Liquidity crunch occurs when financial institutions face sudden shortages of cash, hindering their ability to meet short-term obligations, often leading to tightened credit conditions and reduced economic activity. Currency crisis involves a rapid devaluation of a nation's currency, triggered by a loss of investor confidence and usually accompanied by capital flight and soaring inflation. Explore the nuances between liquidity crunch and currency crisis to better understand their distinct impacts on the economy.
Why it is important
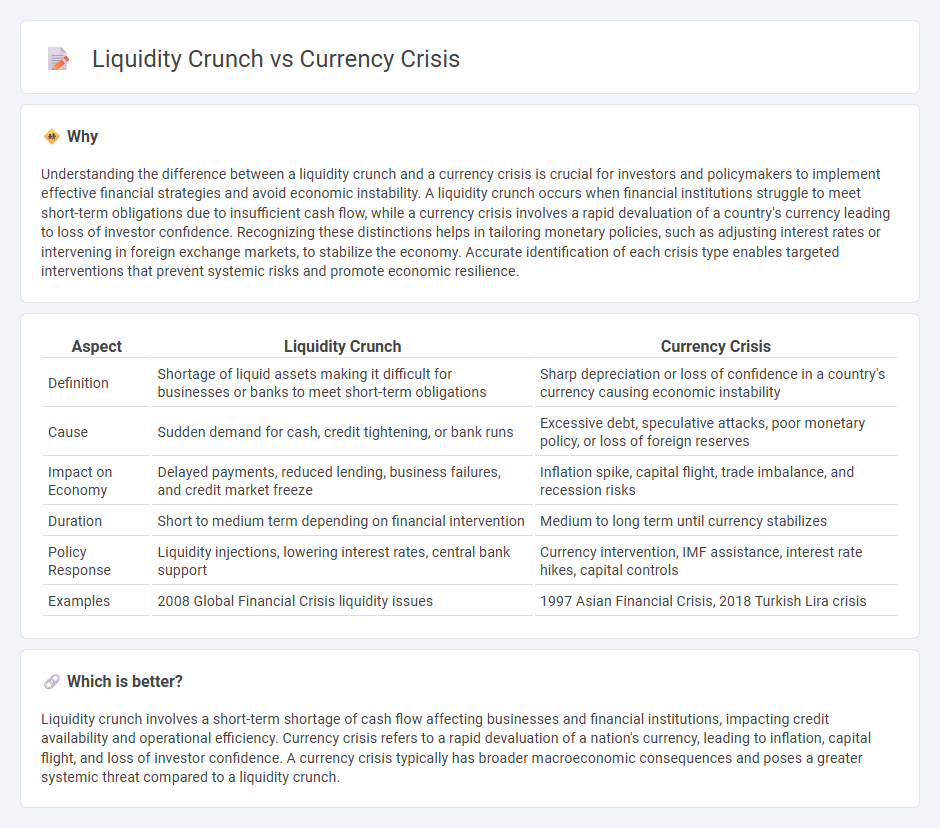
Understanding the difference between a liquidity crunch and a currency crisis is crucial for investors and policymakers to implement effective financial strategies and avoid economic instability. A liquidity crunch occurs when financial institutions struggle to meet short-term obligations due to insufficient cash flow, while a currency crisis involves a rapid devaluation of a country's currency leading to loss of investor confidence. Recognizing these distinctions helps in tailoring monetary policies, such as adjusting interest rates or intervening in foreign exchange markets, to stabilize the economy. Accurate identification of each crisis type enables targeted interventions that prevent systemic risks and promote economic resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquidity Crunch | Currency Crisis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shortage of liquid assets making it difficult for businesses or banks to meet short-term obligations | Sharp depreciation or loss of confidence in a country's currency causing economic instability |
| Cause | Sudden demand for cash, credit tightening, or bank runs | Excessive debt, speculative attacks, poor monetary policy, or loss of foreign reserves |
| Impact on Economy | Delayed payments, reduced lending, business failures, and credit market freeze | Inflation spike, capital flight, trade imbalance, and recession risks |
| Duration | Short to medium term depending on financial intervention | Medium to long term until currency stabilizes |
| Policy Response | Liquidity injections, lowering interest rates, central bank support | Currency intervention, IMF assistance, interest rate hikes, capital controls |
| Examples | 2008 Global Financial Crisis liquidity issues | 1997 Asian Financial Crisis, 2018 Turkish Lira crisis |
Which is better?
Liquidity crunch involves a short-term shortage of cash flow affecting businesses and financial institutions, impacting credit availability and operational efficiency. Currency crisis refers to a rapid devaluation of a nation's currency, leading to inflation, capital flight, and loss of investor confidence. A currency crisis typically has broader macroeconomic consequences and poses a greater systemic threat compared to a liquidity crunch.
Connection
A liquidity crunch occurs when financial institutions or markets face a severe shortage of liquid assets, restricting their ability to meet immediate demands or fund operations. This scarcity of liquidity can trigger or exacerbate a currency crisis, as investors lose confidence and rapidly withdraw foreign capital, causing sharp depreciation of the domestic currency. Central banks often struggle to stabilize the currency during such times without sufficient foreign reserves or liquidity support, intensifying economic instability.
Key Terms
Currency Crisis:
A currency crisis occurs when a country's currency rapidly depreciates due to loss of investor confidence, excessive foreign debt, or political instability, leading to inflation and economic turmoil. The sharp devaluation can trigger capital flight, reduce foreign reserves, and force governments to intervene through interest rate hikes or currency controls. Discover how these dynamics impact global markets and develop strategies to mitigate associated risks.
Exchange Rate
A currency crisis occurs when a country's exchange rate experiences a sudden, sharp depreciation, often driven by speculative attacks and loss of investor confidence, leading to a collapse in the currency's value. A liquidity crunch, by contrast, involves a shortage of liquid assets in the financial system, restricting banks' ability to lend and indirectly putting pressure on the exchange rate due to capital outflows and tighter monetary conditions. To understand the distinct impacts on exchange rate dynamics, explore the detailed mechanisms behind currency crises and liquidity crunches.
Capital Flight
A currency crisis occurs when a nation's currency faces a sharp depreciation due to factors like capital flight, which involves investors rapidly withdrawing assets and converting local currency into foreign reserves. A liquidity crunch refers to a sudden shortage of cash or easily sellable assets in the financial system, often exacerbated by capital flight that drains domestic capital and restricts lending. Explore the dynamics between these financial disturbances and capital flight to understand their impacts on economic stability.
Source and External Links
Currency Crisis - Definition, Signs, Inflation - A currency crisis is characterized by a sudden loss of value in a currency relative to others, often following socio-political or financial crises.
Currency crisis - A currency crisis is a type of financial crisis associated with real economic problems, often involving speculative attacks and balance of payments deficits.
Currency Crises - This document from the National Bureau of Economic Research discusses models and examples of currency crises, including the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com