Gigification transforms traditional employment by segmenting work into short-term, skill-specific gigs, enhancing workforce flexibility and catering to the growing demand for project-based tasks. Freelancing involves individuals offering specialized services independently, often managing multiple clients simultaneously, which fosters entrepreneurial opportunities and diverse income streams. Explore how gigification and freelancing reshape modern economies and career landscapes by diving deeper into their impacts.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between gigification and freelancing is crucial for navigating the modern economy, as gigification refers to the structuring of work around short-term, flexible tasks often facilitated by digital platforms, while freelancing typically involves independent professionals offering specialized services on a per-project basis. Recognizing these distinctions helps workers optimize income strategies and benefits management within dynamic labor markets. Employers benefit from this knowledge by tailoring workforce policies to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Clarity in these terms also informs policymakers when designing regulations and protections for non-traditional workers.
Comparison Table
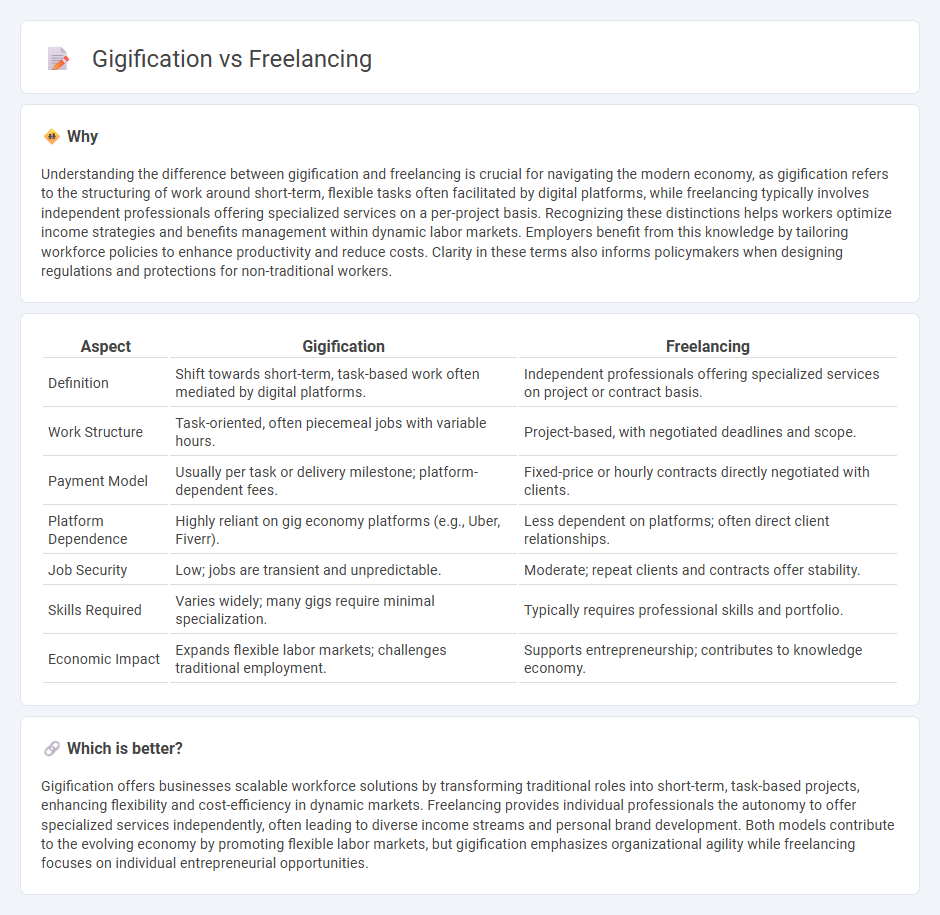
| Aspect | Gigification | Freelancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shift towards short-term, task-based work often mediated by digital platforms. | Independent professionals offering specialized services on project or contract basis. |
| Work Structure | Task-oriented, often piecemeal jobs with variable hours. | Project-based, with negotiated deadlines and scope. |
| Payment Model | Usually per task or delivery milestone; platform-dependent fees. | Fixed-price or hourly contracts directly negotiated with clients. |
| Platform Dependence | Highly reliant on gig economy platforms (e.g., Uber, Fiverr). | Less dependent on platforms; often direct client relationships. |
| Job Security | Low; jobs are transient and unpredictable. | Moderate; repeat clients and contracts offer stability. |
| Skills Required | Varies widely; many gigs require minimal specialization. | Typically requires professional skills and portfolio. |
| Economic Impact | Expands flexible labor markets; challenges traditional employment. | Supports entrepreneurship; contributes to knowledge economy. |
Which is better?
Gigification offers businesses scalable workforce solutions by transforming traditional roles into short-term, task-based projects, enhancing flexibility and cost-efficiency in dynamic markets. Freelancing provides individual professionals the autonomy to offer specialized services independently, often leading to diverse income streams and personal brand development. Both models contribute to the evolving economy by promoting flexible labor markets, but gigification emphasizes organizational agility while freelancing focuses on individual entrepreneurial opportunities.
Connection
Gigification transforms traditional employment by promoting short-term, project-based work, which closely aligns with freelancing's model of independent contract jobs. Freelancers thrive in a gigified economy where digital platforms facilitate access to diverse, flexible opportunities without long-term commitments. This synergy boosts economic dynamism by enabling workforce adaptability and expanding income sources across global markets.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Freelancing offers professionals high autonomy and control over project selection, work hours, and client relationships, enhancing personalized flexibility in career management. Gigification transforms traditional employment into task-based assignments, providing quick access to varied short-term opportunities but often with limited long-term stability or benefits. Explore deeper insights into how freelancing and gigification impact flexibility and career growth in the modern workplace.
Income Stability
Freelancing offers variable income streams that depend heavily on client acquisition and project completion rates, resulting in potential fluctuations in monthly earnings. Gigification typically involves short-term, task-based work on digital platforms that promise rapid job access but often lack consistent income and benefits. Explore how income stability compares between these models to identify the best fit for your financial goals.
Labor Rights
Freelancing often lacks standardized labor protections, exposing workers to inconsistent contracts and limited access to benefits, while gigification further intensifies these challenges through algorithm-driven work allocation and precarious income stability. Labor rights advocates emphasize the need for robust regulations that ensure fair wages, social security, and collective bargaining opportunities for both freelancers and gig workers. Explore more to understand how evolving labor frameworks can protect gig and freelance workforce rights effectively.
Source and External Links
What Is Freelancing? Basics and Popular Jobs in 2025 - Freelancing means working independently for clients without full-time employment, managing your own schedule, business, and taxes as a self-employed individual.
Freelancing 101: What is Freelancing? - Freelancers are self-employed professionals who choose their clients, projects, and working hours, enabled by the internet to work remotely from anywhere in the world.
25 best freelance websites to find work in 2025 - Freelancing offers flexibility to select projects and clients, set your own rates, and develop professionally while working on your own terms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com