: Pros, Cons, and History - TechTarget - Globalization facilitates the movement of goods, knowledge, and services worldwide, transforming trade, labor markets, and cultural exchange, but also bringing challenges like disease spread and political instability.
A brief history of globalization - The World Economic Forum - Globalization 4.0 marks a new digital era of globalization dominated by cyber economy and AI, facing new challenges such as climate change impact and rising protectionism.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com