Dollarization involves a country adopting the US dollar as its official currency to stabilize inflation and attract foreign investment, while euroization refers to using the euro for similar economic benefits within certain European and neighboring states. Both strategies aim to enhance financial stability, reduce exchange rate risk, and integrate more closely with global markets, but they differ in geopolitical implications and monetary policy control. Explore the detailed impacts of dollarization and euroization on emerging economies to understand their long-term economic prospects.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dollarization and euroization is crucial for assessing economic stability and monetary policy effectiveness in countries that adopt foreign currencies. Dollarization refers to the use of the US dollar, while euroization involves the use of the euro as a legal tender outside their respective countries. Each impacts inflation rates, exchange rate risk, and foreign investment differently. Knowing these distinctions helps policymakers manage currency risks and attract international trade.
Comparison Table
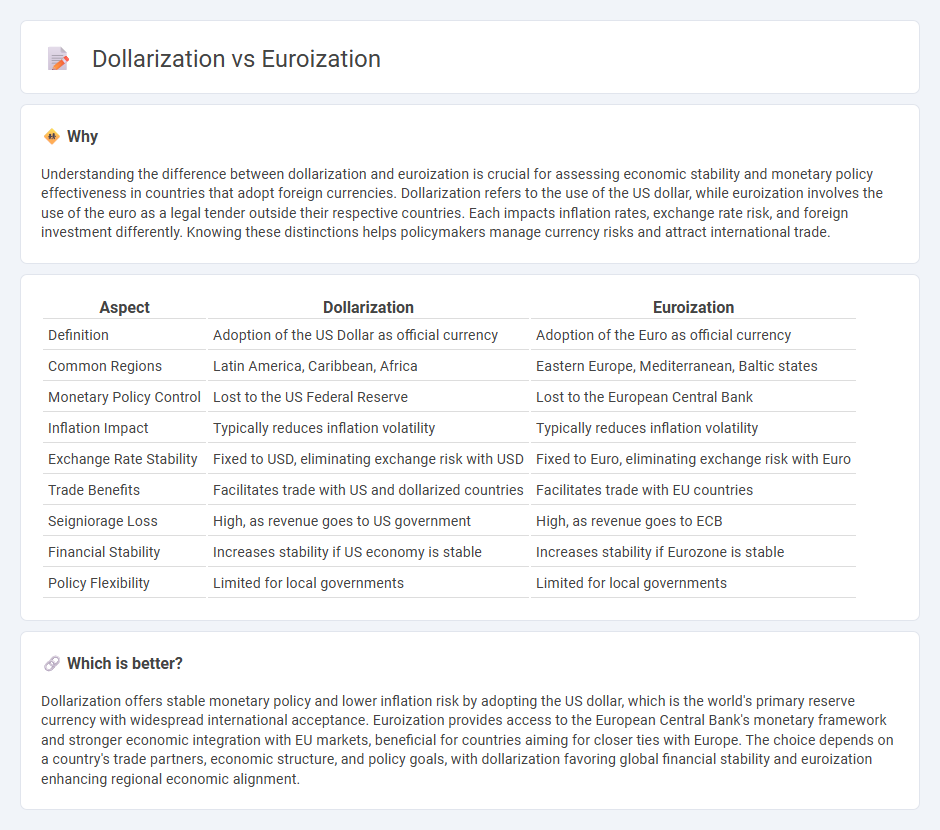
| Aspect | Dollarization | Euroization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adoption of the US Dollar as official currency | Adoption of the Euro as official currency |
| Common Regions | Latin America, Caribbean, Africa | Eastern Europe, Mediterranean, Baltic states |
| Monetary Policy Control | Lost to the US Federal Reserve | Lost to the European Central Bank |
| Inflation Impact | Typically reduces inflation volatility | Typically reduces inflation volatility |
| Exchange Rate Stability | Fixed to USD, eliminating exchange risk with USD | Fixed to Euro, eliminating exchange risk with Euro |
| Trade Benefits | Facilitates trade with US and dollarized countries | Facilitates trade with EU countries |
| Seigniorage Loss | High, as revenue goes to US government | High, as revenue goes to ECB |
| Financial Stability | Increases stability if US economy is stable | Increases stability if Eurozone is stable |
| Policy Flexibility | Limited for local governments | Limited for local governments |
Which is better?
Dollarization offers stable monetary policy and lower inflation risk by adopting the US dollar, which is the world's primary reserve currency with widespread international acceptance. Euroization provides access to the European Central Bank's monetary framework and stronger economic integration with EU markets, beneficial for countries aiming for closer ties with Europe. The choice depends on a country's trade partners, economic structure, and policy goals, with dollarization favoring global financial stability and euroization enhancing regional economic alignment.
Connection
Dollarization and euroization refer to the processes where countries adopt the US dollar or the euro as a significant part of their monetary system, often to stabilize their economy and control inflation. Both phenomena highlight the loss of monetary sovereignty, as local currencies are supplanted by foreign currencies to facilitate trade, attract investment, and enhance economic stability. The use of these dominant global currencies connects economies to larger financial networks and impacts exchange rate policies and capital flows.
Key Terms
Currency Substitution
Currency substitution occurs when residents of a country adopt a foreign currency in place of the domestic currency, often to stabilize the economy or curb hyperinflation. Euroization refers specifically to the adoption of the euro outside the Eurozone, while dollarization involves the use of the US dollar as an alternative legal tender or parallel currency. Explore the distinctions and economic impacts of both to understand how currency substitution shapes monetary policy.
Monetary Sovereignty
Euroization and dollarization both involve adopting a foreign currency to stabilize an economy, but euroization uses the euro, while dollarization uses the US dollar. These practices significantly reduce a country's monetary sovereignty by relinquishing control over national monetary policy, including interest rates and money supply adjustments. Explore further to understand their impacts on economic stability and policy autonomy.
Exchange Rate Regime
Euroization involves adopting the euro as the official currency, stabilizing exchange rates directly with the European Central Bank's monetary policy, while dollarization refers to using the US dollar, aligning exchange rates with the Federal Reserve's policies. Both regimes eliminate currency risk by removing local currency fluctuations but differ in geopolitical influences and economic integration levels. Explore further to understand how these exchange rate regimes impact inflation control, trade balance, and financial stability in emerging economies.
Source and External Links
Euroization Drivers and Effective Policy Response - Euroization occurs when a foreign currency (euro) partially replaces the domestic currency as a store of value, often due to macroeconomic instability, entrenched expectations of depreciation, or as a hedge against exchange rate volatility.
Dollarization and Euroization: A Post-Keynesian ... - Euroized economies lose independent monetary and exchange rate policies, making them more vulnerable to asymmetric shocks and dependent on trade and investment links with euro area countries.
De-euroization Package - High euroization reduces the effectiveness of macroeconomic policies, increases exposure to exchange rate risks, and imposes costs on central banks through higher foreign exchange reserves and lost seigniorage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com