Grey market imports bypass official distribution channels, often offering products at lower prices but without manufacturer warranties or support, impacting brand reputation and market dynamics. Franchising establishes authorized networks with standardized products and services, ensuring quality control and legal compliance while expanding brand presence. Explore how these contrasting approaches influence business strategies and consumer choices.
Why it is important
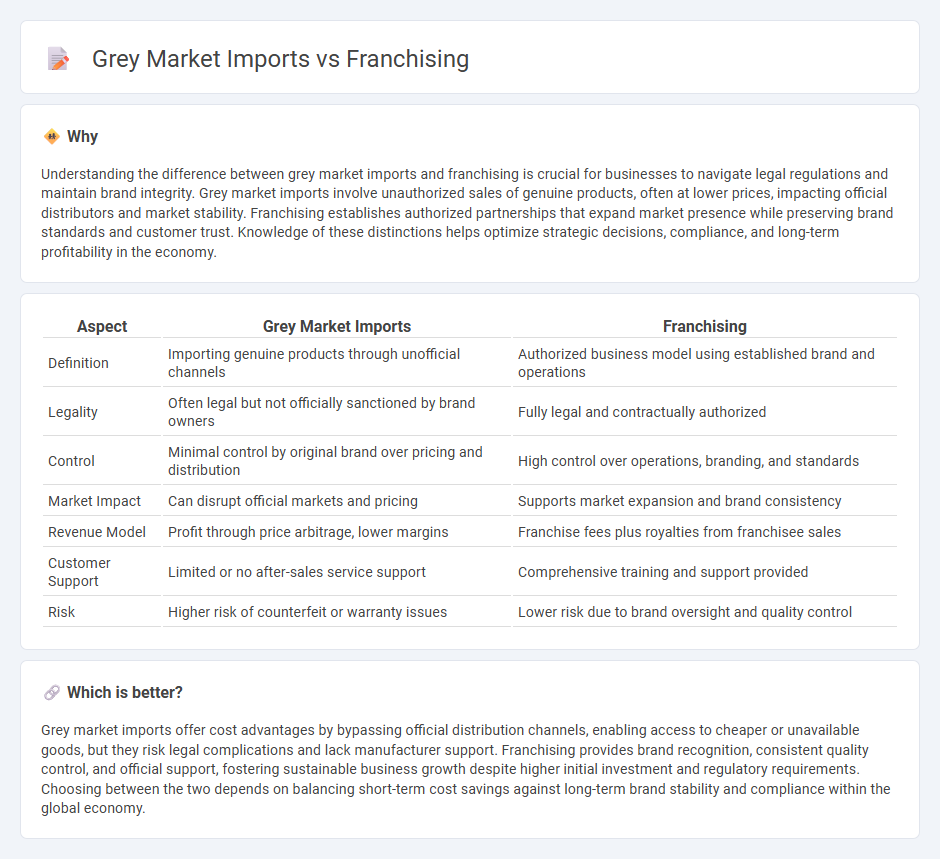
Understanding the difference between grey market imports and franchising is crucial for businesses to navigate legal regulations and maintain brand integrity. Grey market imports involve unauthorized sales of genuine products, often at lower prices, impacting official distributors and market stability. Franchising establishes authorized partnerships that expand market presence while preserving brand standards and customer trust. Knowledge of these distinctions helps optimize strategic decisions, compliance, and long-term profitability in the economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grey Market Imports | Franchising |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Importing genuine products through unofficial channels | Authorized business model using established brand and operations |
| Legality | Often legal but not officially sanctioned by brand owners | Fully legal and contractually authorized |
| Control | Minimal control by original brand over pricing and distribution | High control over operations, branding, and standards |
| Market Impact | Can disrupt official markets and pricing | Supports market expansion and brand consistency |
| Revenue Model | Profit through price arbitrage, lower margins | Franchise fees plus royalties from franchisee sales |
| Customer Support | Limited or no after-sales service support | Comprehensive training and support provided |
| Risk | Higher risk of counterfeit or warranty issues | Lower risk due to brand oversight and quality control |
Which is better?
Grey market imports offer cost advantages by bypassing official distribution channels, enabling access to cheaper or unavailable goods, but they risk legal complications and lack manufacturer support. Franchising provides brand recognition, consistent quality control, and official support, fostering sustainable business growth despite higher initial investment and regulatory requirements. Choosing between the two depends on balancing short-term cost savings against long-term brand stability and compliance within the global economy.
Connection
Grey market imports impact the economy by bypassing authorized franchising channels, leading to revenue losses for official franchise operators and tax authorities. Franchising relies on controlled distribution and brand consistency, which grey market imports undermine by introducing unauthorized products and services. This disruption affects market pricing, consumer trust, and overall economic stability within regulated industries.
Key Terms
Intellectual Property Rights
Franchising ensures stringent protection of intellectual property rights by legally binding franchisees to uphold brand standards and avoid unauthorized use of trademarks and patents. Grey market imports often circumvent these protections, leading to unauthorized distribution of genuine products, which can dilute brand reputation and infringe on IP rights. Discover how businesses navigate these challenges to safeguard their intellectual property more effectively.
Distribution Channels
Franchising ensures authorized distribution channels with consistent brand control, official warranties, and localized customer support, enhancing consumer trust and market penetration. Grey market imports bypass authorized distributors, leading to potential warranty issues, inconsistent pricing, and risks of counterfeit or substandard products. Explore the impact of these distribution channels on brand reputation and consumer choice for a deeper understanding.
Parallel Trade
Franchising ensures brand consistency and authorized distribution through official channels, maintaining product quality and customer trust, while grey market imports, often linked to parallel trade, involve unauthorized sellers distributing genuine products outside sanctioned networks, potentially affecting warranties and pricing models. Parallel trade facilitates the movement of legally purchased goods across borders to exploit price differentials, impacting franchised businesses by undermining pricing strategies and market segmentation. Explore the nuances of franchising and grey market dynamics to better understand their implications on global commerce.
Source and External Links
Franchising - Franchising is a business strategy where a franchisor licenses its brand, business model, and operational know-how to a franchisee, who pays fees and follows specific obligations in exchange for the right to operate under the franchisor's system.
What is a Franchise - Franchising is a method of business expansion and distribution in which the franchisor grants the franchisee the right to use its brand and systems, providing ongoing support and training in return for fees.
Franchising - Entrepreneur Small Business Encyclopedia - In franchising, the franchisee pays initial and ongoing fees to the franchisor for the right to use its trademark, business system, and receive ongoing support to sell the franchisor's products or services.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com